Digital art harnesses advanced technology to create visually compelling pieces that push the boundaries of traditional media. Artists use software, tablets, and digital tools to blend creativity with innovation, producing everything from intricate illustrations to immersive virtual environments. Discover how digital art transforms your creative expression by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
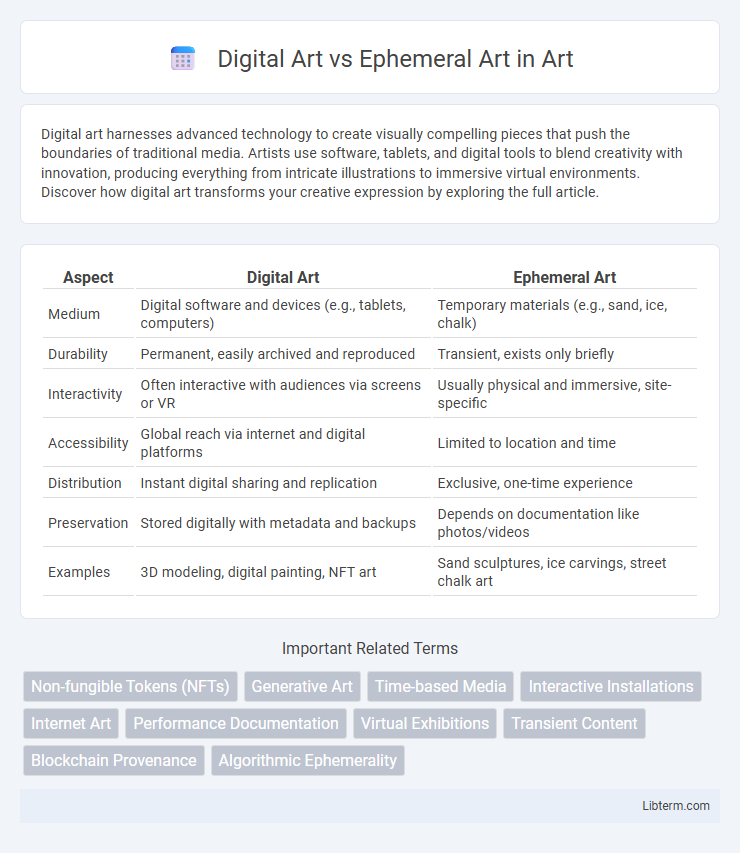
| Aspect | Digital Art | Ephemeral Art |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Digital software and devices (e.g., tablets, computers) | Temporary materials (e.g., sand, ice, chalk) |
| Durability | Permanent, easily archived and reproduced | Transient, exists only briefly |
| Interactivity | Often interactive with audiences via screens or VR | Usually physical and immersive, site-specific |
| Accessibility | Global reach via internet and digital platforms | Limited to location and time |
| Distribution | Instant digital sharing and replication | Exclusive, one-time experience |
| Preservation | Stored digitally with metadata and backups | Depends on documentation like photos/videos |
| Examples | 3D modeling, digital painting, NFT art | Sand sculptures, ice carvings, street chalk art |
Introduction to Digital Art and Ephemeral Art
Digital art utilizes technology such as computers, software, and digital tools to create visually dynamic and easily reproducible works, often characterized by its virtual and multimedia capabilities. Ephemeral art, in contrast, emphasizes temporality and transience, existing only briefly through mediums like performance, street art, or natural materials that degrade over time. Both forms challenge traditional art paradigms by questioning permanence and accessibility while engaging audiences through innovative experiences.
Defining Characteristics of Digital Art
Digital art is defined by its creation, manipulation, and presentation through digital technology, characterized by its use of software, algorithms, and digital devices such as tablets and computers. The defining characteristics include reproducibility without quality loss, interactivity, and the capability for infinite modification and distribution across digital platforms. Unlike ephemeral art, which exists temporarily and often in physical spaces, digital art offers permanence and accessibility through cloud storage and online galleries.
What Makes Art Ephemeral?
Ephemeral art is characterized by its temporary nature, often created with materials or in settings that are inherently transient, such as sand sculptures, ice carvings, or performance art. The defining feature of ephemeral art lies in its impermanence, embracing change, decay, and disappearance as integral parts of the artistic experience. Unlike digital art, which can be preserved indefinitely in virtual formats, ephemeral art exists momentarily, highlighting the beauty of fleeting moments and the passage of time.
Historical Contexts and Evolution
Digital art emerged in the late 20th century, revolutionizing creative expression through technology and software, contrasting with ephemeral art, which dates back to ancient traditions emphasizing impermanence and sensory experience. Ephemeral art, including sand paintings, ice sculptures, and performance art, reflects cultural and ritualistic values across civilizations, while digital art embodies the rapid evolution of digital tools and global connectivity. The historical context of each reveals a shift from transient, tactile forms to enduring, replicable digital creations, showcasing evolving definitions of art over time.
Creation Processes: Tools and Techniques
Digital art creation relies on software like Adobe Photoshop, Procreate, and 3D modeling programs, utilizing techniques such as layering, digital painting, and vector manipulation to produce intricate and editable works. Ephemeral art involves natural or transient materials like sand, ice, and organic elements, created through processes including sand sculpting, ice carving, and performance-based installations that emphasize temporality. The tools in ephemeral art are often manual and site-specific, highlighting the process of creation as part of the artwork's inherent impermanence.
Permanence vs Impermanence in Art
Digital art offers a form of permanence through cloud storage and digital backups, enabling artworks to be preserved indefinitely and accessed globally. Ephemeral art, characterized by its transient nature such as sand mandalas or ice sculptures, emphasizes impermanence and the experiential value of art that exists only momentarily. The contrast between digital art's lasting presence and ephemeral art's intentional temporality highlights evolving perspectives on the lifecycle and preservation of creative expression.
Audience Interaction and Experience
Digital art leverages interactive technologies such as VR, AR, and touchscreens to create immersive experiences that actively engage audiences, allowing real-time manipulation and personalized content. Ephemeral art emphasizes transient, site-specific interactions that provoke a unique, moment-bound emotional response, often dissolving after the experience to highlight impermanence. Audience engagement in digital art fosters prolonged exploration and accessibility, whereas ephemeral art prioritizes immediate, sensory impact and the significance of temporal presence.
Preservation and Documentation Challenges
Digital art faces significant preservation challenges due to rapid technological obsolescence, file format incompatibility, and reliance on specific software or hardware, which complicate long-term access and authenticity verification. In contrast, ephemeral art, such as performance or installation art, presents documentation difficulties as its transient nature resists static capture, requiring innovative recording methods like high-resolution video, 3D scanning, and detailed artist notes to preserve context and experience. Both art forms demand evolving archival strategies that integrate digital repositories, metadata standards, and collaborative conservation efforts to ensure enduring accessibility and cultural value.
Impact on Art Markets and Collectibility
Digital art leverages blockchain technology and NFTs, enabling provable ownership and global accessibility, which reshapes traditional art markets by introducing new avenues for sales and artist royalties. Ephemeral art, characterized by its temporality and site-specific experiences, challenges conventional notions of collectibility due to its transient nature, often relying on documentation or replicas for market value. The contrasting modalities impact collector behavior, with digital art fostering liquidity and verifiable provenance, while ephemeral art emphasizes exclusivity and experiential significance, influencing demand and valuation within contemporary art economies.
Future Trends: Blending Digital and Ephemeral Arts
Future trends indicate a growing convergence between digital art and ephemeral art, leveraging augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies to create immersive, transient experiences. Artists are utilizing blockchain for digital provenance, ensuring authenticity and temporal uniqueness in both digital and ephemeral mediums. This fusion fosters innovative art forms that challenge traditional notions of permanence, audience engagement, and artistic value in the evolving art landscape.
Digital Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com