Horizontal integration involves a company acquiring or merging with competitors operating at the same stage of the production process to increase market share, reduce competition, and achieve economies of scale. This strategy can lead to enhanced efficiency, greater bargaining power, and expanded customer base. Discover how horizontal integration can transform your business and explore its benefits in detail throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
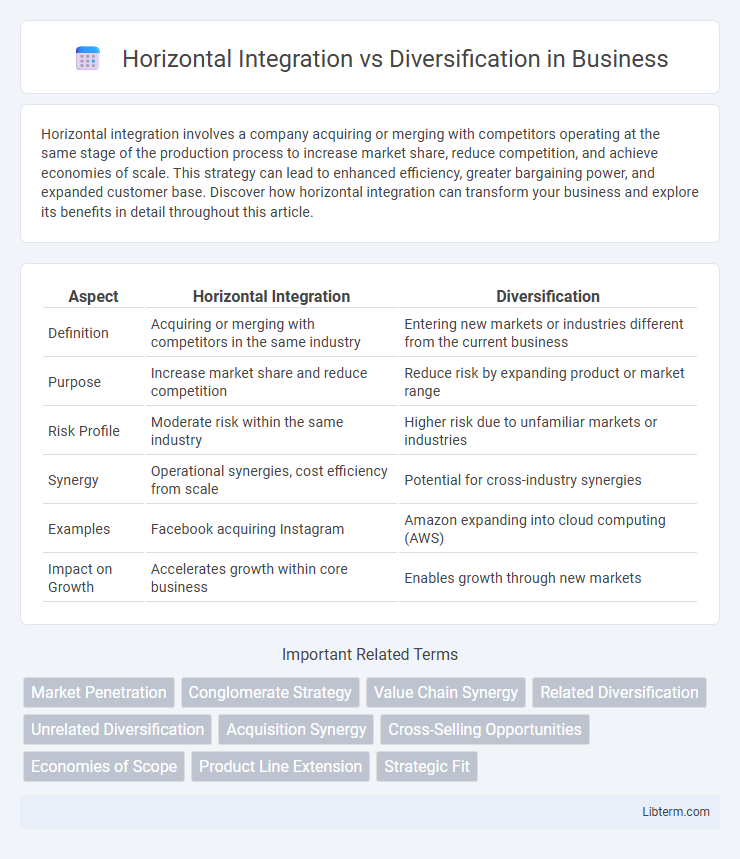
| Aspect | Horizontal Integration | Diversification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring or merging with competitors in the same industry | Entering new markets or industries different from the current business |
| Purpose | Increase market share and reduce competition | Reduce risk by expanding product or market range |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk within the same industry | Higher risk due to unfamiliar markets or industries |
| Synergy | Operational synergies, cost efficiency from scale | Potential for cross-industry synergies |
| Examples | Facebook acquiring Instagram | Amazon expanding into cloud computing (AWS) |
| Impact on Growth | Accelerates growth within core business | Enables growth through new markets |
Introduction to Horizontal Integration and Diversification
Horizontal integration involves a company expanding its operations by acquiring or merging with competitors within the same industry to increase market share and reduce competition. Diversification refers to a strategic approach where a business enters new markets or industries to spread risk and explore new revenue streams. Both strategies aim to strengthen a company's market position but differ in scope and risk management.
Defining Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration refers to the process by which a company acquires or merges with other firms operating at the same stage of the production or distribution chain within the same industry. This strategy aims to increase market share, reduce competition, achieve economies of scale, and enhance operational efficiency by consolidating similar business activities. Examples include major corporations in technology, such as Facebook acquiring Instagram, to expand their user base and control over the social media market.
Defining Diversification
Diversification involves expanding a company's operations into new markets or product lines distinct from its existing business activities to reduce risk and capitalize on growth opportunities. This strategy contrasts with horizontal integration, which focuses on acquiring or merging with competitors within the same industry to increase market share. Effective diversification enhances a firm's resilience by spreading risk across different sectors and leveraging core competencies in multiple domains.
Key Differences Between Horizontal Integration and Diversification
Horizontal integration involves acquiring or merging with companies operating in the same industry at the same production stage to increase market share and reduce competition, while diversification entails expanding into different industries or markets to spread risk and create new revenue streams. Horizontal integration typically enhances economies of scale and synergies within a core business, whereas diversification aims to minimize overall business risk by entering unrelated or related sectors. The primary difference lies in horizontal integration's focus on industry consolidation versus diversification's strategy of portfolio expansion and risk mitigation.
Strategic Objectives of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration aims to increase market share and reduce competition by acquiring or merging with competitors within the same industry. This strategy enhances economies of scale, streamlines operations, and boosts bargaining power with suppliers and customers. Companies pursue horizontal integration to achieve rapid growth, access new markets, and improve product or service offerings through synergies.
Strategic Objectives of Diversification
Diversification aims to enhance corporate growth by entering new markets or industries, reducing dependency on a single revenue stream and spreading business risks. It targets achieving synergy through leveraging core competencies across different products or sectors to increase overall firm value. Strategic objectives include capturing new customer segments, accessing advanced technologies, and balancing portfolio performance to sustain long-term competitive advantage.
Benefits and Risks of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration enhances market share and economies of scale by acquiring or merging with competitors, leading to reduced competition and increased pricing power. It facilitates access to a broader customer base and improved operational efficiency but carries risks such as regulatory scrutiny, cultural clashes, and potential antitrust violations. Overreliance on a single industry or market also exposes companies to sector-specific downturns and reduced innovation incentives.
Advantages and Challenges of Diversification
Diversification allows companies to spread risk across different markets or products, enhancing stability and growth potential by reducing dependence on a single revenue source. This strategy enables access to new customer segments and opportunities for innovation, but it demands significant management expertise to handle varied business operations and maintain focus. Challenges include increased complexity, higher operational costs, and potential dilution of core competencies, which can strain resources and reduce overall efficiency.
Industry Examples: Horizontal Integration vs Diversification
Horizontal integration in the tech industry is exemplified by Facebook's acquisition of Instagram, enhancing its market share within social media. Diversification is demonstrated by Amazon expanding from e-commerce into cloud computing with AWS, reducing reliance on a single market. Both strategies reshape competitive dynamics but serve different goals: horizontal integration consolidates within the same industry, while diversification spreads risk across distinct sectors.
Choosing the Right Growth Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right growth strategy between horizontal integration and diversification depends primarily on a company's market position, resource capabilities, and risk tolerance. Horizontal integration focuses on expanding within the same industry to increase market share and achieve economies of scale, while diversification involves entering new markets or industries to spread risk and capitalize on new opportunities. Key factors include analyzing competitive advantage, evaluating industry attractiveness, assessing financial strength, and aligning with long-term strategic goals to ensure sustainable growth.
Horizontal Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com