Deferred compensation plans allow you to postpone receiving a portion of your earnings until a later date, often to reduce current tax liabilities and enhance retirement savings. These arrangements can include employer-sponsored plans like 401(k)s or nonqualified plans designed for key employees, providing flexibility in financial and tax planning. Explore the rest of this article to understand how deferred compensation could benefit your long-term financial strategy.
Table of Comparison
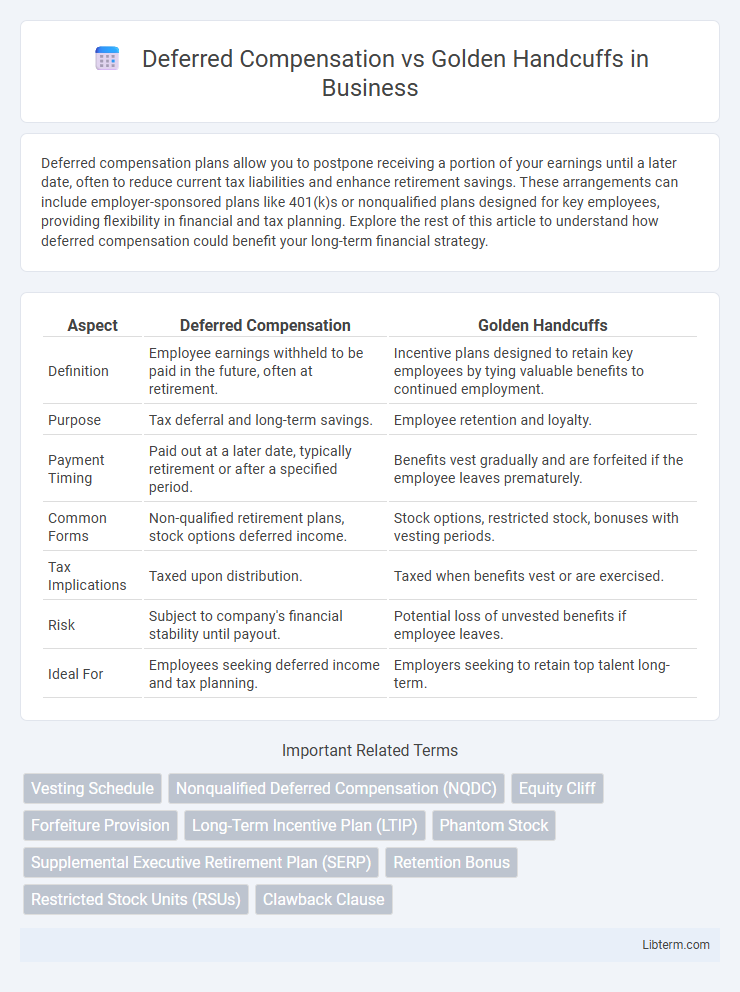
| Aspect | Deferred Compensation | Golden Handcuffs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee earnings withheld to be paid in the future, often at retirement. | Incentive plans designed to retain key employees by tying valuable benefits to continued employment. |
| Purpose | Tax deferral and long-term savings. | Employee retention and loyalty. |
| Payment Timing | Paid out at a later date, typically retirement or after a specified period. | Benefits vest gradually and are forfeited if the employee leaves prematurely. |
| Common Forms | Non-qualified retirement plans, stock options deferred income. | Stock options, restricted stock, bonuses with vesting periods. |
| Tax Implications | Taxed upon distribution. | Taxed when benefits vest or are exercised. |
| Risk | Subject to company's financial stability until payout. | Potential loss of unvested benefits if employee leaves. |
| Ideal For | Employees seeking deferred income and tax planning. | Employers seeking to retain top talent long-term. |
Introduction to Deferred Compensation and Golden Handcuffs
Deferred compensation refers to an arrangement where employees earn wages that are paid out at a later date, often to reduce current tax liability or as a retirement benefit. Golden handcuffs are financial incentives, such as deferred compensation plans or stock options, designed to retain key employees by rewarding them for staying with the company long-term. Both tools align employee interests with company goals by providing substantial future financial rewards contingent on continued employment.
Defining Deferred Compensation: Key Features
Deferred compensation is a financial arrangement where an employee earns income that is paid out at a later date, often during retirement, to manage tax liabilities and enhance long-term savings. Key features include tax deferral, vesting schedules, and employer contributions that may depend on performance or tenure. This strategy contrasts with golden handcuffs, which are incentives designed to retain employees through restricted stock or bonuses tied to continued employment.
Understanding Golden Handcuffs: What Are They?
Golden handcuffs are financial incentives offered by employers to retain key employees through deferred compensation plans that vest over time, often including stock options, bonuses, or retirement benefits. These arrangements create a significant financial cost for employees if they leave the company prematurely, effectively encouraging long-term commitment. By aligning employee interests with corporate goals, golden handcuffs foster stability and reduce turnover in critical roles.
Core Differences Between Deferred Compensation and Golden Handcuffs
Deferred compensation refers to an agreement where employees receive a portion of their income at a later date, often to benefit from tax advantages and long-term savings, while golden handcuffs are incentives designed to retain key employees by offering benefits or bonuses that vest over time. Deferred compensation plans typically emphasize financial deferral and tax strategies, whereas golden handcuffs focus on retention through restricted stock, stock options, or clawback provisions. The core difference lies in deferred compensation's emphasis on timing income distribution, compared to golden handcuffs' emphasis on locking in talent and reducing turnover risk.
Benefits of Deferred Compensation Plans
Deferred compensation plans provide significant tax advantages by allowing employees to postpone income taxes until funds are withdrawn, typically during retirement when tax rates may be lower. These plans enhance employee retention by offering a long-term financial incentive beyond regular salary, often with potential for investment growth. Employers benefit from the ability to attract and retain key talent while managing compensation expenses more effectively with structured future payouts.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Golden Handcuffs
Golden handcuffs offer significant advantages by incentivizing employee retention through substantial financial rewards, such as stock options or bonuses that vest over time, aligning employee interests with company performance. However, the drawbacks include reduced employee mobility and potential dissatisfaction due to perceived restrictions on leaving the company, which can impact morale and limit career growth. Despite these drawbacks, golden handcuffs remain a powerful strategic tool for companies aiming to secure key talent in competitive industries.
Tax Implications: Deferred Compensation vs Golden Handcuffs
Deferred compensation plans defer income tax liability until the funds are distributed, typically at retirement, potentially reducing the current tax burden and allowing for tax-deferred growth. Golden handcuffs often include stock options or restricted stock units, which trigger tax events upon vesting or exercise, leading to immediate taxable income based on the fair market value. Understanding the timing and nature of taxation in both deferred compensation and golden handcuffs arrangements is crucial for optimizing overall tax strategy and maximizing net financial benefits.
Employer Perspectives: Attraction and Retention Strategies
Employers use deferred compensation to attract high-level talent by offering future financial rewards that promote long-term commitment and align employee interests with company success. Golden handcuffs are structured incentives, like stock options or bonuses, designed to retain key employees by imposing financial penalties or forfeitures if they leave prematurely. Both strategies enhance retention and reduce turnover costs, with deferred compensation emphasizing future gains and golden handcuffs focusing on immediate retention leverage.
Employee Considerations: Choosing the Right Option
Employees should evaluate long-term financial goals and job stability when deciding between deferred compensation and golden handcuffs. Deferred compensation offers tax advantages and flexibility but requires commitment to the employer, while golden handcuffs provide retention incentives through stock options or bonuses that vest over time. Understanding vesting schedules, tax implications, and personal career plans is crucial for selecting the most beneficial compensation strategy.
Conclusion: Which Approach Is Best For You?
Choosing between deferred compensation and golden handcuffs depends on your financial goals and career plans. Deferred compensation offers tax advantages and long-term savings growth, ideal for those prioritizing retirement funding. Golden handcuffs provide retention incentives with potential forfeiture risks, suitable if your primary goal is job stability and loyalty within a company.
Deferred Compensation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com