Monochromy explores the use of a single color or varying shades within a design, creating cohesive and visually striking compositions. This technique enhances focus, evokes specific emotions, and simplifies complex visuals by relying on tonal contrast and texture. Discover how embracing monochromy can transform your aesthetic by reading the rest of the article.
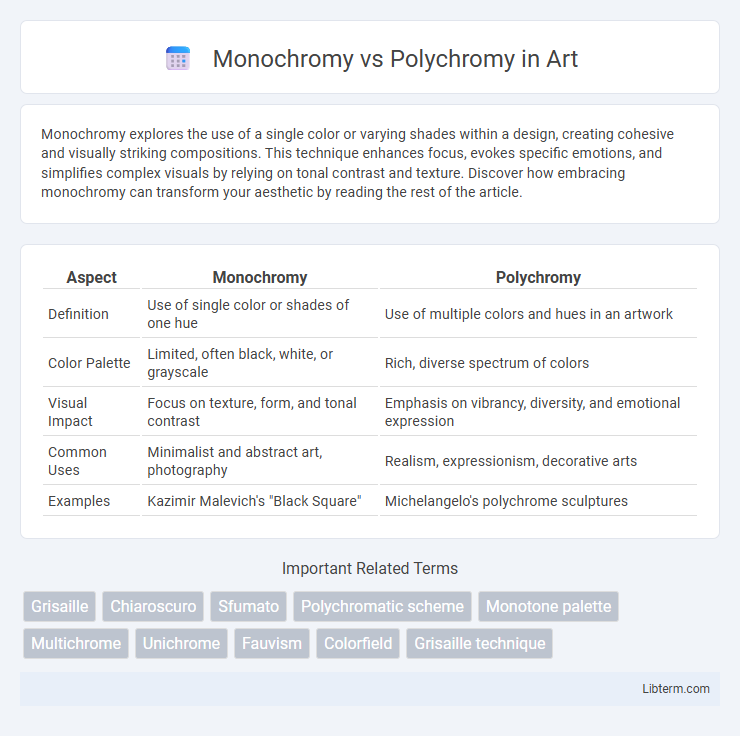
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Monochromy | Polychromy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of single color or shades of one hue | Use of multiple colors and hues in an artwork |
| Color Palette | Limited, often black, white, or grayscale | Rich, diverse spectrum of colors |
| Visual Impact | Focus on texture, form, and tonal contrast | Emphasis on vibrancy, diversity, and emotional expression |
| Common Uses | Minimalist and abstract art, photography | Realism, expressionism, decorative arts |
| Examples | Kazimir Malevich's "Black Square" | Michelangelo's polychrome sculptures |
Introduction to Monochromy and Polychromy
Monochromy refers to the use of a single color or varying shades of one color in art, design, and visual presentations, emphasizing simplicity and uniformity. Polychromy involves multiple colors within a composition, enhancing vibrancy, depth, and visual interest through diverse color palettes. Understanding these concepts is crucial in fields such as painting, architecture, and graphic design for effective color strategy and emotional impact.
Historical Origins of Monochromic Art
Monochromic art traces its origins to prehistoric cave paintings, where early humans employed single-color pigments to depict animals and rituals. Ancient Egyptian and Greek sculptures initially emphasized monochrome techniques, focusing on form and texture before the later adoption of polychromy enhanced realism. The Renaissance period revived monochromatic approaches through chiaroscuro, using light and shadow to achieve depth without relying on multiple colors.
Evolution of Polychromatic Expressions
Polychromatic expressions evolved significantly from the monochromy era by incorporating multiple hues to enrich visual narratives and emotional depth. Early polychromy appeared in ancient architectural decorations and sculptures, where vibrant pigments enhanced realism and symbolic meaning. Advances in pigment technology and artistic techniques during the Renaissance accelerated polychromy's complexity, leading to more sophisticated color harmonies and layered visual storytelling.
Cultural Significance of Color Use
Monochromy emphasizes a single color palette, often symbolizing unity, purity, or spiritual focus within cultural contexts, seen in Buddhist meditation practices or traditional Japanese ink paintings. Polychromy, with its vibrant use of multiple colors, conveys diversity, richness, and complexity, reflecting social status, religious symbolism, or cultural identity in ancient Egyptian tombs and Renaissance art. The deliberate choice of monochromatic or polychromatic schemes reveals deep cultural values and communicates nuanced messages beyond mere aesthetics.
Techniques in Monochromatic Artwork
Monochromatic artwork employs techniques such as varying tonal values, shading, and texture to create depth and dimension using a single hue's range. Artists utilize gradients, hatching, and layering methods to explore contrast and light effects without relying on multiple colors. Precision in brushwork and subtle shifts in saturation enhance the visual impact within the monochrome palette, emphasizing form and composition.
Methods and Materials in Polychromy
Polychromy employs a diverse range of materials including mineral-based pigments, natural dyes, and binders such as egg tempera, wax, or lime plaster to achieve vibrant and durable coloration on sculptures, architecture, and paintings. Methods in polychromy involve layering pigments, often mixed with binders, onto primed surfaces, with techniques like gilding, inlay, and glazing enhancing texture and depth. This approach contrasts with monochromy's reliance on a single color or tone, emphasizing polychromy's complexity through varied materials and multi-step application processes that preserve color fidelity over time.
Symbolism Behind Monochromy
Monochromy, characterized by a single color palette, symbolizes purity, simplicity, and focus, reflecting an uncluttered aesthetic that emphasizes form and texture over chromatic variety. This restraint often conveys themes of introspection, minimalism, and spiritual clarity, contrasting with the vibrant complexity associated with polychromy. In art and design, monochromy leverages its limited hues to evoke deeper emotional responses and highlight symbolic meaning tied to the chosen color.
Emotional Impact of Polychromy
Polychromy, characterized by the use of multiple vibrant colors, significantly enhances emotional impact by creating dynamic visual experiences that evoke feelings of warmth, excitement, and complexity. Unlike monochromy, which relies on variations of a single hue, polychromy stimulates neural responses linked to mood regulation and emotional arousal through its diverse palette. This rich color diversity in art and design fosters deeper psychological engagement and can influence viewers' perceptions and emotional states more intensely.
Monochromy vs Polychromy in Contemporary Art
Monochromy in contemporary art emphasizes a singular color palette, often exploring depth, texture, and subtle tonal variations to evoke minimalism and focus on form. Polychromy, by contrast, employs multiple colors to create dynamic compositions that convey complexity, emotion, and cultural narratives. Artists like Yves Klein championed monochrome with his International Klein Blue, while artists such as Kehinde Wiley exemplify polychromy through vibrant, multi-hued portraits reflecting modern identity.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Monochromy and Polychromy
Choosing between monochromy and polychromy depends largely on the desired visual impact and emotional tone of the project. Monochromy emphasizes simplicity, unity, and subtlety by using variations within a single color, making it ideal for minimalist designs and conveying calmness. Polychromy utilizes multiple colors to create vibrant, dynamic, and diverse aesthetics, suitable for projects aiming to attract attention, express complexity, or evoke a lively atmosphere.
Monochromy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com