Insolvency occurs when an individual or business cannot meet their financial obligations as debts become due, leading to potential legal proceedings or restructuring. Understanding insolvency is crucial for protecting your assets and exploring options such as liquidation or bankruptcy. Discover more about how insolvency impacts your finances and the steps you can take in the following article.
Table of Comparison
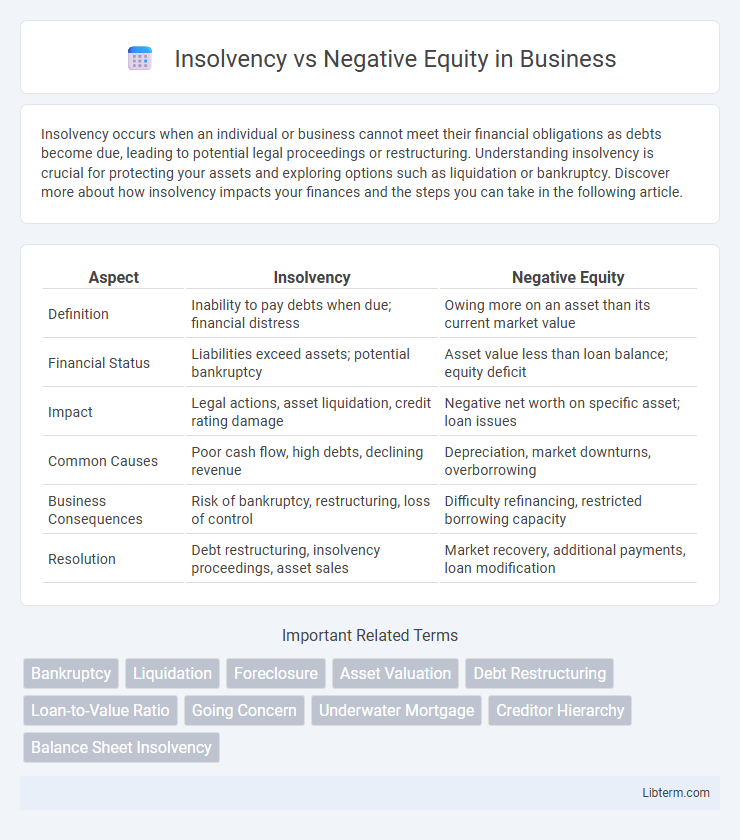
| Aspect | Insolvency | Negative Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inability to pay debts when due; financial distress | Owing more on an asset than its current market value |
| Financial Status | Liabilities exceed assets; potential bankruptcy | Asset value less than loan balance; equity deficit |
| Impact | Legal actions, asset liquidation, credit rating damage | Negative net worth on specific asset; loan issues |
| Common Causes | Poor cash flow, high debts, declining revenue | Depreciation, market downturns, overborrowing |
| Business Consequences | Risk of bankruptcy, restructuring, loss of control | Difficulty refinancing, restricted borrowing capacity |
| Resolution | Debt restructuring, insolvency proceedings, asset sales | Market recovery, additional payments, loan modification |
Understanding Insolvency: Definition and Key Concepts
Insolvency occurs when a person or company cannot meet their debt obligations as they come due, signaling a financial state where liabilities exceed assets or cash flow is insufficient. Key concepts include cash-flow insolvency, which is the inability to pay debts on time, and balance-sheet insolvency, where total liabilities surpass total assets. Understanding insolvency is critical for assessing financial health and determining the necessity of restructuring or bankruptcy proceedings.
What is Negative Equity? Explained Simply
Negative equity occurs when the outstanding balance on a loan exceeds the current value of the asset purchased with that loan, commonly seen in mortgages or car financing. This situation means the borrower owes more than the asset is worth, limiting the ability to sell or refinance without incurring a loss. Negative equity is a financial risk indicator that can lead to insolvency if asset values persistently decline while debt obligations remain high.
Major Differences Between Insolvency and Negative Equity
Insolvency occurs when a company's liabilities exceed its assets, rendering it unable to meet debt obligations, whereas negative equity refers specifically to a situation where the value of an asset, such as a home or vehicle, is less than the outstanding loan balance. Insolvency impacts overall financial viability and often leads to bankruptcy proceedings, while negative equity is typically a temporary financial setback affecting asset liquidation or refinancing options. Understanding these distinctions is critical for financial analysis, risk management, and strategic decision-making in both personal finance and corporate contexts.
Causes of Insolvency: Common Financial Triggers
Insolvency often stems from cash flow problems such as declining revenues, escalating operational costs, or excessive debt burdens, which prevent a company from meeting its financial obligations. Negative equity, a condition where liabilities exceed assets, can be both a symptom and a cause of insolvency by eroding a firm's net worth and creditor confidence. Key financial triggers include poor management decisions, economic downturns, and unfavorable market conditions that disrupt profitability and liquidity.
How Negative Equity Occurs in Real Estate and Loans
Negative equity in real estate occurs when the outstanding loan balance on a property exceeds its current market value, often due to declining property prices or an initial high loan-to-value ratio. This situation arises when homeowners owe more on their mortgage than the home is worth, commonly triggered by market downturns, falling home prices, or economic factors affecting property values. Loans with high interest rates or insufficient down payments increase the risk of negative equity, as they amplify the gap between debt owed and asset worth.
Legal Implications of Insolvency vs Negative Equity
Insolvency legally obliges a debtor to address unpaid debts through court proceedings, potentially resulting in bankruptcy or restructuring orders, while negative equity lacks immediate legal consequences but signals financial distress by where liabilities exceed asset values. Insolvency triggers statutory duties, including creditor notifications and possible asset liquidation, whereas negative equity primarily influences creditworthiness and borrowing conditions without direct statutory intervention. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for legal compliance and financial strategy in managing distressed assets or debt burdens.
Signs Your Business Is Heading Toward Insolvency
Consistent cash flow problems, such as missed payments to suppliers and employees, often signal your business is heading toward insolvency, indicating liabilities exceed liquid assets. Negative equity occurs when a company's total liabilities surpass its total assets, but insolvency is defined by the inability to meet debt obligations as they fall due. Monitoring declining working capital ratios and increasing creditor pressures can help identify insolvency risks early, allowing for timely strategic interventions.
Strategies for Managing and Recovering from Negative Equity
Effective strategies for managing and recovering from negative equity involve renegotiating loan terms with lenders to reduce interest rates or extend repayment periods, which lowers monthly payments and eases financial pressure. Selling the asset at a controlled loss or refinancing through a loan modification can help realign the loan balance with the asset's market value, facilitating a quicker exit from negative equity. Building equity through consistent additional payments or investing in asset improvements enhances value, accelerating recovery and avoiding insolvency risks.
Insolvency Solutions: Options and Resources
Insolvency solutions encompass various options such as debt restructuring, bankruptcy filings, and negotiated settlements to manage financial distress effectively. Resources including credit counseling, legal aid, and government programs provide critical support for individuals and businesses facing insolvency. Understanding these measures helps mitigate the impact of insolvency and facilitates a path toward financial recovery.
Protecting Your Finances: Prevention Tips for Insolvency and Negative Equity
Protecting your finances from insolvency and negative equity involves regularly monitoring your cash flow and asset values to avoid overextending credit or depleting reserves. Implementing a strict budget, prioritizing debt repayment, and maintaining an emergency fund can shield against sudden financial downturns that exacerbate insolvency risks and negative equity impacts. Utilizing professional financial advice for restructuring debts or asset management proactively enhances your ability to prevent severe financial distress.
Insolvency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com