Drawing enhances creativity, improves hand-eye coordination, and serves as a powerful form of self-expression. Mastering various techniques, from sketching to shading, allows Your artwork to convey emotion and tell compelling stories. Discover practical tips and inspiring ideas to elevate Your drawing skills throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
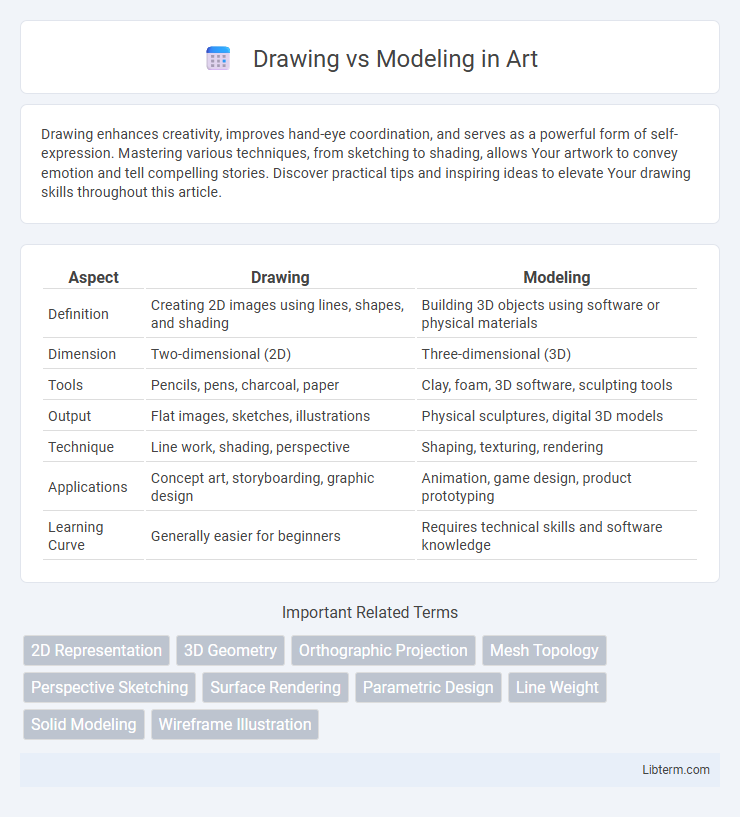
| Aspect | Drawing | Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating 2D images using lines, shapes, and shading | Building 3D objects using software or physical materials |
| Dimension | Two-dimensional (2D) | Three-dimensional (3D) |
| Tools | Pencils, pens, charcoal, paper | Clay, foam, 3D software, sculpting tools |
| Output | Flat images, sketches, illustrations | Physical sculptures, digital 3D models |
| Technique | Line work, shading, perspective | Shaping, texturing, rendering |
| Applications | Concept art, storyboarding, graphic design | Animation, game design, product prototyping |
| Learning Curve | Generally easier for beginners | Requires technical skills and software knowledge |
Introduction to Drawing and Modeling
Drawing involves creating two-dimensional representations using lines, shapes, and shading techniques to convey form and depth on a flat surface. Modeling refers to the process of developing three-dimensional digital or physical representations, often using software or sculpting materials, to visualize objects with volume and spatial attributes. Both drawing and modeling play crucial roles in fields like design, architecture, and animation, offering distinct approaches to visual communication and conceptualization.
Defining Drawing: Concepts and Techniques
Drawing involves creating images through manual application of lines, shapes, and shading to represent objects or ideas on a two-dimensional surface. Key techniques include contour drawing, hatching, cross-hatching, and blending, which help define form, texture, and depth. Drawing emphasizes observation and interpretation, serving as a foundational skill for artists to visualize concepts before advancing to more complex modeling processes.
Understanding Modeling: Basics and Applications
Modeling involves creating three-dimensional digital representations of objects or scenes using software such as Blender, AutoCAD, or SketchUp, essential for industries like architecture, animation, and engineering. Unlike drawing, which is typically two-dimensional and focuses on lines and shapes, modeling allows for manipulation of volume, texture, and lighting, enabling realistic visualization and simulation. Fundamental concepts in modeling include polygonal mesh construction, surface shading techniques, and UV mapping, which are crucial for producing accurate and detailed digital models for various applications.
Key Differences Between Drawing and Modeling
Drawing involves creating two-dimensional representations using lines, shading, and textures to convey ideas and visuals, relying heavily on manual skills or digital tools like tablets. Modeling produces three-dimensional digital or physical objects, emphasizing volume, depth, and spatial relationships through software such as CAD or sculpting materials. Key differences include the dimensionality--drawing is typically 2D while modeling is 3D--and the application focus, where drawing captures form and detail visually, and modeling enables interaction and manipulation of the object in a three-dimensional space.
Tools Used in Drawing vs Modeling
Drawing relies on traditional tools such as pencils, pens, charcoal, and paper, along with digital tablets and styluses for digital sketches. Modeling utilizes software platforms like Autodesk Maya, Blender, and 3ds Max, featuring specialized tools for creating, sculpting, and texturing 3D objects and environments. Each set of tools caters to distinct creative processes, with drawing focusing on 2D expression and modeling on 3D visualization.
Skill Development: Drawing vs Modeling
Drawing hones hand-eye coordination, spatial awareness, and observational skills, enabling artists to capture detailed textures, light, and shadow on a two-dimensional plane. Modeling strengthens technical expertise in 3D software, enhances understanding of geometry, and cultivates proficiency in manipulating digital forms for realistic rendering and animation. Both skill sets contribute uniquely to visual storytelling, with drawing emphasizing foundational artistic expression and modeling focusing on digital precision and versatility.
Advantages of Drawing for Creatives
Drawing offers creatives unparalleled freedom in expressing ideas quickly and intuitively, fostering immediate visual experimentation without technical constraints. It enhances hand-eye coordination and observational skills, allowing artists to capture nuances and emotions more effectively than modeling tools. The tactile nature of drawing materials also promotes a deeper connection to the creative process, enabling more organic and spontaneous concept development.
Benefits of Modeling in Design Processes
Modeling enhances design processes by enabling precise visualization and manipulation of 3D objects, facilitating better spatial understanding and reducing errors before production. It supports iterative testing and modifications, allowing designers to explore multiple scenarios quickly and optimize functionality and aesthetics. Integration with simulation tools further improves decision-making by predicting performance and ensuring design feasibility.
Integrating Drawing and Modeling in Projects
Integrating drawing and modeling in projects enhances accuracy and communication by combining the precision of 3D CAD modeling with the clarity of 2D technical drawings. Utilizing BIM (Building Information Modeling) software allows seamless updates between models and drawings, reducing errors and streamlining workflows. This integration supports multidisciplinary collaboration, ensuring consistency across architectural, structural, and MEP designs.
Future Trends in Drawing and Modeling
Future trends in drawing showcase an integration of augmented reality (AR) and AI-powered tools that enhance precision and creativity, revolutionizing architectural and industrial design workflows. Modeling is rapidly advancing with generative design algorithms and real-time simulation capabilities, enabling designers to create complex, optimized structures more efficiently. The convergence of cloud-based collaboration platforms with immersive 3D environments accelerates project iterations and fosters innovation across drawing and modeling disciplines.
Drawing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com