A portrait captures the essence and personality of its subject through skillful expression and composition, creating a lasting impression beyond mere appearance. Mastery in lighting, pose, and emotion transforms a simple image into a powerful storytelling tool that resonates deeply with viewers. Explore the rest of the article to discover how to create impactful portraits that truly reflect your vision.
Table of Comparison
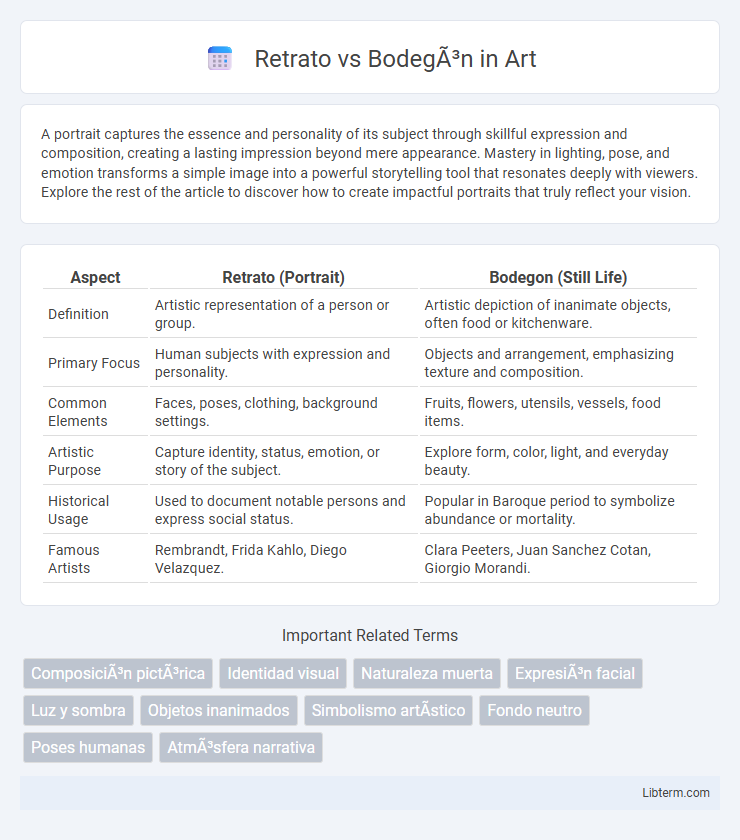
| Aspect | Retrato (Portrait) | Bodegon (Still Life) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic representation of a person or group. | Artistic depiction of inanimate objects, often food or kitchenware. |
| Primary Focus | Human subjects with expression and personality. | Objects and arrangement, emphasizing texture and composition. |
| Common Elements | Faces, poses, clothing, background settings. | Fruits, flowers, utensils, vessels, food items. |
| Artistic Purpose | Capture identity, status, emotion, or story of the subject. | Explore form, color, light, and everyday beauty. |
| Historical Usage | Used to document notable persons and express social status. | Popular in Baroque period to symbolize abundance or mortality. |
| Famous Artists | Rembrandt, Frida Kahlo, Diego Velazquez. | Clara Peeters, Juan Sanchez Cotan, Giorgio Morandi. |
Definición de Retrato
Retrato is a genre of art focused on representing the image, personality, and essence of a person, emphasizing facial features, expressions, and posture to convey identity and emotion. In contrast, bodegon refers to still life paintings that depict inanimate objects such as food, flowers, and everyday items arranged in a composition. The primary goal of retrato is to capture the likeness and psychological depth of the subject, often highlighting individuality and character.
Definición de Bodegón
Bodegon is a genre of still life painting that emphasizes the arrangement of inanimate objects, often including food, kitchen utensils, and flowers, to highlight texture, composition, and light. Unlike retrato, which centers on the realistic depiction of human subjects, bodegon captures everyday objects with symbolic or aesthetic significance in a carefully constructed setting. This genre emerged prominently in Spanish Baroque art, reflecting both domestic life and deeper allegorical meanings.
Orígenes Históricos del Retrato
TheOrigins of portraiture trace back to ancient civilizations where early depictions aimed to capture individual identity and social status, contrasting significantly with bodegon, which emerged later emphasizing still life arrangements mostly from the Spanish Golden Age. Portraits served as tools for preserving lineage and asserting power across cultures, often commissioned by nobility and religious figures to convey authority and personality. This historical development highlights the intrinsic human desire to immortalize the self, diverging from bolegon's focus on everyday objects and symbolic meanings.
Evolución del Bodegón en el Arte
The evolution of Bodegon in art traces its origins to 17th-century Spain, where still life paintings depicted everyday objects with meticulous realism, emphasizing texture and light. Over time, Bodegones integrated symbolic meanings and complex compositions, reflecting cultural and philosophical shifts, notably in Baroque and Dutch Golden Age art. Contemporary Bodegones incorporate abstract elements and mixed media, demonstrating the genre's adaptability and continued relevance in modern art.
Elementos Clave del Retrato
Elementos clave del retrato incluyen la representacion precisa del rostro, la expresion facial y la postura que reflejan la personalidad o el estado emocional del sujeto. Contrariamente al bodegon, que se centra en objetos inanimados como frutas, flores o utensilios, el retrato resalta detalles como la iluminacion del rostro, la direccion de la mirada y la textura de la piel. Estos elementos permiten captar la esencia individual y psicologica, fundamental para diferenciar el retrato dentro del genero artistico.
Características Distintivas del Bodegón
El bodegon se caracteriza por la representacion detallada y equilibrada de objetos inanimados, como frutas, flores, vajilla y utensilios, dispuestos cuidadosamente para resaltar texturas, colores y formas. A diferencia del retrato, que se centra en capturar la expresion y personalidad de sujetos humanos, el bodegon busca exaltar la belleza cotidiana y la composicion visual de elementos estaticos. La atmosfera del bodegon suele ser intima y mesurada, enfatizando el simbolismo y la armonia estetica en lugar del dinamismo o emocion personal.
Técnicas Populares en Retratos
Tecnicas populares en retratos incluyen el oleo sobre lienzo, acuarela y lapiz, cada una destacando detalles faciales y expresiones emocionales para capturar la esencia del sujeto. Estas tecnicas permiten un enfoque meticuloso en la iluminacion, sombras y texturas de la piel, logrando realismo y profundidad en la imagen. En contraste con el bodegon, que enfatiza objetos inanimados, el retrato se centra en la representacion humana y la psicologia visual.
Composición y Estética en Bodegones
La composicion en bodegones se caracteriza por la disposicion meticulosa de objetos cotidianos que realzan la textura, forma y color para crear equilibrio visual. La estetica en bodegones enfatiza el juego de luces y sombras, contrastes y armonias cromaticas, resaltando detalles que transmiten sensaciones tactiles y atmosfericas. Este enfoque busca evocar una reflexion sobre lo efimero y la belleza en lo cotidiano, diferenciandose de la representacion directa del retrato centrado en la figura humana.
Importancia Cultural de Cada Género
Retrato captures individual identity and social status through detailed depictions of facial expressions and attire, serving as a historical record of personal and cultural heritage. Bodegon, or still life, reflects daily life, emphasizing the symbolic value of objects that illustrate societal norms, economic conditions, and religious beliefs in its time. Both genres provide critical insights into cultural values, shaping collective memory and artistic traditions across different periods.
Retrato vs Bodegón: Diferencias y Similitudes
Retrato and bodegon represent distinct genres in visual arts, with retrato focusing on capturing the likeness and personality of a person, highlighting facial expressions and emotions. Bodegon, or still life, emphasizes the detailed depiction of inanimate objects such as food, flowers, and household items, showcasing texture and composition. Both genres share an emphasis on meticulous detail and composition, yet retrato centers on human subjects while bodegon concentrates on objects and their symbolic meanings.
Retrato Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com