Traditional brush painting captures timeless artistry through delicate strokes and natural pigments, embodying cultural heritage and aesthetic philosophy. Mastery of brush control and ink wash techniques creates expressive landscapes and intricate details that evoke emotion and tranquility. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding and appreciate the nuances behind traditional brush painting methods.
Table of Comparison
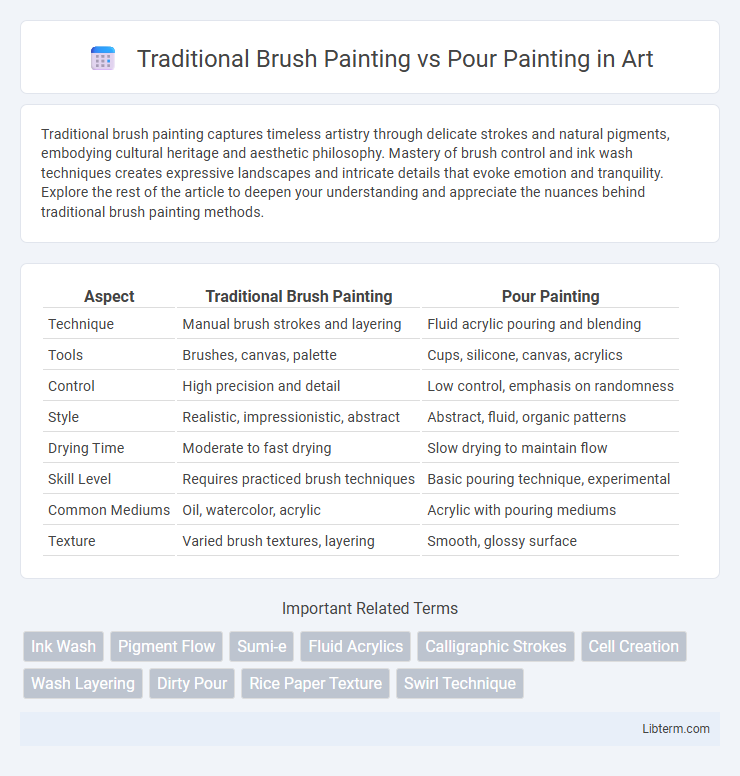
| Aspect | Traditional Brush Painting | Pour Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Manual brush strokes and layering | Fluid acrylic pouring and blending |
| Tools | Brushes, canvas, palette | Cups, silicone, canvas, acrylics |
| Control | High precision and detail | Low control, emphasis on randomness |
| Style | Realistic, impressionistic, abstract | Abstract, fluid, organic patterns |
| Drying Time | Moderate to fast drying | Slow drying to maintain flow |
| Skill Level | Requires practiced brush techniques | Basic pouring technique, experimental |
| Common Mediums | Oil, watercolor, acrylic | Acrylic with pouring mediums |
| Texture | Varied brush textures, layering | Smooth, glossy surface |
Introduction to Brush Painting and Pour Painting
Traditional brush painting involves applying pigment to a surface using various brush techniques to create detailed and controlled imagery, emphasizing precision and texture. Pour painting, on the other hand, entails pouring and manipulating fluid paint directly onto the canvas, resulting in abstract patterns driven by color flow and natural movement. Both methods showcase distinct artistic expressions, with brush painting rooted in deliberate strokes and pour painting highlighting spontaneity and fluidity.
Historical Background of Traditional Brush Painting
Traditional brush painting traces its roots to East Asian cultures, particularly Chinese ink wash painting dating back over a thousand years during the Tang Dynasty. This art form emphasizes fluid brushstrokes using handmade brushes and natural ink on rice paper, capturing landscapes, flora, and fauna with spiritual and philosophical depth. Mastery of brush techniques aligns with Confucian and Taoist principles, reflecting an enduring heritage preserved through classical calligraphy and painting schools.
Origins and Evolution of Pour Painting
Traditional brush painting traces its origins to ancient civilizations such as China and Egypt, where artists used controlled brush strokes to create detailed imagery on silk and papyrus. Pour painting, also known as fluid art, emerged in the mid-20th century, evolving from abstract expressionism and experimental techniques that emphasized spontaneity and the unpredictable flow of liquid paints. This method gained popularity as artists explored the interplay of colors and forms without traditional tools, marking a significant shift from deliberate brushwork to dynamic, organic patterns.
Core Techniques in Traditional Brush Painting
Traditional brush painting emphasizes precise brush control, varying pressure, and stroke speed to create intricate textures and fluid lines. Artists utilize techniques such as layering washes, dry brushing, and calligraphic strokes to achieve depth and tonal variation. Mastery of brush angle and ink or paint consistency is essential for the distinct expressiveness characteristic of traditional brush artwork.
Fundamental Methods Used in Pour Painting
Pour painting uses fluid acrylics poured directly onto the canvas, creating spontaneous patterns through layering and tilting, contrasting with traditional brush painting's controlled, stroke-based application. The fundamental methods in pour painting include dirty pour, flip cup, and puddle pour, each relying on gravity and paint viscosity to blend colors naturally. Mastery of pouring mediums and paint consistency is crucial for achieving desired effects without cracking or uneven drying.
Material Differences: Brushes, Canvases, and Paints
Traditional brush painting utilizes various types of brushes, including sable or synthetic bristles, designed for precise strokes on canvas or textured paper, often employing oil or acrylic paints for rich color layering. Pour painting relies on a fluid consistency acrylic paint mixed with pouring mediums to achieve smooth flows and cells on primed, sealed canvases or wood panels that support the liquid paint's movement. The material differences primarily involve brush types suited for controlled application in traditional methods versus the viscosity and canvas preparation optimized for spontaneous spreading in pour painting.
Artistic Styles and Visual Outcomes
Traditional brush painting emphasizes precise strokes and controlled techniques, resulting in detailed, textured compositions that highlight the artist's craftsmanship and cultural heritage. Pour painting employs fluid dynamics and unpredictable blending of colors, producing abstract, organic patterns with a glossy, marbled appearance that highlights spontaneity and movement. Both styles offer distinct visual experiences: traditional brush painting impresses with intentional detail, while pour painting captivates through vibrant, flowing color interactions.
Cultural Significance and Symbolism
Traditional brush painting, rooted in East Asian cultures, employs precise techniques to convey spiritual harmony and nature's essence, symbolizing balance and mindfulness. Pour painting, emerging from contemporary Western art, emphasizes fluidity and spontaneity, representing freedom and emotional expression through abstract forms. The cultural significance of brush painting lies in its historical continuity and ritualistic practice, while pour painting reflects modern ideals of individuality and creative liberation.
Accessibility for Beginners and Skill Requirements
Traditional brush painting demands precise hand control and familiarity with brush techniques, making it more challenging for beginners to master detailed strokes and blending. Pour painting offers an accessible entry point with minimal skill requirements, as it relies on fluid dynamics and layering of acrylics to create abstract effects without detailed brushwork. Beginners often find pour painting more approachable due to its forgiving nature and emphasis on experimentation rather than technical precision.
Contemporary Trends and Future Directions
Traditional brush painting emphasizes precise brushwork and texture control, maintaining classical techniques that highlight craftsmanship and cultural heritage. Pour painting, gaining popularity in contemporary art, involves fluid dynamics and abstract expression, appealing through vibrant color blends and spontaneous patterns. Future directions suggest hybrid approaches that merge traditional precision with the unpredictable aesthetics of pour painting, driven by advancements in materials and digital integration.
Traditional Brush Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com