A conglomerate merger combines companies from unrelated industries, expanding diverse business portfolios and reducing market risks. This strategy promotes growth by leveraging different market opportunities and resources. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your business can benefit from a conglomerate merger.
Table of Comparison
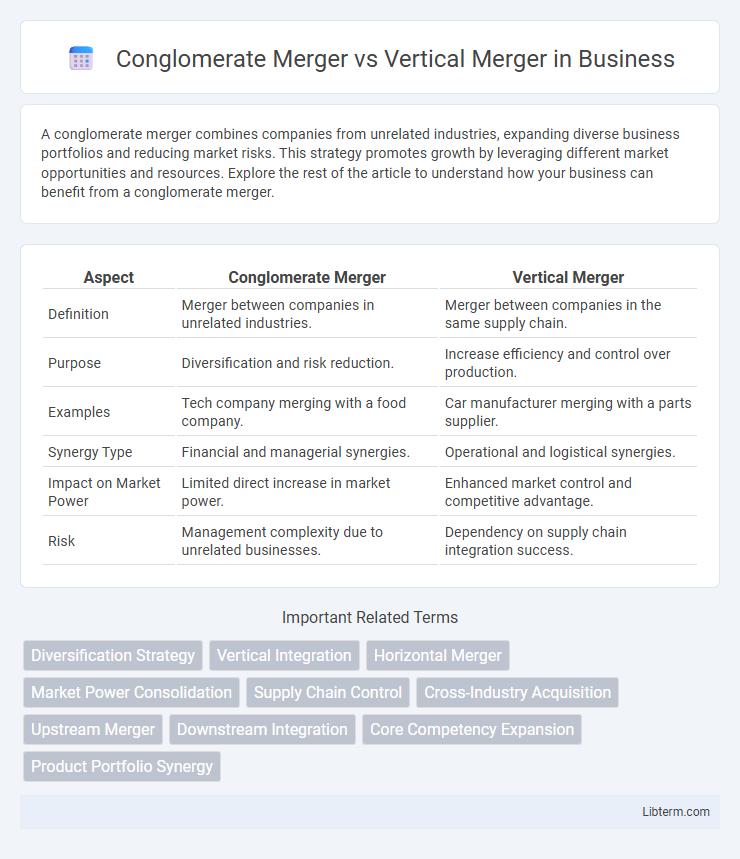
| Aspect | Conglomerate Merger | Vertical Merger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Merger between companies in unrelated industries. | Merger between companies in the same supply chain. |
| Purpose | Diversification and risk reduction. | Increase efficiency and control over production. |
| Examples | Tech company merging with a food company. | Car manufacturer merging with a parts supplier. |
| Synergy Type | Financial and managerial synergies. | Operational and logistical synergies. |
| Impact on Market Power | Limited direct increase in market power. | Enhanced market control and competitive advantage. |
| Risk | Management complexity due to unrelated businesses. | Dependency on supply chain integration success. |
Understanding Merger Types: Conglomerate vs Vertical
Conglomerate mergers involve the combination of firms operating in unrelated industries, aiming to diversify business risk and expand market reach without direct operational overlap. Vertical mergers occur between companies at different stages of the production or supply chain within the same industry, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing transaction costs. Understanding these distinctions clarifies strategic objectives: conglomerate mergers focus on diversification, while vertical mergers emphasize integration and control over the value chain.
Defining Conglomerate Mergers
Conglomerate mergers involve the combination of two companies that operate in entirely different industries, aiming to diversify business activities and reduce risk exposure. Unlike vertical mergers, which integrate firms along the same supply chain to improve operational efficiency, conglomerate mergers focus on broadening market reach and product offerings without direct market overlap. These mergers often help corporations capitalize on cross-industry synergies and financial stability in volatile markets.
Defining Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers occur when companies operating at different stages of the same industry's supply chain combine, aiming to improve efficiency and reduce production costs. This type of merger contrasts with conglomerate mergers, where unrelated businesses unify to diversify their market presence. By integrating upstream suppliers with downstream distributors, vertical mergers enhance coordination, control over the supply chain, and competitive advantage.
Key Differences Between Conglomerate and Vertical Mergers
Conglomerate mergers involve the combination of companies operating in unrelated business activities, which aims to diversify business risks and expand market reach without overlapping product lines or supply chains. Vertical mergers occur between firms at different stages of the production process within the same industry, designed to improve operational efficiency and reduce supply chain costs by integrating suppliers or distributors. The key difference lies in the strategic intent: conglomerate mergers focus on diversification, while vertical mergers emphasize control over the production and distribution process.
Strategic Objectives Behind Each Merger Type
Conglomerate mergers aim to diversify business operations and reduce market risk by combining companies from unrelated industries, enhancing financial stability and fostering innovation across distinct sectors. Vertical mergers focus on controlling the supply chain by integrating companies at different stages of production or distribution, improving operational efficiency and securing crucial inputs or market access. Both strategies seek long-term competitive advantages but through diversification or supply chain optimization respectively.
Advantages of Conglomerate Mergers
Conglomerate mergers enhance diversification by combining companies from unrelated industries, reducing overall business risk and stabilizing earnings. They create opportunities for cross-selling and expanding market reach without the constraints of market overlap. Financial synergies and improved capital allocation often result from conglomerate mergers, boosting shareholder value through a broader portfolio.
Advantages of Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers enhance supply chain efficiency by integrating different stages of production, reducing costs and improving coordination between suppliers and manufacturers. They increase market control and create barriers to entry for competitors by consolidating key resources and distribution channels. Furthermore, vertical mergers promote innovation through closer collaboration and information sharing, leading to improved product quality and faster time-to-market.
Challenges and Risks of Conglomerate Mergers
Conglomerate mergers often face significant challenges such as cultural clashes, integration difficulties due to disparate business operations, and regulatory scrutiny stemming from concerns about market monopolization. The risks include potential inefficiencies from managing unrelated business segments, dilution of management focus, and unpredictable financial performance due to lack of synergy between merged entities. These challenges can result in value destruction and decreased shareholder confidence if not carefully managed.
Challenges and Risks of Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers face challenges such as integration difficulties between different stages of production, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased costs. Regulatory risks also pose significant threats, as authorities scrutinize potential anti-competitive behavior and market monopolization. Supply chain dependencies and cultural clashes further exacerbate the risks, impacting long-term sustainability and value creation.
Real-World Examples: Conglomerate and Vertical Mergers
The Walt Disney Company's acquisition of 21st Century Fox in 2019 exemplifies a vertical merger, combining content production with distribution channels to enhance market control. In contrast, Berkshire Hathaway's diverse portfolio, including stakes in industries from insurance to manufacturing, illustrates a conglomerate merger strategy aimed at risk diversification and capital allocation across unrelated sectors. These real-world examples highlight how vertical mergers concentrate on supply chain integration, while conglomerate mergers focus on broad market presence without direct business overlaps.
Conglomerate Merger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com