Mergers and acquisitions reshape industries by combining companies to enhance market share, resources, and profitability through strategic collaboration or takeover. Understanding the complex financial, legal, and cultural aspects is crucial for navigating these transactions successfully. Explore this article to learn how your business can leverage mergers and acquisitions for sustainable growth.
Table of Comparison
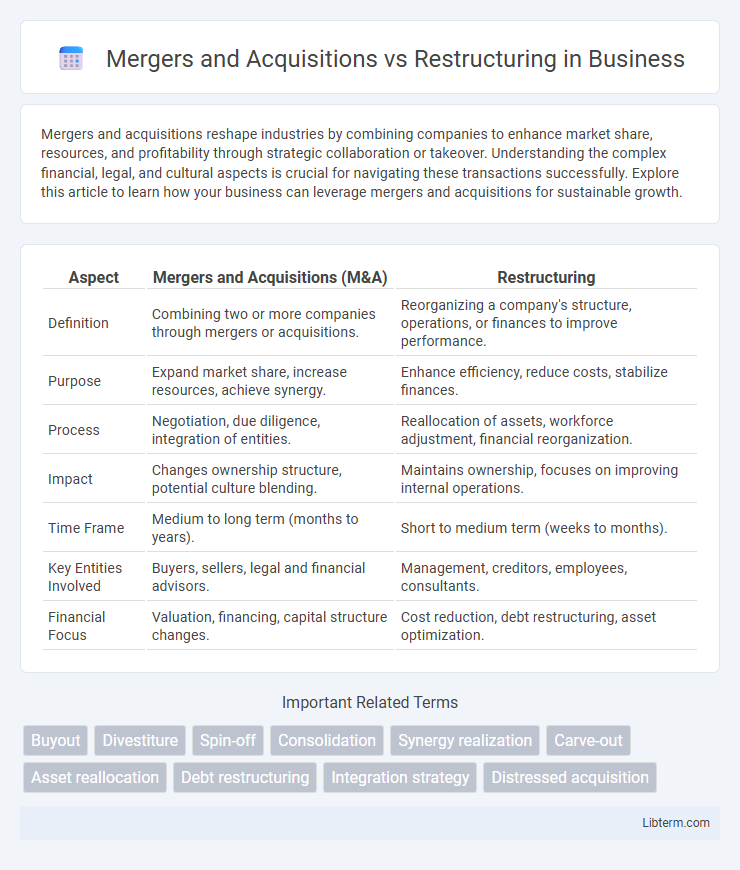
| Aspect | Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) | Restructuring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining two or more companies through mergers or acquisitions. | Reorganizing a company's structure, operations, or finances to improve performance. |
| Purpose | Expand market share, increase resources, achieve synergy. | Enhance efficiency, reduce costs, stabilize finances. |
| Process | Negotiation, due diligence, integration of entities. | Reallocation of assets, workforce adjustment, financial reorganization. |
| Impact | Changes ownership structure, potential culture blending. | Maintains ownership, focuses on improving internal operations. |
| Time Frame | Medium to long term (months to years). | Short to medium term (weeks to months). |
| Key Entities Involved | Buyers, sellers, legal and financial advisors. | Management, creditors, employees, consultants. |
| Financial Focus | Valuation, financing, capital structure changes. | Cost reduction, debt restructuring, asset optimization. |
Introduction to Mergers and Acquisitions vs Restructuring
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) involve the consolidation of companies or assets to enhance market share, achieve synergies, and drive growth. Restructuring focuses on reorganizing a company's financial and operational structures to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and address financial challenges. Both strategies are essential corporate finance tools but serve distinct purposes: M&A for expansion and competitiveness, restructuring for stabilization and optimization.
Defining Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) involve the consolidation of companies or assets, where mergers combine two firms into one, and acquisitions entail one company purchasing another. M&A strategies aim to achieve growth, increase market share, or acquire new technologies and resources. Key components of M&A include due diligence, valuation, negotiation, and integration processes that drive corporate expansion and competitive advantage.
Understanding Corporate Restructuring
Corporate restructuring involves reorganizing a company's structure, operations, or finances to improve efficiency, competitiveness, and profitability. Unlike mergers and acquisitions, which focus on combining entities or purchasing companies, restructuring aims to optimize internal processes through measures like asset divestitures, debt refinancing, or management changes. Effective restructuring enhances corporate agility and financial health, positioning the business for long-term growth and sustainability.
Key Differences Between M&A and Restructuring
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) involve combining two or more companies to achieve growth, market expansion, or competitive advantage, whereas restructuring focuses on reorganizing a company's internal operations to improve efficiency and financial stability. M&A typically results in new ownership or control, while restructuring maintains ownership but alters the organizational structure, debt, or asset management. Key differences include the strategic objectives, scope of change, and impact on stakeholders, with M&A emphasizing external growth and restructuring addressing internal optimization.
Strategic Objectives: M&A vs Restructuring
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) primarily aim to achieve growth through market expansion, diversification, or gaining competitive advantages by combining resources and capabilities. In contrast, restructuring focuses on improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and realigning business processes to enhance profitability and adapt to changing market conditions. Both strategies serve distinct strategic objectives: M&A drives external growth and market positioning, whereas restructuring targets internal optimization and organizational agility.
Common Types of Mergers, Acquisitions, and Restructuring
Common types of mergers include horizontal mergers, where companies in the same industry combine to increase market share, vertical mergers that integrate suppliers and distributors, and conglomerate mergers which unite firms in unrelated businesses to diversify risk. Acquisitions typically occur through stock purchases, asset purchases, or hostile takeovers, each serving strategic goals such as expanding product lines or eliminating competition. Restructuring commonly involves financial restructuring to improve cash flow, operational restructuring to boost efficiency, and organizational restructuring aimed at realigning management or workforce for better performance.
Financial Implications and Outcomes
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) typically involve significant financial investment and can lead to increased market share, revenue growth, and economies of scale, but also entail risks such as high debt levels and integration costs. Restructuring focuses on optimizing existing assets and operations to improve financial stability, reduce costs, and enhance cash flow without the extensive capital outlay associated with M&A. The financial outcomes of M&A often include asset consolidation and potential valuation increases, while restructuring aims for debt reduction, operational efficiency, and improved profitability metrics.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Mergers and acquisitions involve complex legal frameworks, requiring thorough compliance with antitrust laws, securities regulations, and due diligence to avoid litigation and regulatory penalties. Restructuring demands adherence to bankruptcy laws, labor regulations, and contractual obligations to ensure lawful reorganization of assets and liabilities. Both processes necessitate engagement with regulatory bodies such as the SEC, FTC, or equivalent authorities to secure approvals and meet disclosure mandates.
Risks and Challenges Comparison
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) present risks such as cultural clashes, integration difficulties, and regulatory hurdles that can disrupt operations and reduce expected synergies. Restructuring challenges often include employee resistance, operational downtime, and maintaining customer trust during organizational changes. Both strategies require careful management of financial risks, but M&A tends to involve higher market and compliance uncertainties, while restructuring focuses more on internal process optimization and workforce realignment.
Choosing Between M&A and Restructuring: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) and restructuring depends on factors such as company objectives, financial health, and market conditions. M&A is suitable for growth, market expansion, or gaining competitive advantage, while restructuring focuses on improving efficiency, reducing costs, or stabilizing a troubled business. Strategic alignment, urgency of change, and resource availability are critical considerations in making the optimal choice.
Mergers and Acquisitions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com