Expressionist portraiture captures the emotional essence of the subject through bold colors, distorted forms, and dynamic brushstrokes, transcending mere physical representation. This art style focuses on conveying inner feelings and psychological states rather than precise likeness, making each piece a profound personal statement. Discover how expressionist techniques can transform your understanding of portrait art by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
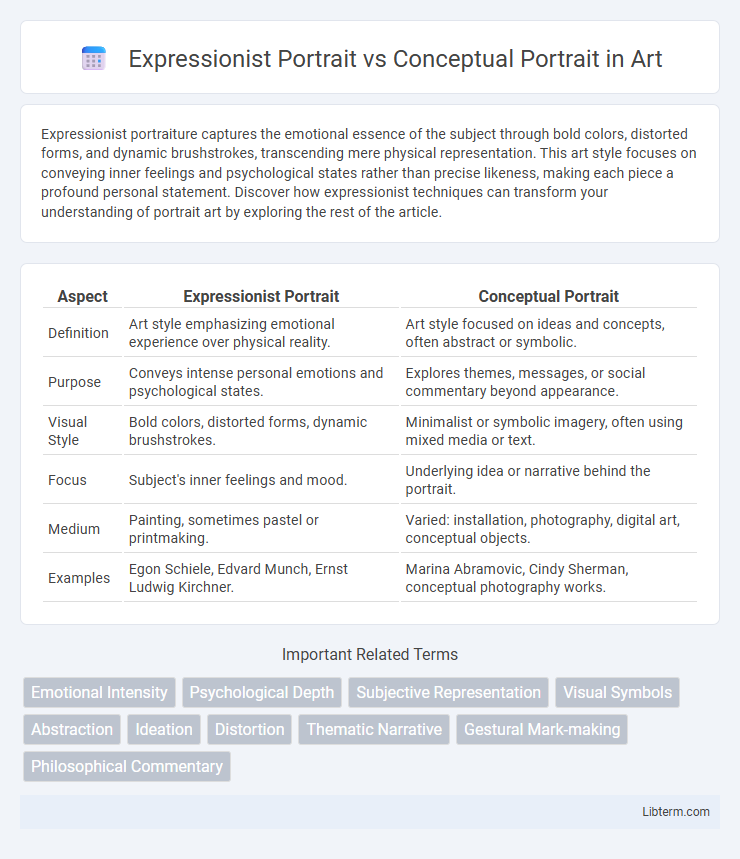
| Aspect | Expressionist Portrait | Conceptual Portrait |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art style emphasizing emotional experience over physical reality. | Art style focused on ideas and concepts, often abstract or symbolic. |
| Purpose | Conveys intense personal emotions and psychological states. | Explores themes, messages, or social commentary beyond appearance. |
| Visual Style | Bold colors, distorted forms, dynamic brushstrokes. | Minimalist or symbolic imagery, often using mixed media or text. |
| Focus | Subject's inner feelings and mood. | Underlying idea or narrative behind the portrait. |
| Medium | Painting, sometimes pastel or printmaking. | Varied: installation, photography, digital art, conceptual objects. |
| Examples | Egon Schiele, Edvard Munch, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner. | Marina Abramovic, Cindy Sherman, conceptual photography works. |
Introduction to Portraiture Genres
Expressionist portraits emphasize emotional intensity and subjective experience through bold colors, distorted forms, and dynamic brushstrokes, allowing artists to convey psychological depth. Conceptual portraits prioritize ideas and narratives, often incorporating symbolic elements or unconventional techniques to challenge traditional representations of identity. Both genres expand the boundaries of portraiture by focusing on internal meaning rather than mere likeness.
Defining Expressionist Portraits
Expressionist portraits emphasize the emotional experience and inner feelings of the subject, often using distorted forms, bold colors, and exaggerated features to evoke intense psychological depth. This style prioritizes subjective interpretation over realistic representation, aiming to capture the artist's emotional response rather than precise likeness. Expressionist portraiture is characterized by its raw, dynamic brushstrokes and a focus on conveying the turmoil or passion inherent in human expression.
Understanding Conceptual Portraits
Conceptual portraits emphasize the idea or message behind the image, often using symbolism, props, or abstract elements to convey complex themes beyond mere physical appearance. Unlike expressionist portraits, which prioritize the emotional experience and exaggerated features to reflect inner feelings, conceptual portraits engage the viewer to interpret deeper meanings and narratives. This approach transforms the subject into a visual representation of intangible concepts, appealing to intellectual and emotional responses simultaneously.
Historical Background and Evolution
Expressionist portraiture emerged in the early 20th century as artists like Edvard Munch and Egon Schiele sought to convey emotional experience rather than physical likeness, emphasizing distorted forms and bold colors. Conceptual portraiture evolved later, particularly gaining prominence during the 1960s and 1970s with artists such as Cindy Sherman, who used photography and performance to explore identity, ideas, and social constructs beyond traditional representation. Both styles reflect broader art movements--Expressionism responding to internal psychological realities, and Conceptualism challenging the nature and purpose of portraiture itself.
Key Techniques in Expressionist Portraiture
Expressionist portraiture employs bold brushstrokes, distorted forms, and exaggerated colors to evoke intense emotional experiences, emphasizing subjective interpretation over realistic representation. Artists use impasto techniques and dynamic lines to capture psychological depth and internal turmoil, creating a visceral connection with the viewer. Contrastingly, conceptual portraits prioritize idea-driven content and symbolism, often incorporating mixed media or external context to engage intellectual reflection.
Artistic Approaches in Conceptual Portraiture
Conceptual portraiture emphasizes ideas and themes over realistic representation, using symbolism, abstraction, and unconventional compositions to communicate complex narratives or emotions. Unlike expressionist portraits, which prioritize the artist's emotional response and stylistic brushwork, conceptual portraits often incorporate mixed media, digital manipulation, or staged environments to challenge viewers' perceptions. This artistic approach transforms the portrait into a platform for intellectual engagement, exploring identity, society, and cultural critique.
Visual and Emotional Impact Comparison
Expressionist portraits emphasize distorted forms and exaggerated colors to evoke intense emotional responses and reveal the artist's subjective experience. Conceptual portraits prioritize intellectual engagement over visual realism, using symbolic elements and minimalistic compositions to provoke thought about identity and meaning. Visually, expressionist works captivate with bold, dynamic aesthetics, while conceptual portraits create emotional impact through ideas and narrative depth.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Expressionist portrait artists like Egon Schiele and Edvard Munch emphasize emotional intensity and distortion, with iconic works such as Schiele's "Self-Portrait with Physalis" and Munch's "The Scream." Conceptual portrait artists including Cindy Sherman and Yoko Ono focus on ideas and identity exploration, exemplified by Sherman's "Untitled Film Stills" series and Ono's "Cut Piece." These distinct approaches highlight how expressionism centers on emotional experience, while conceptualism challenges traditional notions of portraiture through intellectual inquiry.
Expressionist vs Conceptual Style: Contemporary Trends
Expressionist portraiture emphasizes raw emotion and exaggerated features to capture the subject's psychological state, often using bold colors and dynamic brushstrokes that reflect the artist's internal vision. In contrast, conceptual portraiture prioritizes the underlying idea or narrative, using symbolism, staged settings, and mixed media to provoke thought rather than depict realistic likeness. Contemporary trends show a blending of these styles, where artists combine emotional intensity with intellectual themes to create portraits that challenge traditional forms and engage viewers on multiple sensory and cognitive levels.
Choosing Between Expressionist and Conceptual Portraits
Choosing between Expressionist and Conceptual portraits depends on the desired emotional impact and narrative depth; Expressionist portraits emphasize vivid emotional expression and subjective interpretation through bold colors and dynamic brushwork, while Conceptual portraits prioritize intellectual ideas and symbolic meaning, often incorporating abstract elements and mixed media. Artists seeking to convey raw human emotion and psychological intensity may prefer Expressionist techniques, whereas those aiming to provoke thought or communicate a complex concept often opt for Conceptual approaches. Understanding the audience and the intended message is crucial in selecting the appropriate portrait style to achieve maximum artistic resonance and engagement.
Expressionist Portrait Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com