Mastering the art of painting transforms blank canvases into vibrant expressions of creativity and emotion. Techniques such as blending, layering, and brushwork elevate your skills and bring depth to every stroke. Explore this article to uncover expert tips and inspiring ideas to enhance your painting journey.
Table of Comparison
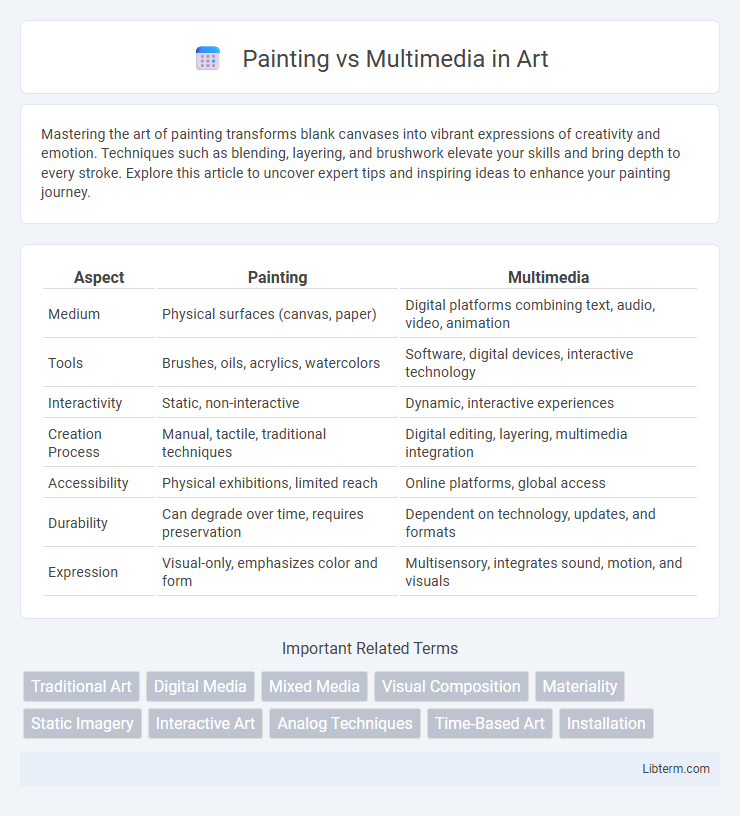
| Aspect | Painting | Multimedia |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Physical surfaces (canvas, paper) | Digital platforms combining text, audio, video, animation |
| Tools | Brushes, oils, acrylics, watercolors | Software, digital devices, interactive technology |
| Interactivity | Static, non-interactive | Dynamic, interactive experiences |
| Creation Process | Manual, tactile, traditional techniques | Digital editing, layering, multimedia integration |
| Accessibility | Physical exhibitions, limited reach | Online platforms, global access |
| Durability | Can degrade over time, requires preservation | Dependent on technology, updates, and formats |
| Expression | Visual-only, emphasizes color and form | Multisensory, integrates sound, motion, and visuals |
Understanding Painting: Traditional Art Form
Painting, a traditional art form dating back thousands of years, relies on techniques such as brushwork, color theory, and composition to create visually compelling works. This medium emphasizes tactile interaction with physical materials like canvas, oil, acrylics, and watercolor, fostering deep sensory engagement. Understanding painting involves appreciating the historical context, symbolism, and craftsmanship that define its enduring cultural significance.
Exploring Multimedia: Modern Artistic Expression
Multimedia integrates diverse digital tools such as video, audio, animation, and interactive elements to create immersive artistic experiences that transcend traditional painting. Unlike classical painting, multimedia art leverages technology to engage multiple senses, offering dynamic visual narratives and real-time viewer interaction. This modern artistic expression expands the boundaries of creativity, enabling artists to explore complex themes through innovative combinations of digital media and traditional techniques.
Historical Evolution of Both Mediums
Painting, one of the oldest art forms, dates back to prehistoric times with cave paintings and evolved through Renaissance masterpieces to contemporary styles, emphasizing color, texture, and form on canvas or other surfaces. Multimedia art emerged in the 20th century, integrating digital technology, video, sound, and interactive elements, transforming traditional artistic practices through tools like computers and software since the 1960s. The historical evolution of painting reflects manual craftsmanship and material exploration, while multimedia art represents a shift towards technology-driven, immersive experiences expanding the boundaries of artistic expression.
Tools and Techniques: Paintbrush vs Digital Interface
Traditional painting relies on physical tools such as paintbrushes, canvases, and various types of paint like oil, acrylic, or watercolor, which allow for tactile control and texture manipulation. Multimedia creation predominantly utilizes digital interfaces, including graphic tablets, styluses, and software like Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator, enabling precise edits, layering, and diverse effects through virtual tools. The contrast between the hands-on, material-based techniques of paintbrushes and the versatile, software-driven methods of digital interfaces highlights distinct creative processes and output possibilities.
Expression of Creativity: Static vs Dynamic
Painting offers a static expression of creativity through fixed visual compositions that capture a moment or emotion on canvas. Multimedia enables dynamic creativity by integrating audio, video, and interactive elements to engage multiple senses and evolve over time. This combination allows for a more immersive and versatile artistic experience compared to traditional painting.
Sensory Experiences: Visual Impact and Beyond
Painting offers a rich visual impact through color, texture, and brushstrokes that engage the viewer's sense of sight and evoke emotional responses. Multimedia incorporates diverse sensory elements such as sound, motion, and interactivity, creating immersive experiences that extend beyond visual perception. These combined stimuli can stimulate multiple senses simultaneously, enhancing engagement and emotional depth in ways traditional painting alone may not.
Accessibility and Audience Engagement
Painting offers tactile and visual accessibility, appealing to audiences through texture, color, and physical presence in galleries or museums, fostering a personal and immersive experience. Multimedia integrates diverse elements such as video, sound, and interactive features that enhance accessibility for varied audiences, including those with disabilities, by providing multiple sensory entry points. This blend of formats increases audience engagement through dynamic storytelling and interactivity, expanding reach beyond traditional gallery spaces into digital platforms.
Permanence and Preservation Challenges
Painting offers greater permanence due to traditional materials like oil and acrylic, which can last centuries with proper care, while multimedia artworks face significant preservation challenges because of rapidly evolving technologies and software obsolescence. Digital files require ongoing migration, backups, and format updates, making multimedia preservation resource-intensive and uncertain over long periods. Conservation efforts for multimedia also demand specialized expertise and emulation strategies to maintain accessibility and authenticity of the original experience.
Market Value and Artistic Recognition
Painting maintains strong market value through established auction records and collector demand, particularly for works by renowned artists such as Picasso and Warhol. Multimedia art gains increasing artistic recognition in contemporary circles due to its innovative use of technology and immersive experiences, attracting younger collectors and digital art investors. While paintings often command higher prices at traditional art fairs, multimedia pieces leverage online platforms and NFT markets to expand their economic reach.
Future Trends in Art: Blending Painting and Multimedia
Future trends in art increasingly emphasize the fusion of traditional painting with multimedia technologies, creating immersive and interactive experiences that push creative boundaries. Artists integrate digital tools such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and projection mapping with classic paint mediums to engage diverse audiences and enhance storytelling. This hybrid approach expands artistic expression, blurring the lines between physical and digital art forms while driving innovation in contemporary art.
Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com