A dual board structure separates management and oversight responsibilities between a management board and a supervisory board, enhancing corporate governance and accountability. This system can improve decision-making by providing distinct roles for strategy implementation and independent monitoring. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this structure benefits your organization and governance practices.
Table of Comparison
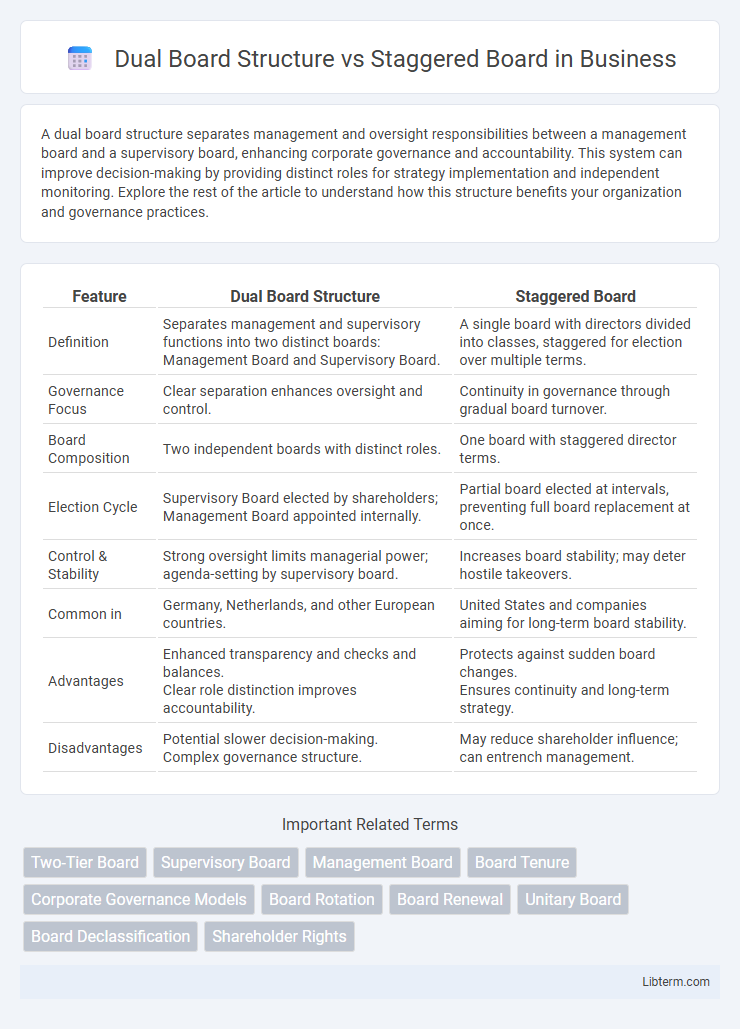
| Feature | Dual Board Structure | Staggered Board |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separates management and supervisory functions into two distinct boards: Management Board and Supervisory Board. | A single board with directors divided into classes, staggered for election over multiple terms. |
| Governance Focus | Clear separation enhances oversight and control. | Continuity in governance through gradual board turnover. |
| Board Composition | Two independent boards with distinct roles. | One board with staggered director terms. |
| Election Cycle | Supervisory Board elected by shareholders; Management Board appointed internally. | Partial board elected at intervals, preventing full board replacement at once. |
| Control & Stability | Strong oversight limits managerial power; agenda-setting by supervisory board. | Increases board stability; may deter hostile takeovers. |
| Common in | Germany, Netherlands, and other European countries. | United States and companies aiming for long-term board stability. |
| Advantages | Enhanced transparency and checks and balances. Clear role distinction improves accountability. |
Protects against sudden board changes. Ensures continuity and long-term strategy. |
| Disadvantages | Potential slower decision-making. Complex governance structure. |
May reduce shareholder influence; can entrench management. |
Understanding Dual Board Structure
Dual board structure, commonly used in countries like Germany and the Netherlands, separates management and supervisory functions into two distinct boards: the management board handles daily operations, while the supervisory board oversees and advises the management. This structure enhances corporate governance by ensuring independent monitoring, reducing conflicts of interest between executives and shareholders. It contrasts with staggered boards, where directors are elected in phases to prevent takeovers but may limit shareholder influence on board composition.
What Is a Staggered Board?
A staggered board, also known as a classified board, divides directors into separate classes with different election cycles, ensuring only a fraction of board members face re-election each year. This structure enhances board stability and continuity by preventing a complete board turnover in a single election, which can protect companies from hostile takeovers. In contrast to a dual board structure featuring separate supervisory and management boards, a staggered board operates as a single board with staggered terms for its members.
Key Differences Between Dual and Staggered Boards
Dual board structure features two separate boards: a management board responsible for daily operations and a supervisory board overseeing strategic decisions, commonly found in European corporations. Staggered boards have directors divided into classes with rotating election cycles, which can entrench management and deter hostile takeovers by limiting board turnover at any single election. Key differences include the separation of oversight and management roles in dual boards, contrasting with staggered boards' focus on gradual director replacement within a single board, impacting governance dynamics and shareholder influence.
Governance Implications of Board Structures
Dual board structure separates management and supervisory responsibilities between two distinct boards, enhancing oversight and reducing conflicts of interest while promoting transparency and accountability in corporate governance. In contrast, staggered boards, where only a fraction of directors are elected each year, can entrench incumbents and limit shareholder influence, potentially weakening board responsiveness and governance effectiveness. Evaluating governance implications requires balancing oversight benefits of dual boards against risks of reduced accountability with staggered terms to optimize board independence and shareholder engagement.
Pros and Cons of Dual Board Structure
The Dual Board Structure separates management and supervisory responsibilities between two distinct boards, enhancing oversight and reducing conflicts of interest by clearly delineating executive and non-executive functions. This system improves corporate governance transparency and protects shareholders by enabling independent supervision; however, it may slow decision-making processes and increase administrative costs due to the dual layers of oversight. Compared to a Staggered Board, which can entrench management and limit board turnover, the Dual Board Structure offers stronger checks but risks inefficiency and complexity in board interactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Staggered Boards
Staggered boards enhance corporate stability by preventing hostile takeovers through limited annual director turnover, which can preserve long-term strategy execution. However, this structure reduces shareholder influence by delaying board-wide changes and may entrench management, potentially leading to less accountability. Investors often view staggered boards skeptically as they can inhibit responsive governance and decrease stock liquidity.
Impact on Shareholder Rights and Power
The Dual Board Structure separates management and supervisory roles, often diluting shareholder influence by empowering the supervisory board to oversee executive decisions, which may limit direct shareholder interventions. In contrast, the Staggered Board system schedules director elections over multiple years, potentially entrenching management and reducing shareholders' ability to swiftly change board composition. Both structures impact shareholder rights by affecting the balance of power between management control and shareholder oversight, with Dual Boards favoring oversight by a distinct supervisory body and Staggered Boards providing stability but limiting immediate shareholder power.
Influence on Corporate Decision-Making
The Dual Board Structure separates management and supervisory functions between the Management Board and Supervisory Board, enhancing oversight and reducing conflicts of interest in corporate decision-making. The Staggered Board, with directors elected in overlapping terms, can entrench management by limiting shareholder influence and slowing changes to the board. This structure often results in more stable but less responsive governance, affecting how quickly strategic decisions are implemented.
Global Practices: Dual vs Staggered Boards
Global corporate governance frequently contrasts the Dual Board Structure, prevalent in Europe and Asia, with the Staggered Board common in the United States. The Dual Board Structure separates supervisory and management roles, enhancing oversight and reducing conflicts of interest, with countries like Germany and Japan adopting this model extensively. In contrast, the Staggered Board, where only a fraction of directors are elected each year, aims to provide continuity and protect against hostile takeovers, but is often criticized for entrenching management and limiting shareholder influence.
Choosing the Right Board Structure for Your Company
Choosing the right board structure for your company depends on factors such as governance goals, regulatory environment, and shareholder interests. A Dual Board Structure separates management and supervisory functions, enhancing oversight and reducing conflicts of interest, commonly favored in European markets. In contrast, a Staggered Board, with directors serving overlapping terms, can protect against hostile takeovers and ensure continuity but may reduce accountability and responsiveness to shareholders.
Dual Board Structure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com