Pentimento reveals the hidden layers beneath a painting's surface where earlier images or corrections become visible over time, showcasing an artist's evolving creative process. This phenomenon provides valuable insight into the artwork's history and the technical methods used by painters. Discover how pentimento can transform your appreciation of art by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
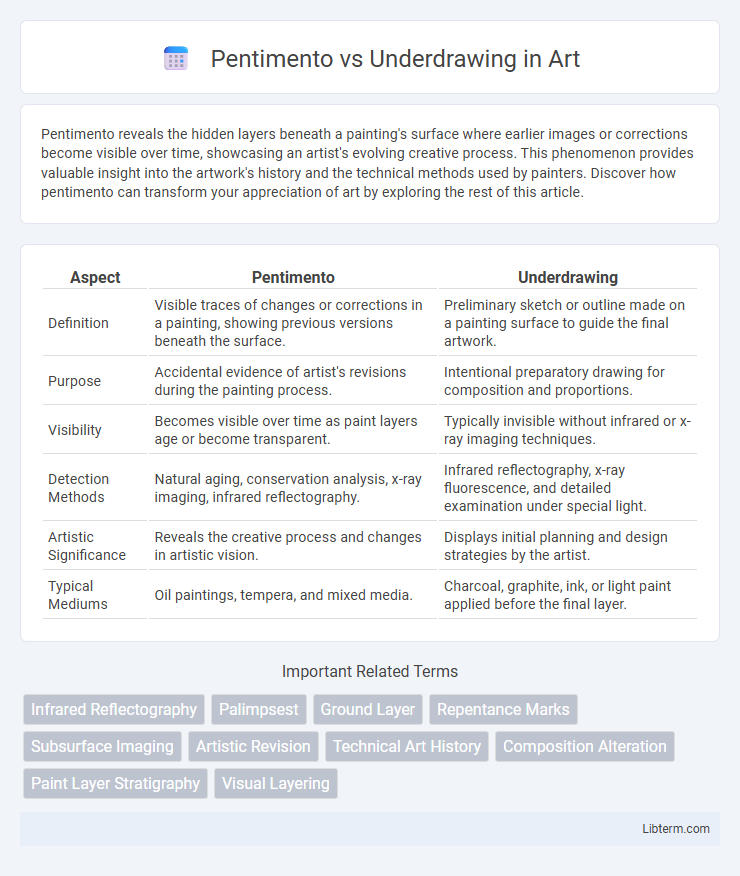
| Aspect | Pentimento | Underdrawing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visible traces of changes or corrections in a painting, showing previous versions beneath the surface. | Preliminary sketch or outline made on a painting surface to guide the final artwork. |
| Purpose | Accidental evidence of artist's revisions during the painting process. | Intentional preparatory drawing for composition and proportions. |
| Visibility | Becomes visible over time as paint layers age or become transparent. | Typically invisible without infrared or x-ray imaging techniques. |
| Detection Methods | Natural aging, conservation analysis, x-ray imaging, infrared reflectography. | Infrared reflectography, x-ray fluorescence, and detailed examination under special light. |
| Artistic Significance | Reveals the creative process and changes in artistic vision. | Displays initial planning and design strategies by the artist. |
| Typical Mediums | Oil paintings, tempera, and mixed media. | Charcoal, graphite, ink, or light paint applied before the final layer. |
Understanding Pentimento: Definition and Origins
Pentimento refers to visible traces of an artist's earlier work beneath the final layers of paint, revealing changes in composition or design during a painting's creation. Originating from the Italian word meaning "repentance" or "change of mind," pentimenti provide insight into the artist's process and decision-making. Unlike underdrawing, which is a preliminary sketch often hidden under paint layers, pentimenti become apparent as paint layers age or become transparent.
Explaining Underdrawing in Art
Underdrawing in art refers to the preliminary sketch or outline artists create on a canvas or paper to plan composition, proportions, and details before applying paint or ink. It serves as a foundational guide, often made with pencil, charcoal, or ink, helping to structure the final artwork accurately. Unlike pentimento, which reveals changes made during the painting process, underdrawing is intentional and an original part of the artist's creative method.
Key Differences Between Pentimento and Underdrawing
Pentimento refers to the visible traces of earlier painting layers that an artist has changed or painted over, revealing modifications in the artwork's composition. Underdrawing is the initial sketch or outline made on a surface before applying paint, serving as a guide for the final image without altering visible layers. Key differences lie in pentimento being a later alteration visible beneath paint layers, while underdrawing is a preparatory mark made at the start of the creative process.
Historical Context of Pentimento
Pentimento, evident in Renaissance and Baroque paintings, reveals artists' shifts in creative decisions through visible alterations beneath the surface layer, reflecting the dynamic process of art-making before varnishes and glazing techniques became widespread. Unlike underdrawing, which serves as an initial structural guideline often executed with charcoal or ink, pentimento represents changes made during or after the painting process as the composition evolved. This historical phenomenon offers valuable insights into the artistic methods and intentions of masters like Rembrandt and Titian, highlighting the fluidity of artistic expression in pre-modern art techniques.
The Role of Underdrawing in Artistic Techniques
Underdrawing serves as a foundational step in artistic techniques, providing artists with an initial sketch that guides composition and detail placement before applying paint. Pentimento, in contrast, reveals changes made during the creative process, often visible in finished artworks as alterations or corrections. Understanding the role of underdrawing highlights its importance in planning and execution, while pentimento offers insights into an artist's evolving vision and technique.
Techniques for Detecting Pentimento
Pentimento is detected through infrared reflectography and X-ray radiography, which reveal underlying modifications and alterations in an artwork's composition by penetrating surface layers. These advanced imaging techniques differentiate pentimenti from underdrawings by displaying changes made during the painting process, while underdrawings are preliminary sketches not altered later. Multispectral imaging further enhances the ability to analyze the materials and layers, offering critical insights into artists' revisions and creative decisions.
Methods Used to Reveal Underdrawing
Infrared reflectography (IRR) is a primary method used to reveal underdrawings beneath paint layers by detecting carbon-based materials, which absorb infrared light. X-ray radiography complements this technique by visualizing denser pigments and changes in composition, helping distinguish between pentimenti and original underdrawings. Multispectral imaging further enhances detection by capturing images at different wavelengths, providing detailed insight into the artist's preliminary sketches and alterations.
Famous Artworks Exhibiting Pentimento
Pentimento refers to visible traces of earlier paintings beneath the surface layer, often revealing an artist's changes, as seen in works like Leonardo da Vinci's "The Virgin of the Rocks" and Rembrandt's "The Night Watch." Underdrawing differs by being a preliminary sketch that guides the painting process, typically invisible without infrared reflectography. Famous artworks exhibiting pentimento provide critical insights into artists' evolving creative processes and techniques during the Renaissance and Baroque periods.
The Importance of Pentimento and Underdrawing in Art Conservation
Pentimento and underdrawing are crucial in art conservation for revealing an artist's original intentions and creative process, aiding in authentication and dating of artworks. Pentimento, the visible traces of earlier painting layers, helps conservators understand modifications and material composition, guiding restoration efforts with historical accuracy. Underdrawing, detected through infrared reflectography, unveils preliminary sketches beneath the surface, providing insights into techniques and enabling non-invasive analysis critical for preserving cultural heritage.
Pentimento vs Underdrawing: Impact on Art Interpretation
Pentimento reveals an artist's process through visible alterations or corrections in a completed painting, providing insight into creative decisions and evolution. Underdrawing, often hidden beneath paint layers, serves as a preliminary guide for composition but remains less apparent to viewers. The presence of pentimento can significantly influence art interpretation by exposing the artwork's developmental history, whereas underdrawing primarily informs technical analysis and authenticity studies.
Pentimento Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com