Dynamic pricing adjusts product or service costs in real-time based on market demand, competitor prices, and customer behavior to maximize revenue. This strategy leverages data analytics and machine learning to optimize prices, ensuring businesses remain competitive and profitable. Discover how dynamic pricing can transform your pricing strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
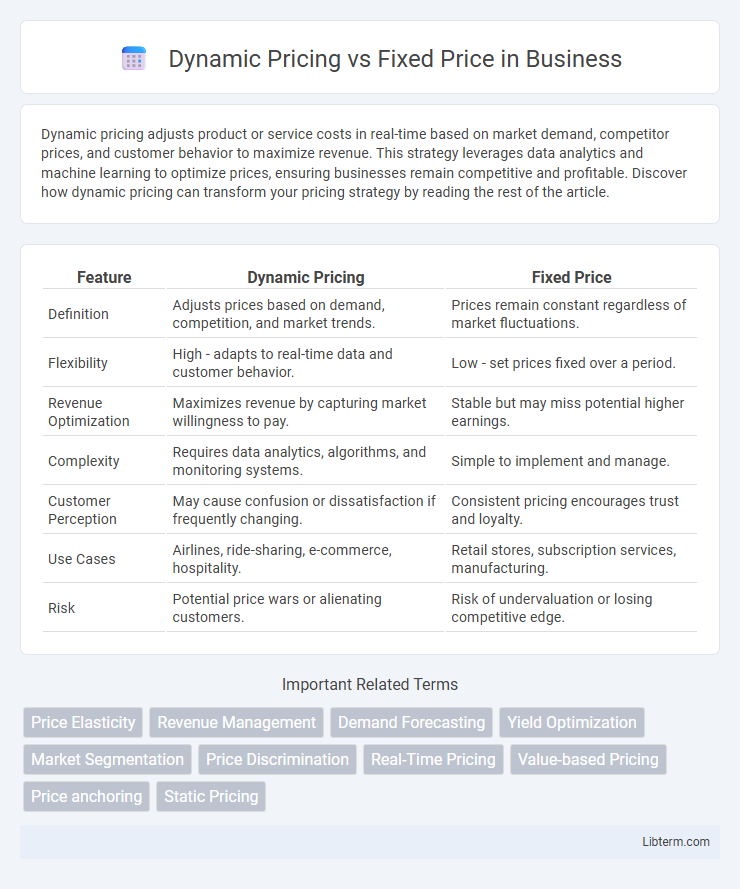
| Feature | Dynamic Pricing | Fixed Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusts prices based on demand, competition, and market trends. | Prices remain constant regardless of market fluctuations. |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to real-time data and customer behavior. | Low - set prices fixed over a period. |
| Revenue Optimization | Maximizes revenue by capturing market willingness to pay. | Stable but may miss potential higher earnings. |
| Complexity | Requires data analytics, algorithms, and monitoring systems. | Simple to implement and manage. |
| Customer Perception | May cause confusion or dissatisfaction if frequently changing. | Consistent pricing encourages trust and loyalty. |
| Use Cases | Airlines, ride-sharing, e-commerce, hospitality. | Retail stores, subscription services, manufacturing. |
| Risk | Potential price wars or alienating customers. | Risk of undervaluation or losing competitive edge. |
Understanding Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on market demand, customer behavior, and competitor actions, maximizing revenue by capitalizing on fluctuations. This strategy utilizes algorithms and data analytics to optimize prices, ensuring businesses remain competitive and responsive to changing conditions. Understanding dynamic pricing involves recognizing its role in industries like airlines, hospitality, and e-commerce, where price flexibility drives profitability and consumer engagement.
What is Fixed Pricing?
Fixed pricing is a pricing strategy where a product or service is sold at a predetermined, unchanging price regardless of market fluctuations or demand variations. This approach provides customers with price stability and transparency, making budget planning easier and reducing uncertainty in purchasing decisions. Businesses using fixed pricing often rely on cost-plus pricing or competitive benchmarking to set a consistent price point.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Fixed Pricing
Dynamic pricing adjusts prices in real-time based on factors like demand, competition, and customer behavior, while fixed pricing sets a constant price regardless of market changes. Dynamic pricing maximizes revenue through flexibility and responsiveness, whereas fixed pricing offers stability and predictability for both sellers and buyers. The key differences lie in price variability, market responsiveness, and strategic goals, with dynamic pricing prioritizing optimization and fixed pricing emphasizing simplicity and transparency.
Advantages of Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing maximizes revenue by adjusting prices based on real-time demand, market conditions, and customer behavior, which enables businesses to capture higher value during peak periods. It enhances competitive advantage by allowing quick responses to competitor pricing and inventory changes. Furthermore, dynamic pricing improves inventory management by optimizing stock turnover and reducing waste.
Benefits of Fixed Price Models
Fixed price models offer budget certainty by locking in costs upfront, eliminating the risk of unexpected price fluctuations. This pricing strategy simplifies financial planning and fosters trust between buyers and sellers, enhancing long-term business relationships. Fixed pricing also minimizes administrative overhead by reducing the need for continuous price adjustments and monitoring.
Challenges of Implementing Dynamic Pricing
Implementing dynamic pricing presents challenges such as accurately predicting market demand and customer behavior, which requires sophisticated algorithms and real-time data analytics. Businesses must also address potential customer dissatisfaction due to perceived unfairness or price volatility, risking brand trust and loyalty. Ensuring compliance with legal regulations and avoiding price discrimination further complicates dynamic pricing strategies compared to fixed price models.
Industries Suited for Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing suits industries with fluctuating demand and real-time market conditions, such as airlines, hospitality, e-commerce, and ride-sharing services. Retailers leverage dynamic pricing to optimize inventory turnover and respond to competitor pricing instantly. Technology and entertainment sectors use dynamic models to maximize revenue during peak periods and special events.
Consumer Reactions to Pricing Strategies
Consumers often perceive dynamic pricing as unfair or unpredictable, leading to distrust and potential dissatisfaction, especially when prices fluctuate frequently based on demand or user behavior. Fixed pricing provides transparency and consistency, fostering consumer confidence and perceived fairness, which can enhance loyalty and reduce purchase hesitation. However, dynamic pricing may appeal to price-sensitive buyers looking for deals, while fixed pricing attracts those valuing stability and simplicity in their purchasing decisions.
Choosing the Right Pricing Strategy
Dynamic pricing allows businesses to adjust prices based on market demand, competitor actions, and consumer behavior, maximizing revenue through real-time optimization. Fixed pricing offers stability and predictability, making it ideal for products with consistent demand and straightforward cost structures. Selecting the right pricing strategy depends on factors such as industry volatility, customer sensitivity, and competitive landscape to balance profitability and market positioning.
Future Trends in Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing leverages real-time data analytics and artificial intelligence to adjust prices based on demand, competition, and customer behavior, leading to more personalized and flexible pricing strategies. Fixed price models remain prevalent in industries valuing price stability and simplicity, but their rigidity limits responsiveness to market fluctuations. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach integrating dynamic algorithms within fixed frameworks, enhancing pricing precision while preserving customer trust and transparency.
Dynamic Pricing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com