Revenue represents the total income generated from sales of goods or services before any expenses are deducted. It is a critical metric for assessing a company's financial health and growth potential. Explore the rest of the article to understand how to analyze and increase your business revenue effectively.
Table of Comparison
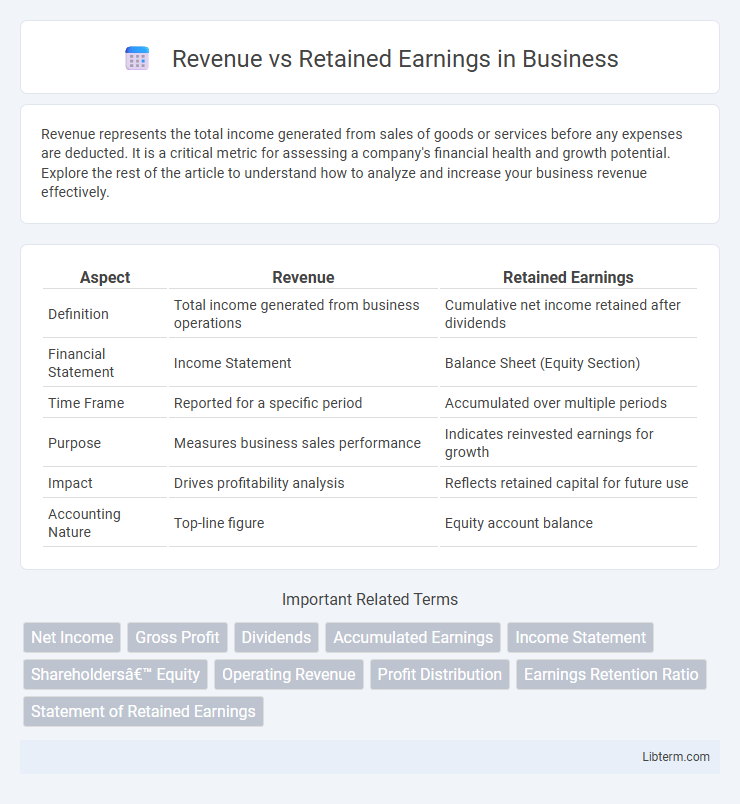
| Aspect | Revenue | Retained Earnings |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total income generated from business operations | Cumulative net income retained after dividends |
| Financial Statement | Income Statement | Balance Sheet (Equity Section) |
| Time Frame | Reported for a specific period | Accumulated over multiple periods |
| Purpose | Measures business sales performance | Indicates reinvested earnings for growth |
| Impact | Drives profitability analysis | Reflects retained capital for future use |
| Accounting Nature | Top-line figure | Equity account balance |
Introduction to Revenue and Retained Earnings
Revenue represents the total income generated from the sale of goods or services within a specific period, reflecting a company's operational performance. Retained earnings are the accumulated net profits that a company keeps after paying dividends to shareholders, serving as a key indicator of financial health and growth potential. Understanding the distinction between revenue and retained earnings is essential for analyzing a company's profitability and reinvestment strategy.
Defining Revenue in Financial Terms
Revenue represents the total income generated from a company's core business operations before any expenses are deducted, serving as a critical indicator of business performance and market demand. It differs from retained earnings, which reflect the accumulated net profit after dividends have been distributed and expenses accounted for. Accurately defining and recognizing revenue in financial terms enables precise financial analysis and reporting essential for investors and stakeholders.
Understanding Retained Earnings
Retained earnings represent the cumulative net income a company retains after paying dividends, reflecting reinvested profits to support growth and operational needs. Unlike revenue, which measures total income from sales before expenses, retained earnings indicate the portion of profit kept within the business over time. Tracking changes in retained earnings is crucial for assessing a company's financial health and long-term sustainability.
Key Differences Between Revenue and Retained Earnings
Revenue represents the total income generated from sales or services during a specific period, reflecting a company's operational performance. Retained earnings illustrate the cumulative net income kept in the business after dividends are paid, indicating profit reinvested for growth. While revenue measures immediate earnings potential, retained earnings provide insight into long-term financial health and capital accumulation.
How Revenue Impacts Financial Statements
Revenue directly increases net income on the income statement, which subsequently raises retained earnings on the balance sheet. Higher revenue improves a company's profitability, leading to a stronger equity position through accumulated retained earnings. This impact enhances financial ratios and overall shareholder value by signaling business growth and operational efficiency.
Role of Retained Earnings in Business Growth
Retained earnings represent the cumulative net income kept within a company rather than distributed as dividends, serving as a critical source of internal financing for business growth. These funds enable reinvestment in operations, research and development, new product launches, and debt reduction, fostering sustainable expansion and improving financial stability. By leveraging retained earnings, businesses can enhance their capital base, avoid external borrowing costs, and maintain control over strategic growth initiatives.
Common Misconceptions: Revenue vs. Retained Earnings
Revenue represents the total income generated from a company's core business activities before expenses, while retained earnings reflect the accumulated net income after dividends over time. A common misconception is confusing revenue with retained earnings, assuming high revenue equates to high retained earnings, ignoring costs and distributions. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate financial analysis and business valuation.
Importance of Tracking Both Metrics
Tracking both revenue and retained earnings is essential for assessing a company's financial health and long-term sustainability. Revenue measures the total income generated from core business operations, while retained earnings reflect the accumulated net income reinvested in the business after dividends. Monitoring these metrics enables informed decisions on growth strategies, cash flow management, and shareholder value optimization.
Impact of Company Decisions on Retained Earnings
Company decisions such as dividend payouts, reinvestment strategies, and expense management directly influence retained earnings by determining the amount of net income retained within the business. Operational efficiency and strategic investments can increase profits, thereby boosting retained earnings, while high dividend distributions reduce the retained earnings balance. Accurate financial planning ensures that retained earnings are optimized to support growth, debt reduction, and shareholder value enhancement.
Conclusion: Balancing Revenue and Retained Earnings for Success
Balancing revenue and retained earnings is essential for sustainable business growth, as revenue drives operational capacity while retained earnings fund reinvestment and long-term stability. Effective management ensures that companies maximize profit generation without compromising reserves needed for innovation, debt reduction, and financial resilience. Prioritizing both metrics creates a strategic equilibrium that supports ongoing success and shareholder value enhancement.
Revenue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com