Money markets provide a platform for short-term borrowing and lending, typically involving instruments like Treasury bills, commercial paper, and certificates of deposit. These markets enhance liquidity management and help financial institutions, corporations, and governments meet their immediate cash flow needs efficiently. Discover how understanding money markets can optimize Your cash management strategies in the full article.
Table of Comparison
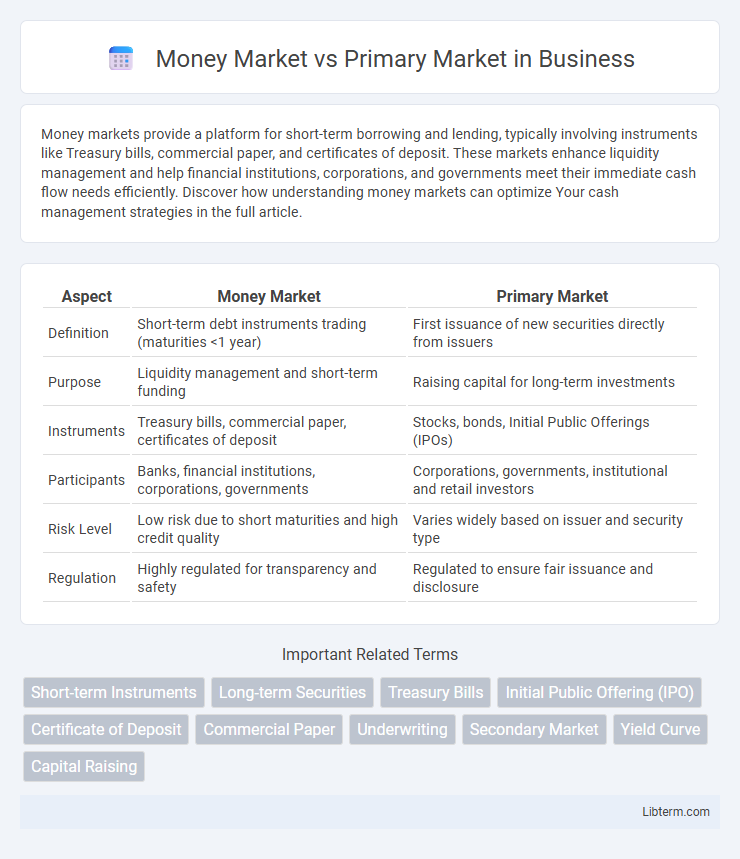
| Aspect | Money Market | Primary Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term debt instruments trading (maturities <1 year) | First issuance of new securities directly from issuers |
| Purpose | Liquidity management and short-term funding | Raising capital for long-term investments |
| Instruments | Treasury bills, commercial paper, certificates of deposit | Stocks, bonds, Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) |
| Participants | Banks, financial institutions, corporations, governments | Corporations, governments, institutional and retail investors |
| Risk Level | Low risk due to short maturities and high credit quality | Varies widely based on issuer and security type |
| Regulation | Highly regulated for transparency and safety | Regulated to ensure fair issuance and disclosure |
Introduction to Money Market and Primary Market
The money market facilitates short-term borrowing and lending of funds, typically with maturities of less than one year, involving instruments such as Treasury bills, commercial paper, and certificates of deposit. The primary market enables corporations and governments to raise capital by issuing new securities directly to investors, including initial public offerings (IPOs) and bond issuances. Both markets play crucial roles in financial systems by providing liquidity, capital formation, and efficient allocation of resources.
Key Definitions: Money Market vs Primary Market
The money market is a sector of the financial market where short-term debt securities with high liquidity and low risk, such as Treasury bills and commercial paper, are traded. The primary market refers to the financial market where new securities, including stocks and bonds, are issued directly by corporations or governments to investors for the first time. While the money market deals with short-term borrowing and lending, the primary market enables capital formation through the creation of new financial instruments.
Main Functions of the Money Market
The Money Market primarily facilitates short-term borrowing and lending of funds with high liquidity and low risk, ensuring businesses and governments can manage their immediate financing needs efficiently. It supports the efficient allocation of capital through instruments like Treasury bills, commercial papers, and certificates of deposit, enabling participants to meet short-term operational expenses and cash flow requirements. Unlike the Primary Market, which deals with the issuance of new securities to raise long-term capital, the Money Market provides a platform for trading financial assets with maturities typically less than one year.
Main Functions of the Primary Market
The primary market facilitates the issuance of new securities, enabling corporations and governments to raise capital directly from investors through initial public offerings (IPOs) and bond sales. It plays a crucial role in price discovery and provides a platform for companies to obtain funding for expansion, research, and development. This market ensures liquidity and transparency, attracting investors by offering fresh investment opportunities before securities enter the secondary market.
Instrument Types in Money Market and Primary Market
Money market instruments primarily include Treasury bills, commercial paper, certificates of deposit, and repurchase agreements, which are short-term debt securities used for liquidity management and short-term funding. Primary market instruments consist of newly issued stocks and bonds, including initial public offerings (IPOs) and government or corporate bond issuances, enabling entities to raise long-term capital directly from investors. The money market focuses on instruments with maturities typically less than one year, while the primary market involves the issuance of long-term securities to finance growth and investment.
Participants and Stakeholders
Money market participants primarily include commercial banks, financial institutions, corporations, and governments seeking short-term liquidity or investments, with instruments like treasury bills and certificates of deposit facilitating these transactions. Primary market stakeholders mainly comprise issuing companies, investment banks underwriting securities, and institutional and retail investors purchasing new stock or bond offerings directly from issuers. Both markets engage regulators such as the Securities and Exchange Commission to ensure transparency and compliance, but their participant roles differ in terms of liquidity needs and security issuance.
Duration and Nature of Securities
Money Market securities are short-term instruments with maturities typically less than one year, including Treasury bills, commercial paper, and certificates of deposit, characterized by high liquidity and low risk. Primary Market securities involve the issuance of new long-term financial instruments such as stocks and bonds, with maturities extending from one year to several decades, facilitating capital raising for governments and corporations. The nature of Money Market securities centers on short-term debt instruments for immediate funding needs, whereas Primary Market securities represent original issuance of equity or debt intended for long-term investment horizons.
Risk and Return Comparison
The Money Market involves short-term debt instruments like Treasury bills and commercial paper, offering lower risk and typically lower returns due to high liquidity and short maturities. The Primary Market facilitates the issuance of new securities such as stocks and bonds, generally presenting higher risk connected to market volatility and issuance uncertainty, but offering potentially higher returns through capital gains and dividend income. Investors seeking safety prioritize the Money Market, while those aiming for growth accept the Primary Market's risk-reward profile.
Regulatory Frameworks
The Money Market is regulated by central banks and financial authorities to ensure short-term liquidity and stability, emphasizing strict guidelines on credit risk and maturity periods. The Primary Market operates under securities laws and stock exchange regulations, mandating disclosure requirements and investor protection during initial public offerings and new securities issuance. Regulatory frameworks in both markets aim to maintain transparency, reduce systemic risks, and foster investor confidence through tailored compliance standards.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Money Market and Primary Market
Choosing between the Money Market and Primary Market depends on investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. The Money Market offers short-term, low-risk liquidity ideal for preserving capital, while the Primary Market provides opportunities to invest in new securities with potential for higher returns and market growth. Investors seeking quick access to funds typically prefer Money Market instruments, whereas those aiming for portfolio diversification and long-term gains lean towards the Primary Market.
Money Market Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com