Vertical integration strategy enhances control over the supply chain by combining multiple production stages, reducing costs, and improving efficiency. Companies adopting this approach can respond faster to market changes and maintain higher quality standards throughout their operations. Discover how implementing a vertical integration strategy can transform your business by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
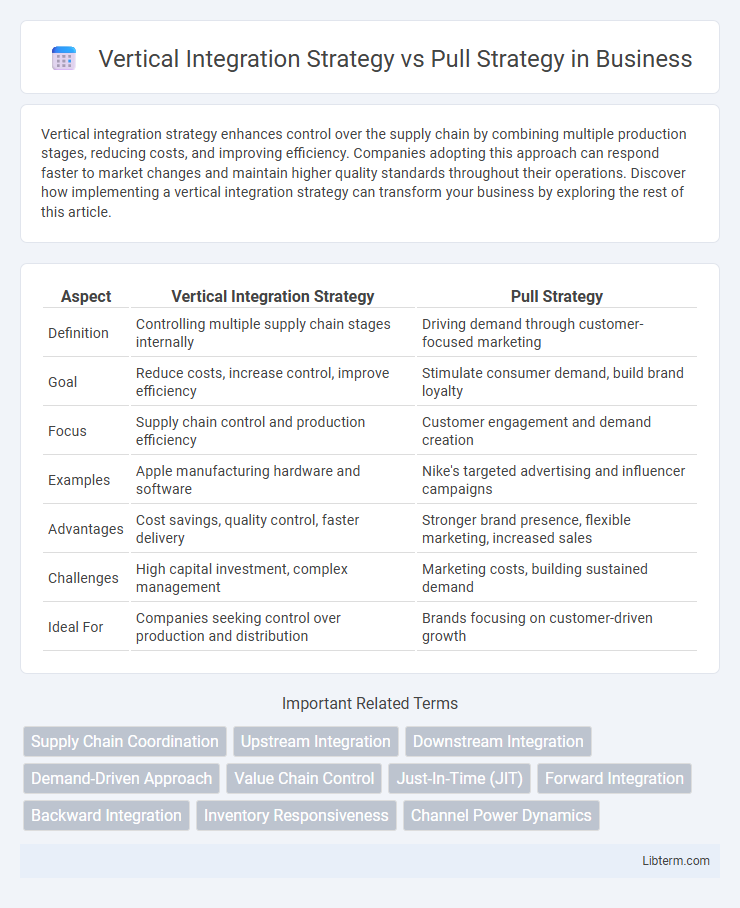
| Aspect | Vertical Integration Strategy | Pull Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlling multiple supply chain stages internally | Driving demand through customer-focused marketing |
| Goal | Reduce costs, increase control, improve efficiency | Stimulate consumer demand, build brand loyalty |
| Focus | Supply chain control and production efficiency | Customer engagement and demand creation |
| Examples | Apple manufacturing hardware and software | Nike's targeted advertising and influencer campaigns |
| Advantages | Cost savings, quality control, faster delivery | Stronger brand presence, flexible marketing, increased sales |
| Challenges | High capital investment, complex management | Marketing costs, building sustained demand |
| Ideal For | Companies seeking control over production and distribution | Brands focusing on customer-driven growth |
Understanding Vertical Integration Strategy
Vertical Integration Strategy involves a company controlling multiple stages of its supply chain, from production to distribution, to increase efficiency and reduce costs. This approach enhances market control, minimizes dependency on external suppliers, and can lead to competitive advantages through improved coordination and quality control. Firms employing vertical integration often benefit from streamlined operations and greater agility in responding to market demands.
Defining Pull Strategy in Modern Business
Pull strategy in modern business focuses on creating strong consumer demand to attract customers directly, leveraging techniques like social media marketing, influencer partnerships, and personalized content to engage target audiences. This approach contrasts with vertical integration by emphasizing brand-driven demand generation over controlling supply chain stages. Pull strategy enhances customer loyalty and brand equity by fostering deeper emotional connections and proactive consumer involvement.
Key Differences between Vertical Integration and Pull Strategy
Vertical integration strategy involves a company controlling multiple stages of production or distribution within its supply chain, enhancing control over quality, costs, and timelines. Pull strategy focuses on generating customer demand to drive product movement through the supply chain, relying heavily on marketing and consumer engagement. Key differences include vertical integration's emphasis on internal supply chain ownership versus pull strategy's reliance on external consumer-driven demand signals.
Benefits of Vertical Integration for Companies
Vertical integration strategy enhances operational control by allowing companies to manage multiple stages of their supply chain, reducing dependency on suppliers and improving product quality consistency. Companies benefit from cost savings through streamlined processes, economies of scale, and increased bargaining power in the market. This strategy also accelerates innovation cycles by fostering closer collaboration between production and distribution units.
Advantages of Implementing a Pull Strategy
Implementing a pull strategy enhances customer responsiveness by aligning production closely with actual demand, reducing inventory costs and minimizing waste. It improves supply chain flexibility and accelerates the feedback loop, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to market trends and consumer preferences. Companies adopting pull strategies benefit from stronger customer relationships and increased competitiveness through just-in-time production methods.
Challenges and Risks of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration strategy often faces significant challenges, including high capital investment requirements and increased operational complexity that can strain management resources. Risks involve reduced flexibility in responding to market changes and potential regulatory scrutiny due to decreased competition. Companies may also encounter supply chain disruptions if internal processes are inefficient, hindering overall agility compared to pull strategies.
Limitations of Pull Strategy in Certain Industries
Pull strategy limitations arise in industries with long production lead times and unpredictable consumer demand, causing stockouts and delayed deliveries. High dependency on accurate demand forecasting increases vulnerability to market fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Certain sectors like manufacturing and electronics face challenges in maintaining just-in-time inventory due to these constraints, impacting overall efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Case Studies: Successful Vertical Integration vs. Pull Strategy
Tesla's vertical integration strategy allowed it to control the entire supply chain, enhancing production efficiency and reducing costs, exemplified by its Gigafactory battery production. In contrast, Apple's pull strategy leverages consumer demand to drive supply chain responsiveness, minimizing inventory risk and optimizing product launches. Both strategies have proven successful by aligning operational tactics with market dynamics and company strengths.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right strategy between vertical integration and pull strategy depends on factors such as control over the supply chain, market demand stability, and resource availability. Vertical integration benefits companies seeking to reduce dependency on suppliers and improve profit margins by owning multiple production stages. Pull strategy suits businesses aiming to respond to customer demand dynamically while minimizing inventory costs and avoiding overproduction.
Future Trends in Vertical Integration and Pull Strategies
Future trends in vertical integration emphasize increased digitalization and AI-driven supply chain management to enhance efficiency and responsiveness, reducing dependency on external suppliers. Pull strategies are evolving with advanced data analytics and real-time consumer behavior tracking to enable highly customized demand generation and inventory optimization. Both approaches are converging with technology adoption to create agile, scalable, and customer-centric business models in dynamic markets.
Vertical Integration Strategy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com