Minimalism focuses on simplifying your life by reducing clutter and prioritizing essentials, creating a peaceful and functional environment. This approach enhances mental clarity, productivity, and overall well-being by eliminating distractions and fostering intentional living. Discover how adopting minimalism can transform your lifestyle and mindset by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
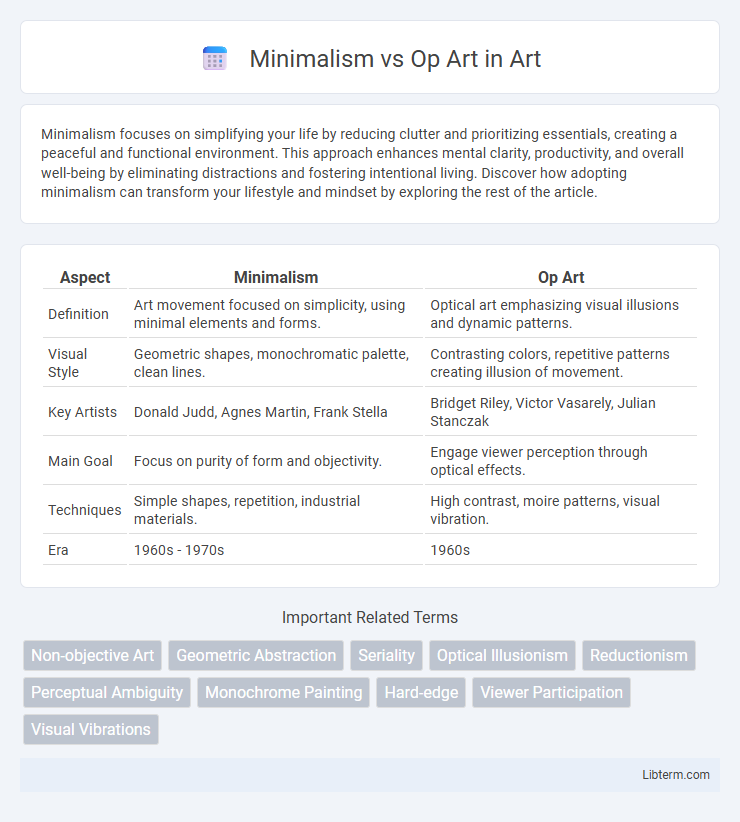
| Aspect | Minimalism | Op Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art movement focused on simplicity, using minimal elements and forms. | Optical art emphasizing visual illusions and dynamic patterns. |
| Visual Style | Geometric shapes, monochromatic palette, clean lines. | Contrasting colors, repetitive patterns creating illusion of movement. |
| Key Artists | Donald Judd, Agnes Martin, Frank Stella | Bridget Riley, Victor Vasarely, Julian Stanczak |
| Main Goal | Focus on purity of form and objectivity. | Engage viewer perception through optical effects. |
| Techniques | Simple shapes, repetition, industrial materials. | High contrast, moire patterns, visual vibration. |
| Era | 1960s - 1970s | 1960s |
Introduction to Minimalism and Op Art
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity, focusing on clean lines, geometric shapes, and monochromatic palettes to evoke clarity and order. Op Art exploits optical illusions through precise patterns and contrasting colors, creating dynamic visual effects that engage the viewer's perception. Both movements challenge traditional art forms by prioritizing experiential interaction, yet Minimalism promotes restraint while Op Art intensifies visual complexity.
Historical Origins and Influences
Minimalism emerged in the late 1950s as a reaction against the emotional intensity of Abstract Expressionism, rooted in the principles of simplicity, geometric forms, and industrial materials. Op Art, developing in the early 1960s, was heavily influenced by the works of artists like Victor Vasarely and Bridget Riley, who explored optical illusions and visual perception through precise patterns and contrasting colors. Both movements drew on Modernist ideas but diverged significantly, with Minimalism emphasizing reduction and materiality while Op Art focused on dynamic visual effects and viewer interaction.
Key Philosophies: Less is More vs Optical Illusions
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity, using basic geometric forms and limited color palettes to highlight purity and essence, embodying the philosophy of "Less is More." Op Art, however, centers on creating dynamic optical illusions through intricate patterns and contrasting colors, engaging viewers' perception and movement. These contrasting approaches reflect Minimalism's focus on reduction versus Op Art's emphasis on visual complexity.
Defining Features of Minimalist Art
Minimalist art emphasizes simplicity through geometric forms, monochromatic palettes, and clean lines, stripping away personal expression to focus on the artwork's physical presence. It often utilizes industrial materials and repetition to create an objective visual experience, contrasting Op Art's reliance on optical illusions and complex patterns. Key figures such as Donald Judd and Agnes Martin exemplify Minimalism's pursuit of purity and clarity in art.
Op Art: Techniques and Visual Impact
Op Art employs precise geometric patterns, contrasting colors, and optical illusions to create dynamic visual effects that engage the viewer's perception. Techniques such as moire patterns, repetitive lines, and color juxtaposition generate movement, vibration, and depth on flat surfaces. This visual impact challenges spatial understanding and encourages active viewer interaction, distinguishing Op Art's experiential emphasis from the simplicity of Minimalism.
Leading Artists in Minimalism and Op Art
Leading artists in Minimalism include Donald Judd, known for his geometric metal and plywood structures, Dan Flavin, who pioneered the use of fluorescent light installations, and Agnes Martin, celebrated for her subtle grid paintings emphasizing simplicity and repetition. In Op Art, Bridget Riley stands out for her black-and-white optical illusions that create dynamic visual effects, Victor Vasarely is recognized as the father of Op Art with his intricate geometric patterns, and Jesus Rafael Soto combined kinetic elements with visual perception to engage viewers in movement and vibration. Both movements focus on visual experience but differ in approach, with Minimalism emphasizing reduction and form, and Op Art exploring perception and optical illusions.
Color, Form, and Space: A Comparative Analysis
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity through limited color palettes, geometric forms, and the use of negative space to create clarity and balance. Op Art employs contrasting colors, dynamic patterns, and illusionistic spatial effects to engage visual perception and produce vibratory movement. The minimalist approach isolates form and color for purity, while Op Art manipulates these elements to challenge depth and dimensionality.
Minimalism in Modern Design and Architecture
Minimalism in modern design and architecture emphasizes simplicity, clean lines, and functional forms that reduce visual clutter and enhance spatial clarity. This design philosophy embraces neutral color palettes, open floor plans, and the use of natural materials like wood, glass, and steel to create serene and timeless environments. Unlike Op Art's dynamic visual effects, Minimalism prioritizes calmness and utility, influencing iconic structures such as Ludwig Mies van der Rohe's Barcelona Pavilion and Tadao Ando's concrete masterpieces.
Op Art’s Legacy in Contemporary Visual Culture
Op Art's legacy in contemporary visual culture is evident through its influence on digital design, fashion, and advertising, where optical illusions and vibrant geometric patterns create dynamic visual experiences. The movement's emphasis on visual perception and movement continues to inspire interactive media and virtual reality environments, enhancing user engagement through sensory manipulation. Its foundational principles challenge conventional aesthetics, encouraging ongoing experimentation with form, color, and spatial interaction in modern artistic practices.
Minimalism vs Op Art: Which Resonates Today?
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity, clean lines, and monochromatic palettes that evoke calm and clarity, appealing to contemporary design trends favoring functionality and reduced distraction. Op Art, characterized by vibrant patterns and optical illusions, creates dynamic visual experiences but can feel overwhelming in modern minimalist spaces. Today's aesthetic preferences favor Minimalism due to its adaptability in digital media, architecture, and lifestyle branding, resonating with audiences seeking balance and focus.
Minimalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com