Printmaking transforms artistic designs into multiple copies using various techniques like etching, lithography, and screenprinting. This process allows artists to explore textures, layers, and color variations, producing unique and collectible works. Discover how printmaking can enrich your creative expression by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
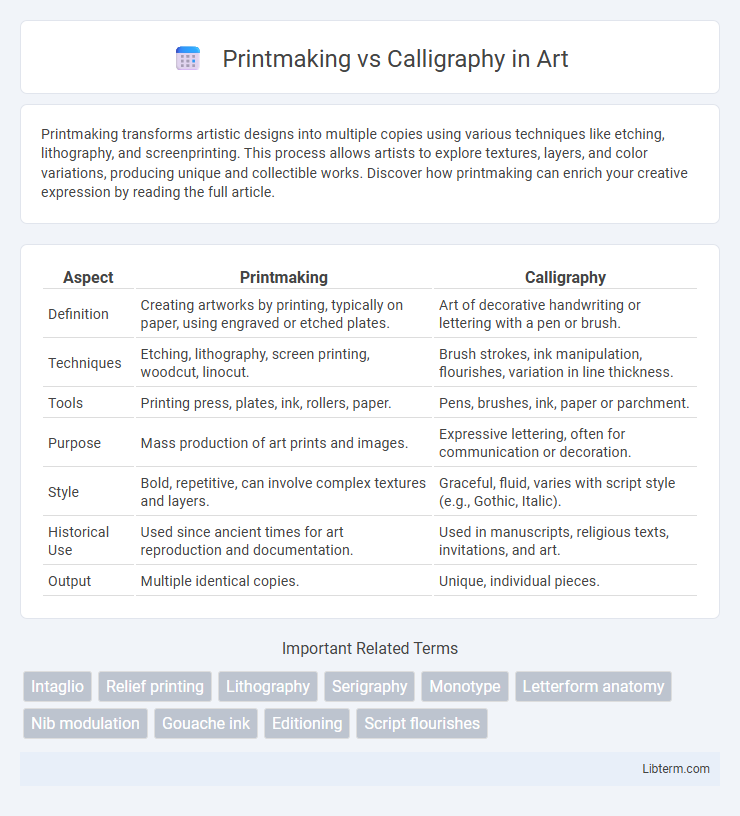
| Aspect | Printmaking | Calligraphy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating artworks by printing, typically on paper, using engraved or etched plates. | Art of decorative handwriting or lettering with a pen or brush. |
| Techniques | Etching, lithography, screen printing, woodcut, linocut. | Brush strokes, ink manipulation, flourishes, variation in line thickness. |
| Tools | Printing press, plates, ink, rollers, paper. | Pens, brushes, ink, paper or parchment. |
| Purpose | Mass production of art prints and images. | Expressive lettering, often for communication or decoration. |
| Style | Bold, repetitive, can involve complex textures and layers. | Graceful, fluid, varies with script style (e.g., Gothic, Italic). |
| Historical Use | Used since ancient times for art reproduction and documentation. | Used in manuscripts, religious texts, invitations, and art. |
| Output | Multiple identical copies. | Unique, individual pieces. |
Introduction to Printmaking and Calligraphy
Printmaking involves creating artworks by transferring ink from a matrix onto paper or fabric, utilizing techniques such as woodcut, etching, and screenprinting to produce multiple copies of an image. Calligraphy is the art of beautiful handwriting, emphasizing the design and execution of letterforms with tools like brushes, pens, and ink to create elegant, expressive text. Both printmaking and calligraphy demand precision and artistic skill, yet printmaking focuses on reproducible imagery while calligraphy highlights unique, handcrafted lettering.
Historical Overview: Printmaking and Calligraphy
Printmaking originated in China during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 AD) and revolutionized mass communication by enabling the reproduction of texts and images on paper. Calligraphy, with roots tracing back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and China, evolved as a revered art form emphasizing expressive handwriting and cultural symbolism. Both practices significantly influenced cultural heritage, with printmaking advancing literary dissemination and calligraphy preserving artistic writing traditions.
Core Techniques: Printmaking vs Calligraphy
Printmaking involves core techniques such as etching, lithography, screen printing, and relief printing, each requiring precise manipulation of plates or screens to transfer ink onto paper or fabric. Calligraphy centers on the controlled use of pens, brushes, or nibs to create fluid, expressive strokes that form intricate letterforms and decorative scripts. Both arts emphasize mastery of tools and materials but differ fundamentally in their approach: printmaking produces multiples of an image through mechanical processes, while calligraphy is a singular, handcrafted expression of written form.
Materials and Tools Compared
Printmaking relies on materials such as linoleum blocks, metal plates, and various inks alongside tools like carving knives, brayers, and printing presses to transfer images onto paper or fabric. Calligraphy uses specialized pens or brushes, including dip pens with metal nibs, fountain pens, and sumi brushes, combined with inks formulated for precision and flow on paper or parchment. Both arts require unique substrates--printmaking often employs heavy-duty papers or textiles, while calligraphy prefers smoother, absorbent surfaces for crisp, clean lettering.
Artistic Styles and Expression
Printmaking harnesses techniques such as etching, lithography, and screen printing to produce multiples of intricate images, emphasizing texture, layering, and bold graphic qualities. Calligraphy centers on the artful formation of letters using brush or pen, showcasing fluid strokes, rhythm, and expressive line variation that convey personality and cultural aesthetics. Both disciplines serve as unique forms of artistic expression, where printmaking captures detailed visual narratives and calligraphy embodies the elegance of written language as visual art.
Popular Applications and Uses
Printmaking excels in producing multiple copies of artworks, commonly used for posters, book illustrations, and fine art prints. Calligraphy is favored for personalized and decorative writing, frequently applied in wedding invitations, certificates, and branding logos. Both techniques have significant roles in visual communication, with printmaking emphasizing reproducibility and calligraphy highlighting artistic handwriting.
Skill Development and Learning Curves
Printmaking demands mastering techniques such as etching, engraving, and screen printing, which require precision, patience, and an understanding of materials and chemical processes; its learning curve is often steep due to technical complexities and equipment use. Calligraphy emphasizes fine motor skills, hand-eye coordination, and an eye for aesthetics, developing muscle memory through repetitive practice of letterforms and strokes; its learning curve can be gradual but consistent with daily handwriting exercises. Both arts enhance creativity and discipline, yet printmaking typically involves more technical skill acquisition while calligraphy focuses more intensely on manual dexterity and stylistic refinement.
Creative Challenges in Each Art Form
Printmaking demands precise control over materials like ink, plates, and presses, challenging artists to anticipate the final image through a reversed and layered process. Calligraphy requires mastery of fluid hand movements and consistent pressure to create harmonious, flowing letterforms, making each stroke a test of discipline and expression. Both art forms push creative boundaries through their unique technical demands and the necessity for meticulous craftsmanship.
Modern Trends and Innovations
Modern printmaking integrates digital technology with traditional techniques, enabling high precision and creative flexibility in producing intricate designs and textures. Calligraphy has evolved through digital tools like graphic tablets and software, allowing artists to blend hand-lettered aesthetics with scalable digital formats for branding and social media. Hybrid approaches combining printmaking and calligraphy harness laser engraving and 3D printing, expanding possibilities in personalized art, packaging, and contemporary visual communication.
Choosing Between Printmaking and Calligraphy
Choosing between printmaking and calligraphy depends on your desired artistic expression and technical preferences. Printmaking offers versatility in producing multiple copies with intricate patterns through techniques like etching and lithography, while calligraphy emphasizes the beauty of hand-drawn letterforms and personal style with tools such as brushes and nib pens. Consider factors like reproducibility, workflow, and the emphasis on text aesthetics when deciding which art form aligns with your creative goals.
Printmaking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com