Outsourcing enables businesses to reduce costs and access specialized expertise by delegating non-core functions to external service providers. This strategic approach improves operational efficiency and allows companies to focus on their primary goals. Discover how outsourcing can transform your business by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
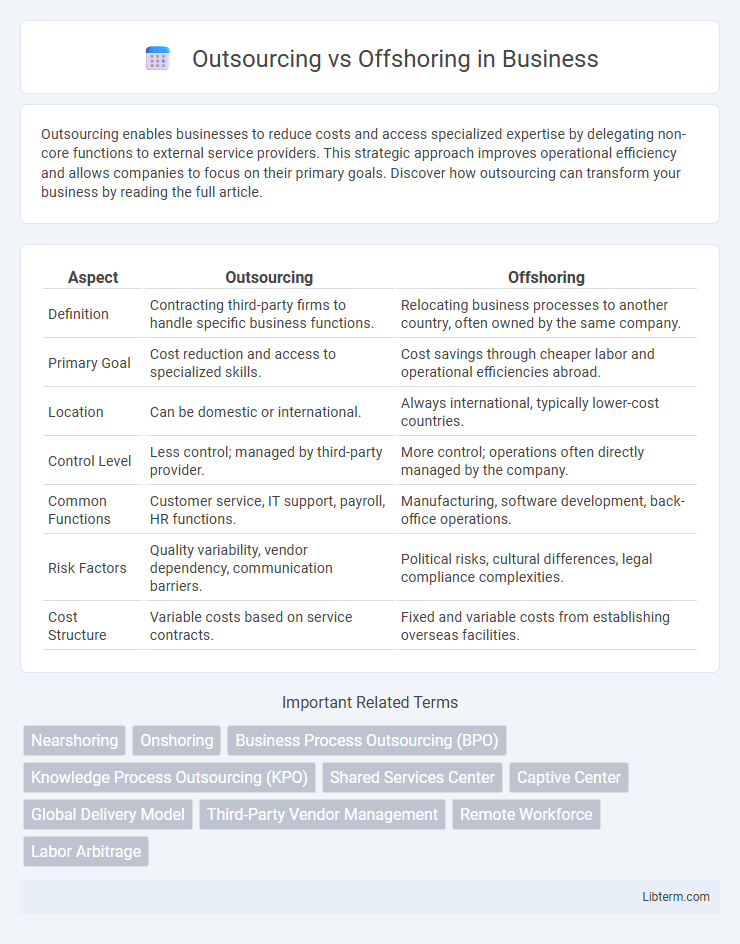
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracting third-party firms to handle specific business functions. | Relocating business processes to another country, often owned by the same company. |
| Primary Goal | Cost reduction and access to specialized skills. | Cost savings through cheaper labor and operational efficiencies abroad. |
| Location | Can be domestic or international. | Always international, typically lower-cost countries. |
| Control Level | Less control; managed by third-party provider. | More control; operations often directly managed by the company. |
| Common Functions | Customer service, IT support, payroll, HR functions. | Manufacturing, software development, back-office operations. |
| Risk Factors | Quality variability, vendor dependency, communication barriers. | Political risks, cultural differences, legal compliance complexities. |
| Cost Structure | Variable costs based on service contracts. | Fixed and variable costs from establishing overseas facilities. |
Understanding Outsourcing and Offshoring
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or services to third-party vendors, often to achieve cost savings, enhance efficiency, or access specialized expertise. Offshoring refers to relocating business operations or services to another country, typically to leverage lower labor costs and access new markets. Understanding outsourcing and offshoring requires recognizing that outsourcing can be done either domestically or internationally, while offshoring always implies a geographic move across national borders.
Key Differences Between Outsourcing and Offshoring
Outsourcing involves contracting specific business processes or services to third-party vendors, often locally or internationally, to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Offshoring refers to relocating business operations or production to a foreign country, typically to leverage lower labor costs and access new markets. Key differences include outsourcing's emphasis on service delegation regardless of location, while offshoring specifically centers on geographic relocation of company functions.
Benefits of Outsourcing for Businesses
Outsourcing offers businesses significant cost savings by leveraging external expertise and reducing operational expenses such as salaries, benefits, and infrastructure. It enhances flexibility, allowing companies to scale resources quickly based on project demands without long-term commitments. Access to a global talent pool improves innovation and efficiency by integrating specialized skills and advanced technologies.
Advantages of Offshoring Operations
Offshoring operations offers significant cost savings by leveraging lower labor and operational expenses in foreign countries. Access to a global talent pool enables companies to utilize specialized skills and expertise not readily available domestically. Furthermore, offshoring enhances operational efficiency by allowing round-the-clock productivity due to time zone differences.
Challenges and Risks of Outsourcing
Outsourcing involves contracting third-party vendors to handle business functions, which can lead to challenges such as loss of control, communication barriers, and inconsistent quality standards. Risks include data security vulnerabilities, dependency on external providers, and potential hidden costs that impact overall project timelines and budgets. Managing these risks requires thorough vendor vetting, robust contractual agreements, and continuous performance monitoring to ensure alignment with business objectives.
Common Offshoring Pitfalls to Avoid
Common offshoring pitfalls to avoid include inadequate communication due to time zone differences and language barriers, which can lead to project delays and misunderstandings. Overlooking cultural differences often results in conflicting work practices and reduced team cohesion, negatively impacting productivity. Failing to conduct thorough vendor due diligence increases risks related to data security, quality standards, and contractual compliance.
Cost Comparison: Outsourcing vs Offshoring
Outsourcing typically involves contracting third-party vendors domestically or internationally, with costs influenced by service provider rates, quality, and location, often leading to moderate savings without relocating operations. Offshoring moves business processes to foreign countries, usually with significantly lower labor costs and operational expenses, providing deeper cost reductions but with potential challenges in management and communication. Evaluating total costs requires considering not only direct expenses but also factors like travel, cultural differences, and compliance when comparing outsourcing versus offshoring strategies.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing between outsourcing and offshoring depends on your business goals, cost structure, and control preferences. Outsourcing allows access to specialized skills and flexible resource management without geographic constraints, whereas offshoring focuses on relocating operations to countries with lower labor costs to achieve savings. Evaluating factors like quality standards, communication needs, and market proximity will guide selecting the optimal model for efficiency and growth.
Best Practices for Successful Outsourcing and Offshoring
Effective communication and clearly defined goals are critical for successful outsourcing and offshoring projects, ensuring alignment between all stakeholders. Implementing robust project management tools and regular performance evaluations enhances transparency and accountability, mitigating risks associated with remote collaboration. Selecting partners with proven expertise and cultural compatibility improves operational efficiency and drives long-term value in global business strategies.
Future Trends in Outsourcing and Offshoring
Future trends in outsourcing and offshoring emphasize increased adoption of automation, artificial intelligence, and cloud technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Companies are shifting toward nearshoring to mitigate risks related to geopolitical instability, supply chain disruptions, and time zone differences. Emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing is driving firms to select partners with strong environmental and social governance practices.
Outsourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com