Market value reflects the current price at which an asset or property can be bought or sold in an open market, influenced by supply, demand, and economic conditions. Understanding your asset's market value is essential for making informed financial decisions and maximizing returns. Explore the rest of the article to learn how market value impacts your investments and strategies.
Table of Comparison
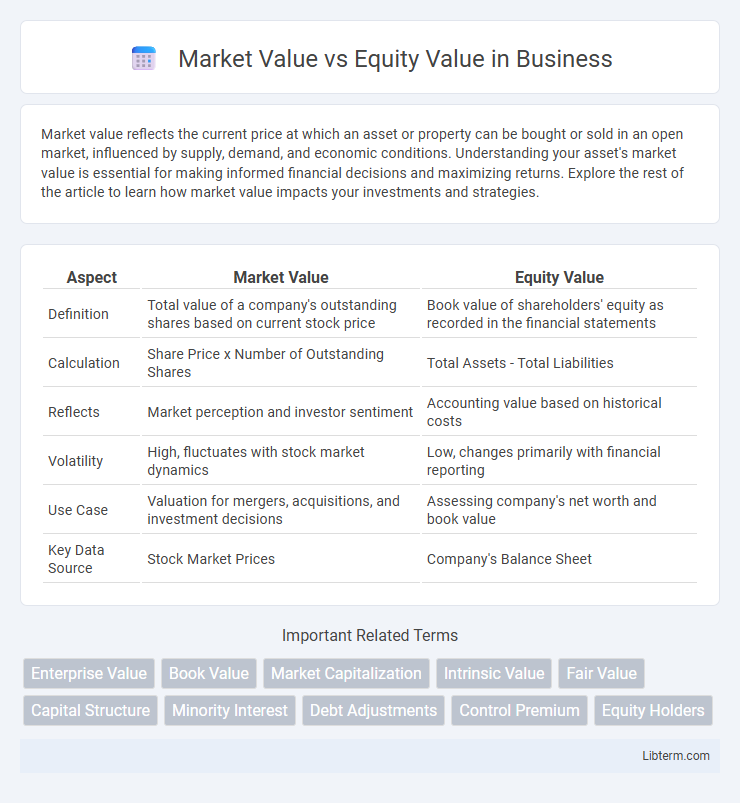
| Aspect | Market Value | Equity Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total value of a company's outstanding shares based on current stock price | Book value of shareholders' equity as recorded in the financial statements |
| Calculation | Share Price x Number of Outstanding Shares | Total Assets - Total Liabilities |
| Reflects | Market perception and investor sentiment | Accounting value based on historical costs |
| Volatility | High, fluctuates with stock market dynamics | Low, changes primarily with financial reporting |
| Use Case | Valuation for mergers, acquisitions, and investment decisions | Assessing company's net worth and book value |
| Key Data Source | Stock Market Prices | Company's Balance Sheet |
Introduction to Market Value and Equity Value
Market Value represents the total worth of a company according to current stock prices multiplied by outstanding shares, reflecting investor perceptions and market conditions. Equity Value, often synonymous with Market Capitalization, measures the ownership value held by shareholders after liabilities are accounted for. Understanding the distinction between Market Value and Equity Value is essential for accurate company valuation and investment decision-making.
Defining Market Value: Key Concepts
Market value represents the total worth of a company's outstanding shares as determined by current stock price multiplied by total shares outstanding, reflecting investor perceptions and market conditions. It differs from equity value, which incorporates additional factors such as debt, cash, and other assets to provide a comprehensive measure of a company's net worth. Understanding market value involves analyzing market capitalization, float-adjusted shares, and stock liquidity to gauge real-time business valuation.
Understanding Equity Value in Business Context
Equity value represents the total value of a company's shares owned by shareholders, reflecting the market value of its outstanding equity. It is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares, providing insight into shareholder ownership and company worth from an equity perspective. Understanding equity value is crucial for assessing a company's market capitalization, evaluating investment potential, and making informed business decisions.
Core Differences Between Market Value and Equity Value
Market value represents the total value of a company based on its current stock price multiplied by the total number of outstanding shares, reflecting the market's perception of the company's worth. Equity value, also known as shareholders' equity, represents the net value attributable to shareholders, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities on the balance sheet. Core differences include market value being forward-looking and influenced by market conditions, while equity value is historical and based on accounting records.
Factors Influencing Market Value
Market value is primarily influenced by external factors such as investor sentiment, market conditions, and economic trends, which directly affect a company's stock price. Company performance metrics, including earnings growth, cash flow stability, and competitive positioning, also play crucial roles in shaping market value. Unlike equity value, which is derived from accounting book values, market value fluctuates with supply and demand dynamics in the open market.
Components Affecting Equity Value
Equity value is primarily affected by the number of outstanding shares, share price, and any dilutive securities such as stock options or convertible debt. Changes in liabilities, cash reserves, and non-operating assets indirectly influence equity value through their impact on enterprise value. Market value reflects the total value of a company's equity while equity value specifically accounts for shareholder ownership after subtracting debt and obligations.
Methods for Calculating Market Value
Market value is commonly calculated using the market capitalization method, which multiplies the current share price by the total number of outstanding shares. Another approach includes Enterprise Value, which incorporates market capitalization, total debt, minority interest, preferred shares, minus cash and cash equivalents. These methods provide a dynamic reflection of a company's worth based on market conditions, unlike equity value, which focuses solely on shareholder ownership.
How to Determine Equity Value Accurately
To determine Equity Value accurately, start with the company's Market Value by multiplying the current share price by the total number of outstanding shares. Then adjust for net debt by subtracting total debt and adding cash and cash equivalents, ensuring that liabilities are fully accounted for. Incorporate other relevant factors such as preferred stock, minority interests, and any dilutive securities like stock options to reflect the true ownership value.
Importance of Market Value vs Equity Value in Investment Decisions
Market value reflects the current market capitalization of a company based on its stock price, while equity value represents the book value of shareholders' ownership on the balance sheet. Investors prioritize market value for assessing a company's true worth and potential growth, as it incorporates market sentiment and future cash flow expectations. Understanding the distinction aids in accurate valuation, risk assessment, and strategic investment decisions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metric for Business Valuation
Market value reflects the current price investors are willing to pay for a company's total outstanding shares, providing a real-time assessment of its worth. Equity value, often used internally, considers the book value of shareholders' ownership and is crucial for understanding the company's net asset value. Selecting between market value and equity value depends on the valuation purpose, with market value preferred for investment decisions and equity value favored for internal financial analysis and acquisition assessments.
Market Value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com