Sgraffito is a decorative technique that involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting layer beneath, commonly used in ceramics, wall art, and glasswork. This method creates intricate designs and textures, enhancing the visual depth and uniqueness of your artwork. Explore the rest of this article to discover how sgraffito can transform your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
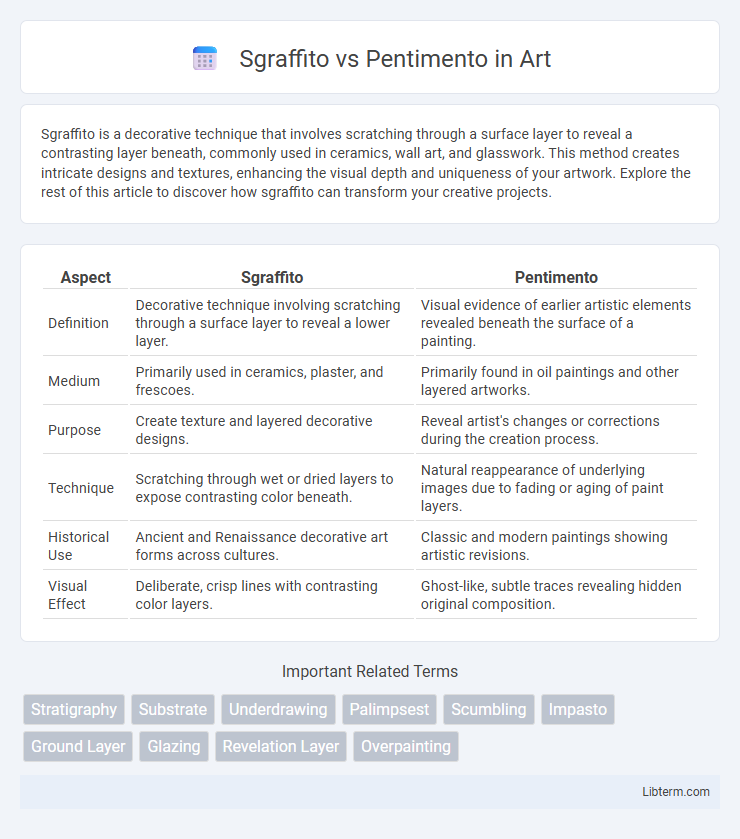
| Aspect | Sgraffito | Pentimento |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decorative technique involving scratching through a surface layer to reveal a lower layer. | Visual evidence of earlier artistic elements revealed beneath the surface of a painting. |
| Medium | Primarily used in ceramics, plaster, and frescoes. | Primarily found in oil paintings and other layered artworks. |
| Purpose | Create texture and layered decorative designs. | Reveal artist's changes or corrections during the creation process. |
| Technique | Scratching through wet or dried layers to expose contrasting color beneath. | Natural reappearance of underlying images due to fading or aging of paint layers. |
| Historical Use | Ancient and Renaissance decorative art forms across cultures. | Classic and modern paintings showing artistic revisions. |
| Visual Effect | Deliberate, crisp lines with contrasting color layers. | Ghost-like, subtle traces revealing hidden original composition. |
Introduction to Sgraffito and Pentimento
Sgraffito is an artistic technique that involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting underlayer, commonly used in ceramics and wall decoration to create intricate designs. Pentimento refers to the visible traces of earlier paintings or sketches beneath a finished artwork, where the artist's changes become perceptible over time due to the aging and transparency of the paint layers. Both techniques reveal underlying elements, with sgraffito highlighting intentional surface manipulation and pentimento exposing historical creative revisions.
Historical Origins of Sgraffito and Pentimento
Sgraffito originated in the Italian Renaissance during the 15th century as a decorative technique involving scratching through layers of plaster or paint to reveal contrasting colors beneath. Pentimento emerged in the 16th-century painting practices, primarily observed in oil paintings where earlier images become visible over time due to the natural aging and translucency of the paint layers. Both techniques reveal the artistic process but differ in purpose: sgraffito is intentional surface decoration, while pentimento indicates changes or corrections made by the artist.
Defining Sgraffito: Technique and Process
Sgraffito is a decorative technique involving scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, commonly used in ceramics, wall art, and pottery. The process requires applying multiple layers of colored plaster or slip, then carefully etching designs to expose the underlying hues, creating intricate textures and patterns. This method highlights craftsmanship and precision, distinguishing it from pentimento, which refers to visible alterations or earlier images beneath a painting's surface.
Understanding Pentimento: Technique and Process
Pentimento reveals an artist's process by showing earlier images or strokes beneath the surface of a painting, often visible as faded or altered forms. This technique occurs naturally over time when the top layers of paint become more transparent, allowing previous work to resurface. Understanding pentimento enhances appreciation of a painting's history and the dynamic nature of artistic creation, distinguishing it from sgraffito, which involves deliberate scratching through layers.
Artistic Purposes: Sgraffito vs Pentimento
Sgraffito and pentimento serve distinct artistic purposes centered on texture and narrative evolution within a painting. Sgraffito is a technique where artists scratch through a top layer of paint to reveal contrasting colors beneath, creating intricate textures and dynamic visual effects that enhance surface detail. Pentimento, on the other hand, reveals an underlying image or previous composition as paint layers become translucent over time, offering insight into the artist's creative process and the artwork's historical development.
Material Differences in Sgraffito and Pentimento
Sgraffito involves scraping layers of plaster or paint to reveal contrasting colors beneath, typically using materials like clay or pigment-laden plaster on walls or ceramics. Pentimento refers to the visible traces of earlier painting or drawing beneath the surface layer of an artwork, often due to changes in the type or thickness of oil paint over time. The material contrast lies in sgraffito's intentional layering and removal of solid pigments or plaster, while pentimento emerges from the natural aging and translucency of oil-based paints.
Visual Effects and Aesthetic Outcomes
Sgraffito creates striking visual effects by subtracting layers to reveal contrasting colors or textures beneath, enhancing depth and tactile interest in the artwork. Pentimento involves visible traces of earlier compositions or corrections, which add historical layers and authenticity, giving the piece a dynamic sense of evolution over time. Both techniques enrich the aesthetic outcome by introducing complexity; sgraffito emphasizes surface contrast and texture, while pentimento conveys an emotional and temporal narrative.
Famous Examples of Sgraffito and Pentimento in Art
Famous examples of sgraffito include the intricate designs on the walls of Pompeii and the Renaissance frescoes by Italian artists such as Andrea Mantegna, showcasing layered textures created through scratching. Notable pentimento instances appear in Leonardo da Vinci's "Lady with an Ermine" and Rembrandt's "The Night Watch," where underlying changes reveal the artist's original intentions beneath visible surfaces. These techniques highlight the evolution and depth of artistic process, providing valuable insights into historical methods and creative decisions.
Contemporary Applications and Innovations
Sgraffito and pentimento techniques have found renewed interest in contemporary art and design, with sgraffito being widely used in modern ceramics and wall murals for its tactile textural effects and vivid layering capabilities. Innovations in digital technology have enabled artists to simulate pentimento, revealing underlying imagery through augmented reality and layered digital compositions, enhancing narrative depth. Both techniques are embraced in contemporary mixed-media practices, leveraging traditional craftsmanship alongside modern materials to create dynamic, multi-dimensional artworks.
Choosing Between Sgraffito and Pentimento for Modern Artists
Modern artists choosing between sgraffito and pentimento must consider the desired visual texture and narrative depth; sgraffito offers a tactile, scratched surface revealing underlying layers, ideal for bold, textured effects, while pentimento involves uncovering previous compositions, adding historical dimension and complexity to the artwork. Sgraffito works well with materials like plaster, ceramics, or thick paint layers, whereas pentimento requires transparent or semi-transparent mediums such as oil paint to allow earlier layers to emerge subtly. The decision hinges on whether the artist prioritizes surface manipulation or the revelation of the painting's evolution to convey meaning.
Sgraffito Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com