A Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) is a contractual arrangement between an energy producer and a buyer, specifying terms for the sale and purchase of electricity. This agreement helps you secure long-term energy supply at predetermined rates, ensuring cost stability and supporting renewable energy projects. Discover how understanding PPAs can optimize your energy strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
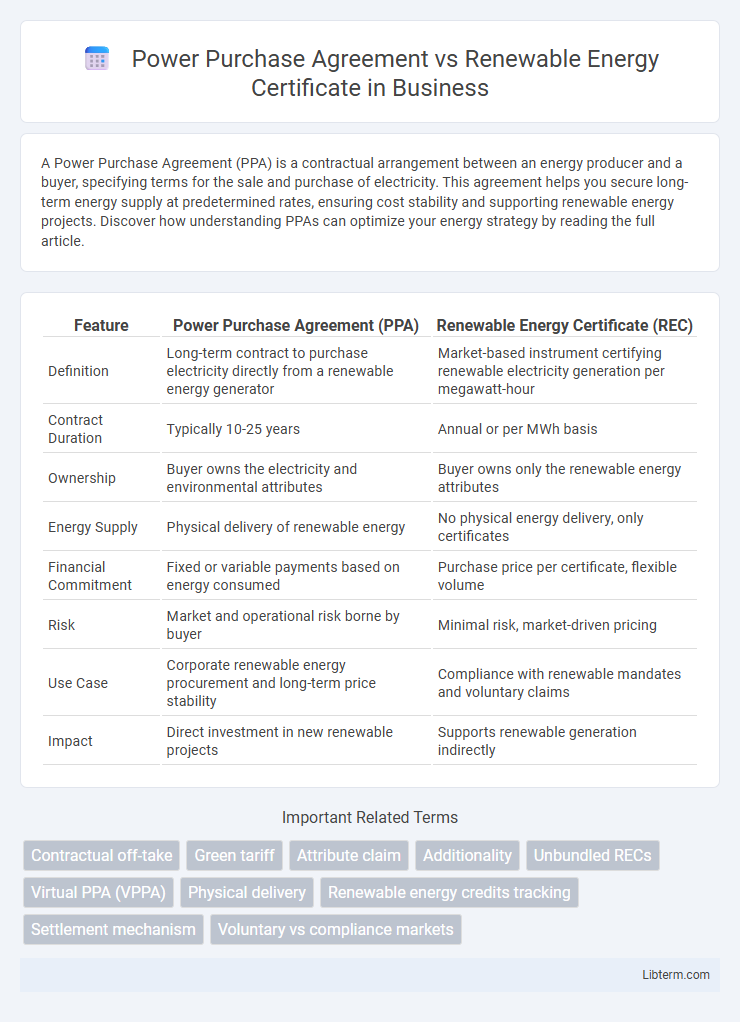
| Feature | Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) | Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term contract to purchase electricity directly from a renewable energy generator | Market-based instrument certifying renewable electricity generation per megawatt-hour |
| Contract Duration | Typically 10-25 years | Annual or per MWh basis |
| Ownership | Buyer owns the electricity and environmental attributes | Buyer owns only the renewable energy attributes |
| Energy Supply | Physical delivery of renewable energy | No physical energy delivery, only certificates |
| Financial Commitment | Fixed or variable payments based on energy consumed | Purchase price per certificate, flexible volume |
| Risk | Market and operational risk borne by buyer | Minimal risk, market-driven pricing |
| Use Case | Corporate renewable energy procurement and long-term price stability | Compliance with renewable mandates and voluntary claims |
| Impact | Direct investment in new renewable projects | Supports renewable generation indirectly |
Understanding Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) are long-term contracts between energy producers and buyers that secure a fixed price for electricity generated from renewable sources, ensuring financial stability and predictability. PPAs facilitate direct investment in renewable energy projects by providing guaranteed revenue streams, making them crucial for project financing and development. In contrast, Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that electricity was generated from a renewable source but do not involve direct power purchase or price agreements.
What Are Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)?
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity was generated from a renewable energy resource and fed into the grid. Companies and individuals purchase RECs to claim the environmental benefits of renewable energy without directly sourcing power through a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA). RECs play a crucial role in tracking and verifying renewable energy generation, enabling compliance with regulatory requirements and supporting sustainability goals.
Key Differences Between PPAs and RECs
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) are contracts enabling the purchase of electricity directly from renewable energy producers at fixed rates, providing long-term price stability and physical energy supply. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent the environmental benefits of renewable energy generation, allowing organizations to claim renewable energy usage without directly receiving the physical electricity. Key differences include PPAs involving direct procurement and delivery of electricity, while RECs focus solely on the ownership of renewable attributes and can be traded independently of energy consumption.
How PPAs Facilitate Renewable Energy Adoption
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) enable large-scale renewable energy projects by providing long-term revenue certainty, attracting investment for wind and solar installations. Unlike Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) that primarily represent proof of green energy generation, PPAs create direct contractual agreements between energy producers and consumers, ensuring consistent demand. This financial stability accelerates the deployment of clean energy infrastructure, reducing carbon emissions and supporting grid decarbonization goals.
The Role of RECs in Green Energy Claims
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) serve as proof that one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity was generated from a renewable energy resource, enabling businesses to claim green energy usage even without direct physical delivery. Unlike Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), which involve long-term contracts to purchase energy directly from renewable generators, RECs provide a flexible mechanism for companies to support renewable energy markets and meet sustainability goals. The role of RECs is crucial in verifying and tracking renewable energy consumption, ensuring transparency and credibility in corporate green energy claims.
Financial Implications: PPAs vs RECs
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) provide long-term price certainty and fixed electricity costs, reducing exposure to market volatility and enabling easier project financing. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) offer flexibility by allowing entities to claim renewable energy usage without directly purchasing electricity, often resulting in lower upfront costs but limited financial predictability. PPAs typically deliver greater financial stability and potential cost savings over time, while RECs serve as a cost-effective option for meeting renewable energy goals with minimal capital investment.
Risk and Contractual Obligations
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) involve long-term contractual obligations where buyers assume risks related to price fluctuations, delivery performance, and creditworthiness of the seller, creating a direct liability for energy procurement. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof of renewable energy generation without binding the holder to energy delivery or price stability, significantly reducing contractual and financial risk. PPAs require detailed risk management strategies and contractual commitments, while RECs offer flexible renewable energy compliance with minimal contractual exposure.
Environmental Impact: Comparing PPAs and RECs
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) directly support the development of renewable energy projects by providing long-term financial commitment, leading to measurable reductions in carbon emissions and fostering cleaner energy infrastructure. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that one megawatt-hour of electricity was generated from a renewable resource, enabling organizations to claim environmental benefits but without necessarily driving new renewable capacity. PPAs have a greater environmental impact by facilitating increased renewable energy generation, while RECs primarily serve as market-based instruments for tracking and verifying renewable energy use.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Organization
Choosing between a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) and Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) depends on your organization's sustainability goals and financial strategy. PPAs offer long-term, fixed-price energy contracts that provide cost certainty and direct investment in renewable projects, while RECs represent proof of renewable energy generation and offer flexible, short-term compliance with renewable energy targets. Evaluating factors like budget constraints, risk tolerance, and desired impact on renewable energy development helps determine the optimal solution for reducing carbon footprint and meeting corporate social responsibility objectives.
Future Trends in PPAs and RECs
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) are evolving with longer contract durations and increased integration of energy storage to enhance grid stability, signaling a shift towards more resilient renewable energy frameworks. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are witnessing growing demand driven by corporate sustainability goals and regulatory mandates, promoting market expansion and heightened transparency through blockchain technology. Future trends indicate a convergence of PPAs and RECs in hybrid models that optimize financial and environmental benefits for stakeholders.
Power Purchase Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com