Zone coverage is a defensive strategy in football where each player is responsible for guarding a specific area of the field rather than a particular opponent. This approach prevents offensive players from finding open spaces and allows defenders to work collectively to intercept passes or tackle ball carriers. Discover how mastering zone coverage can elevate Your defensive game by exploring the techniques and benefits detailed in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
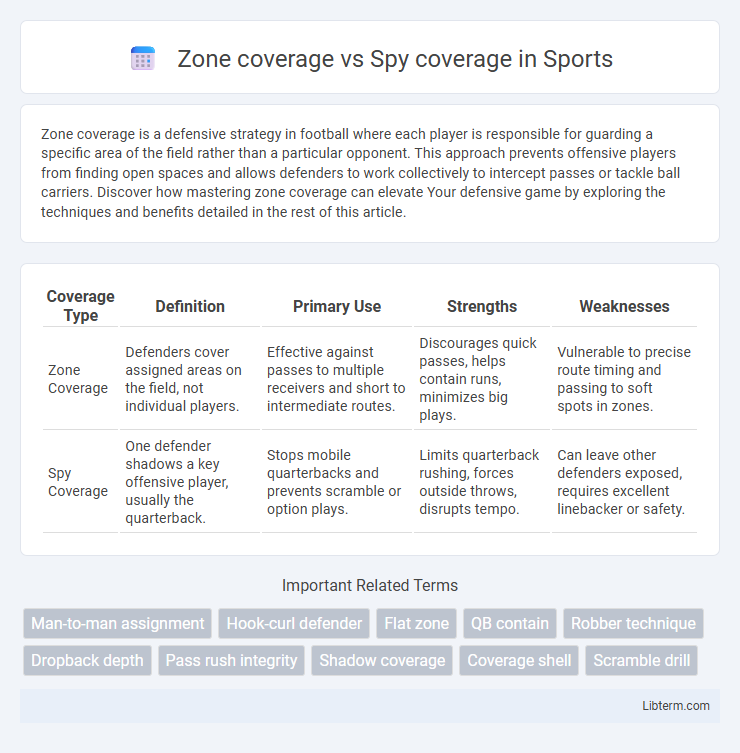
| Coverage Type | Definition | Primary Use | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone Coverage | Defenders cover assigned areas on the field, not individual players. | Effective against passes to multiple receivers and short to intermediate routes. | Discourages quick passes, helps contain runs, minimizes big plays. | Vulnerable to precise route timing and passing to soft spots in zones. |
| Spy Coverage | One defender shadows a key offensive player, usually the quarterback. | Stops mobile quarterbacks and prevents scramble or option plays. | Limits quarterback rushing, forces outside throws, disrupts tempo. | Can leave other defenders exposed, requires excellent linebacker or safety. |
Understanding Zone Coverage: Definition and Purpose
Zone coverage is a defensive strategy in football where each defender is responsible for covering a specific area of the field, rather than marking an individual opponent. The primary purpose of zone coverage is to limit passing options within assigned zones and prevent big plays by maintaining spatial awareness and communication among defenders. This approach increases flexibility in reading the quarterback's intentions and adjusting to offensive formations against diverse passing attacks.
Core Principles of Spy Coverage
Spy coverage emphasizes tracking a specific opponent's movements and actions throughout the game, prioritizing individual accountability and real-time adjustments over defending an area. Core principles include maintaining close, disciplined proximity to the assigned player to limit their ball-handling and scoring opportunities, while anticipating cuts and screens to disrupt offensive flow. This man-to-man approach contrasts with zone coverage, which focuses on guarding designated areas rather than individual players.
Key Differences: Zone vs Spy Coverage
Zone coverage assigns defenders to specific field areas, emphasizing team coordination and spatial awareness to prevent passes and runs within those zones. Spy coverage involves a designated defender, typically a linebacker or safety, who focuses on monitoring and reacting to a single offensive player, often the quarterback, to contain their mobility and limit big plays. The primary difference lies in zone coverage's area responsibility versus spy coverage's targeted man-to-man focus.
Situational Uses: When to Deploy Each Coverage
Zone coverage excels in defending against passing plays by assigning defenders to specific field areas, making it ideal for situations with multiple receivers or unpredictable routes. Spy coverage is best utilized against mobile quarterbacks, providing a dedicated defender who monitors and contains the quarterback's movement while allowing the rest of the defense to focus on coverage or pass rush. Teams often deploy zone coverage in obvious passing downs and use spy coverage when anticipating quarterback scrambles or designed runs, optimizing defensive effectiveness based on offensive tendencies.
Player Roles in Zone and Spy Schemes
In zone coverage, players are assigned specific areas of the field to defend, with defensive backs and linebackers reading the quarterback and reacting to receivers entering their zones, emphasizing spatial awareness and communication. Spy coverage allocates a dedicated player, often a linebacker or safety, to track a single offensive threat--usually the quarterback--focusing on containment and disruption of mobility rather than covering areas. The success of zone schemes relies heavily on coordinated team dynamics and zone integrity, while spy coverage depends on the individual player's ability to shadow and neutralize the designated target.
Advantages of Zone Coverage in Modern Football
Zone coverage offers defensive players the advantage of defending specific areas rather than following a single offensive player, enhancing team coordination against passing attacks in modern football. It enables defenders to quickly respond to multiple threats, improving overall pass defense efficiency and reducing big-play opportunities. This coverage strategy also allows linebackers and defensive backs to read the quarterback's intentions more effectively, leading to increased interceptions and timely pass breakups.
Benefits and Limitations of Spy Assignments
Spy coverage offers benefits such as tracking specific key opponents closely, enabling real-time adjustments to neutralize their impact and disrupt offensive flow. Limitations include vulnerability if the spy loses focus or stamina, potentially leaving gaps in pass coverage or defensive assignments. Unlike zone coverage, spy assignments demand high discipline and physical endurance but provide tailored containment against star players.
Common Mistakes in Zone and Spy Coverage
Common mistakes in zone coverage include defenders failing to pass off receivers at zone boundaries, leading to coverage gaps and missed assignments. In spy coverage, errors often arise when the spy gets too focused on the quarterback, neglecting other offensive threats or overcommitting too early. Both coverage types require disciplined communication and situational awareness to avoid giving up big plays.
Adjusting Coverage for Mobile Quarterbacks
Zone coverage against mobile quarterbacks requires defensive backs to prioritize spatial awareness and maintain loose zones, allowing rapid reactions to scramble attempts and short passes. Spy coverage assigns a specific defender, often a linebacker or safety, to shadow the quarterback closely, limiting their ability to escape the pocket and extend plays. Adjusting coverage strategies includes blending zone drops with dedicated spies to counter both passing threats and quarterback mobility effectively.
Strategic Integration: Blending Zone and Spy Techniques
Strategic integration of zone and spy coverage maximizes defensive effectiveness by combining spatial responsibility with targeted man-tracking to disrupt offensive plays. Zone coverage emphasizes guarding specific field areas, while spy coverage focuses on monitoring a key player, often the quarterback, to prevent escapes or long gains. Blending these techniques allows defenses to adapt dynamically, maintaining area control while neutralizing high-impact threats through focused surveillance.
Zone coverage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com