Sculpture transforms raw materials into expressive, three-dimensional art that captures movement, emotion, and form. This timeless art form spans from classical marble statues to contemporary installations, reflecting cultural history and innovative techniques. Discover how sculpture can inspire your creativity and deepen your appreciation of artistic expression by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
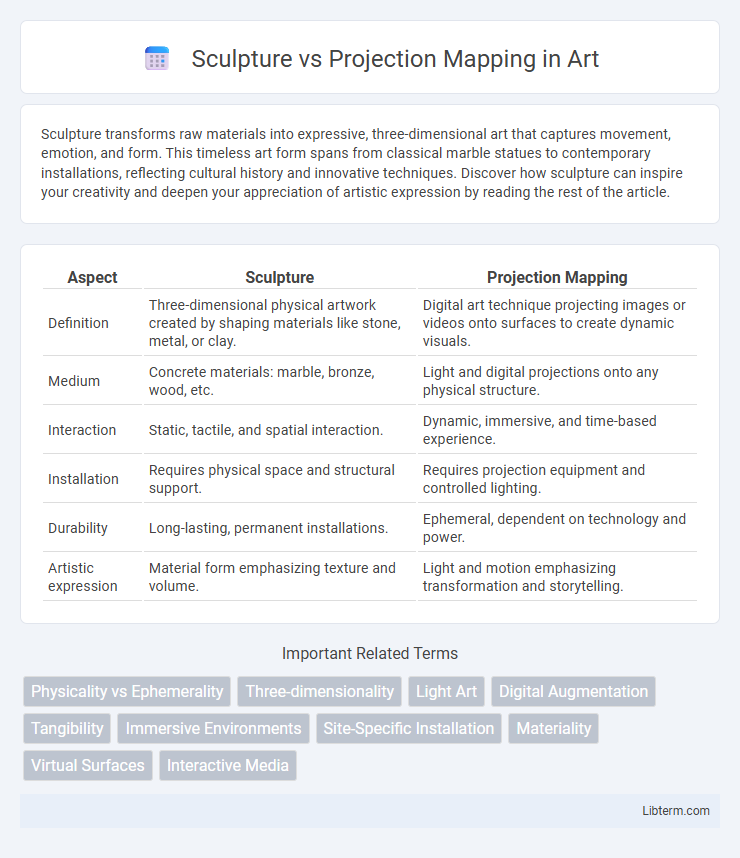
| Aspect | Sculpture | Projection Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Three-dimensional physical artwork created by shaping materials like stone, metal, or clay. | Digital art technique projecting images or videos onto surfaces to create dynamic visuals. |
| Medium | Concrete materials: marble, bronze, wood, etc. | Light and digital projections onto any physical structure. |
| Interaction | Static, tactile, and spatial interaction. | Dynamic, immersive, and time-based experience. |
| Installation | Requires physical space and structural support. | Requires projection equipment and controlled lighting. |
| Durability | Long-lasting, permanent installations. | Ephemeral, dependent on technology and power. |
| Artistic expression | Material form emphasizing texture and volume. | Light and motion emphasizing transformation and storytelling. |
Introduction to Sculpture and Projection Mapping
Sculpture is a three-dimensional art form created by shaping materials such as clay, stone, metal, or wood to represent figures, forms, or abstract concepts. Projection mapping, also known as video mapping, involves projecting images or videos onto irregular surfaces, transforming physical objects into dynamic displays through light and motion. Both techniques merge art and technology but differ fundamentally in medium and interaction with space.
History and Evolution of Sculpture
Sculpture, one of the oldest forms of artistic expression, dates back to prehistoric times with examples such as the Venus of Willendorf, reflecting early human creativity in three-dimensional forms carved from stone, wood, and clay. Over centuries, sculpture evolved through diverse materials and styles, from the intricate marble statues of the Renaissance to modern abstract works using metal and mixed media. Projection mapping, emerging in the late 20th century, contrasts with traditional sculpture by integrating digital technology to project dynamic imagery onto static surfaces, expanding the boundaries of visual storytelling and art installation.
The Rise of Projection Mapping in Art
Projection mapping has transformed the art world by allowing artists to project dynamic visuals onto three-dimensional surfaces, creating immersive experiences that traditional sculpture alone cannot achieve. This technology enables the integration of light, motion, and sound, expanding the boundaries of artistic expression beyond static forms. The rise of projection mapping exemplifies the fusion of digital innovation with physical structures, attracting widespread attention at festivals, museums, and public art installations globally.
Core Materials and Techniques Compared
Sculpture relies on traditional core materials such as stone, metal, clay, and wood, shaped through carving, casting, or assembling to create three-dimensional, tactile art pieces. Projection mapping uses digital projectors, specialized software, and surfaces like buildings or sculptures as canvases to overlay dynamic, light-based images and animations. While sculpture emphasizes physical form and texture, projection mapping focuses on visual transformation and interactive experiences through technology.
Physical Presence vs Digital Experience
Sculpture offers a tangible, three-dimensional artwork that occupies physical space, allowing viewers to engage with texture, form, and materiality firsthand. Projection mapping transforms surfaces through dynamic digital visuals, creating immersive experiences that change perception without altering the object's physical structure. The contrast lies in sculpture's enduring presence versus projection mapping's ephemeral and adaptable digital display.
Impact on Viewer Engagement
Sculpture offers tangible, three-dimensional forms that invite viewers to physically explore texture, shape, and space, creating a lasting sensory impact through direct interaction. Projection mapping transforms surfaces with dynamic light and imagery, capturing attention through vivid motion and immersive storytelling that adapts to the environment. Both mediums significantly enhance viewer engagement by stimulating different sensory experiences--sculpture through tactile presence and projection mapping through visual innovation and adaptability.
Flexibility and Limitations of Each Medium
Sculpture offers tactile, three-dimensional form with a physical presence that can be experienced from multiple angles but is limited by static materials and fixed shapes. Projection mapping provides dynamic visual content capable of transforming any surface, allowing for temporal and spatial flexibility, though it relies on suitable projection environments and may lack physical tangibility. Both mediums serve distinct artistic purposes, with sculpture excelling in permanence and texture, while projection mapping thrives in adaptability and ephemeral expression.
Notable Artists and Landmark Works
Sculpture boasts iconic artists like Auguste Rodin, whose work *The Thinker* revolutionized modern sculpture, and Michelangelo, renowned for the marble masterpiece *David*. Projection mapping features innovators such as Refik Anadol, known for immersive digital installations like *Melting Memories*, and Urbanscreen, acclaimed for large-scale urban projections in cities worldwide. These landmark works highlight the tangible permanence of traditional sculpture versus the dynamic, ephemeral nature of projection mapping art.
Integration of Sculpture and Projection Mapping
Integration of sculpture and projection mapping creates immersive visual experiences by combining three-dimensional physical forms with dynamic digital content. This fusion enhances storytelling and artistic expression, allowing projections to interact precisely with a sculpture's contours, textures, and features, resulting in a seamless blend of tactile and virtual elements. Advanced mapping software and high-resolution projectors are essential tools for aligning visuals onto sculptures, transforming static art into vibrant, evolving displays that engage viewers on multiple sensory levels.
Future Trends in Artistic Expression
Sculpture and projection mapping are converging as future artistic expression trends integrate physical form with dynamic digital media, creating immersive, multisensory experiences. Advances in augmented reality and AI-driven visuals enable artists to transform static sculptures into interactive displays, enhancing viewer engagement and narrative depth. This fusion empowers new creative possibilities, redefining public art and exhibition design in the digital age.
Sculpture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com