Back-end developers specialize in server-side logic, databases, and application programming interfaces (APIs) to ensure seamless functionality between the server and client. Mastery of languages like Python, Java, or Node.js is essential for creating efficient, scalable systems that support front-end interactions. Explore the article further to uncover key skills and best practices for advancing your career as a back-end developer.
Table of Comparison
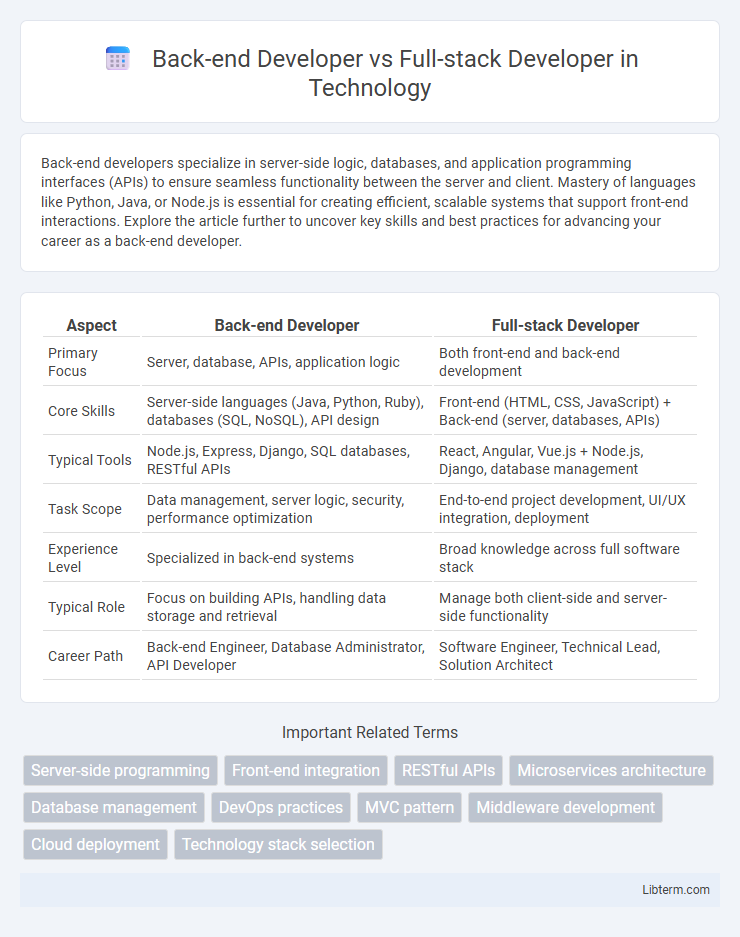
| Aspect | Back-end Developer | Full-stack Developer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Server, database, APIs, application logic | Both front-end and back-end development |
| Core Skills | Server-side languages (Java, Python, Ruby), databases (SQL, NoSQL), API design | Front-end (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) + Back-end (server, databases, APIs) |
| Typical Tools | Node.js, Express, Django, SQL databases, RESTful APIs | React, Angular, Vue.js + Node.js, Django, database management |
| Task Scope | Data management, server logic, security, performance optimization | End-to-end project development, UI/UX integration, deployment |
| Experience Level | Specialized in back-end systems | Broad knowledge across full software stack |
| Typical Role | Focus on building APIs, handling data storage and retrieval | Manage both client-side and server-side functionality |
| Career Path | Back-end Engineer, Database Administrator, API Developer | Software Engineer, Technical Lead, Solution Architect |
Introduction to Developer Roles
Back-end developers specialize in server-side logic, database management, and application integration, ensuring data flow and storage efficiency. Full-stack developers possess expertise in both front-end and back-end technologies, enabling them to build complete web applications from user interface design to server configuration. Understanding the distinctions between these roles helps align project needs with specific technical skills and development workflows.
Defining Back-end Development
Back-end development centers on server-side programming, managing databases, server logic, authentication, and API integrations to ensure smooth communication between the client and server. Back-end developers utilize technologies such as Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, and frameworks like Express or Django to build scalable and secure applications. Their primary focus is to create, maintain, and optimize the infrastructure that supports front-end functionalities and user interactions.
Understanding Full-stack Development
Full-stack development encompasses both front-end and back-end technologies, enabling developers to build complete web applications from the user interface to the server-side logic and database management. Unlike back-end developers who specialize exclusively in server, database, and API integration, full-stack developers possess a diverse skill set including HTML, CSS, JavaScript frameworks, server-side languages like Node.js or Python, and knowledge of DevOps tools for deployment. Mastery of full-stack development facilitates seamless communication between client-side and server-side components, optimizing application performance and accelerating development cycles.
Core Skills of a Back-end Developer
Core skills of a Back-end Developer include proficiency in server-side languages like Java, Python, Ruby, or Node.js, as well as expertise in database management using SQL or NoSQL systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB. Strong understanding of API development, RESTful services, and server architecture is essential for efficient data processing and integration. Additionally, skills in version control systems like Git, security protocols, and performance optimization contribute to building robust and scalable back-end infrastructures.
Essential Skills for Full-stack Developers
Full-stack developers must possess essential skills in both front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and back-end frameworks such as Node.js, Django, or Ruby on Rails. Proficiency in database management systems including SQL and NoSQL, along with API development and version control tools like Git, is crucial for seamless integration across the stack. Understanding deployment processes, cloud services, and containerization further distinguishes full-stack developers from back-end specialists by enabling end-to-end project management.
Common Technologies and Tools
Back-end developers primarily work with server-side languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, and frameworks like Node.js, Django, or Spring, focusing on databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB for data management. Full-stack developers combine these back-end technologies with front-end tools like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue.js to build complete web applications. Both roles utilize version control systems like Git, containerization tools like Docker, and cloud platforms such as AWS or Azure to streamline development and deployment processes.
Typical Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Back-end Developers specialize in server-side logic, database management, API creation, and ensuring application performance and security. Full-stack Developers handle both front-end and back-end tasks, including UI development, server-side logic, database management, and integration. Daily tasks for Full-stack Developers often involve coding, debugging, system architecture design, and collaborating with cross-functional teams to deliver end-to-end solutions.
Career Opportunities and Salary Comparison
Back-end developers specialize in server-side logic, database management, and API integration, often commanding competitive salaries that range from $70,000 to $120,000 annually depending on experience and location. Full-stack developers possess a broader skill set that includes both front-end and back-end technologies, which expands their career opportunities in startups, tech firms, and enterprise environments, typically earning between $80,000 and $130,000 per year. Versatility in full-stack development can lead to higher demand and salary growth, while back-end roles benefit from deep expertise in scalable system architecture and optimized database design.
Pros and Cons of Each Role
Back-end developers specialize in server-side logic, database management, and application performance, offering deep expertise that ensures robust and scalable systems but may lack front-end design experience. Full-stack developers handle both front-end and back-end tasks, providing versatile project contributions and faster deployment cycles while potentially sacrificing depth in either area due to broad skill requirements. Choosing between these roles depends on project complexity, the need for specialized knowledge versus flexibility, and team size constraints.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career
Back-end developers specialize in server-side logic, databases, and application architecture, making them essential for building robust, scalable systems. Full-stack developers possess a broader skill set, handling both front-end and back-end technologies, which provides flexibility and end-to-end project ownership. Choosing the right path depends on your interest in depth versus breadth of expertise, career goals, and the demand for specialized roles versus versatile developers in the job market.
Back-end Developer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com