Underwriting commission is the fee paid to investment bankers or underwriters for managing the issuance and distribution of securities during an initial public offering (IPO) or other stock offerings. This fee compensates underwriters for the risk they assume and the services they provide, such as pricing, marketing, and selling the securities to investors. To understand how underwriting commissions impact your investment and the overall cost of capital, continue reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
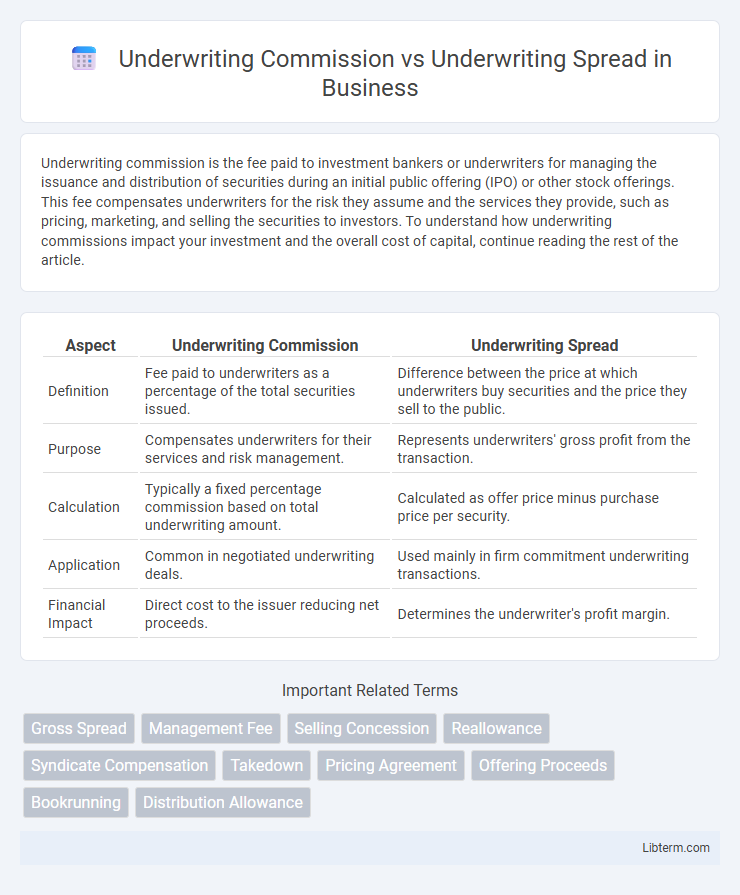
| Aspect | Underwriting Commission | Underwriting Spread |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fee paid to underwriters as a percentage of the total securities issued. | Difference between the price at which underwriters buy securities and the price they sell to the public. |
| Purpose | Compensates underwriters for their services and risk management. | Represents underwriters' gross profit from the transaction. |
| Calculation | Typically a fixed percentage commission based on total underwriting amount. | Calculated as offer price minus purchase price per security. |
| Application | Common in negotiated underwriting deals. | Used mainly in firm commitment underwriting transactions. |
| Financial Impact | Direct cost to the issuer reducing net proceeds. | Determines the underwriter's profit margin. |
Introduction to Underwriting in Finance
Underwriting commission refers to the fee paid to underwriters as compensation for assuming the risk of distributing new securities, typically expressed as a percentage of the total issue amount. Underwriting spread is the difference between the price the underwriters pay to the issuer and the price at which they sell the securities to the public, representing the gross profit earned by underwriters. Both concepts are central in investment banking, influencing the cost structure and risk management of securities offerings.
Defining Underwriting Commission
Underwriting commission refers to the fee paid to investment bankers or underwriters for managing and distributing a securities offering, typically expressed as a percentage of the total offering amount. It compensates the underwriters for assuming the risk of buying securities from the issuer and reselling them to investors. In contrast, underwriting spread represents the difference between the price paid by investors and the amount received by the issuer, encompassing both the underwriting commission and other fees.
Understanding Underwriting Spread
Underwriting spread represents the difference between the price at which underwriters purchase securities from an issuer and the price at which they sell them to the public, reflecting the underwriters' compensation and risk. It comprises components like the manager's fee, underwriting fee, and selling concession, which collectively determine the gross spread. Understanding underwriting spread is crucial for evaluating the cost of capital for issuers and the profitability margin for underwriters in public offerings.
Key Differences Between Commission and Spread
Underwriting commission refers to the fee paid to underwriters for their services in managing and distributing a securities offering, usually expressed as a percentage of the total amount raised. Underwriting spread, on the other hand, is the difference between the price at which underwriters buy securities from the issuer and the price at which they sell to the public, representing the gross profit margin. The key difference lies in underwriting commission being a direct fee for service, while underwriting spread encompasses the overall profit margin including commission and other expenses.
Calculation Methods for Underwriting Commission
Underwriting commission is calculated as a fixed percentage of the total underwriting amount or the gross proceeds raised in a securities offering, typically ranging from 1% to 7%, depending on deal size and complexity. In contrast, the underwriting spread represents the difference between the price paid by underwriters to the issuer and the price at which securities are sold to the public, encompassing the total compensation including commissions and other expenses. The underwriting commission calculation focuses specifically on the percentage agreed upon in the underwriting agreement, applied directly to the gross offering proceeds or the number of securities sold.
How Underwriting Spread is Determined
The underwriting spread is determined by the difference between the price at which underwriters purchase securities from the issuer and the price at which they sell them to the public, reflecting the underwriters' compensation for risk and distribution costs. Factors influencing this spread include market conditions, issuer credit quality, deal size, and investor demand, which collectively impact the discount underwriters require. This spread typically covers expenses such as underwriting fees, selling concessions, and management fees, ensuring underwriters are incentivized to distribute the securities effectively.
Impact on Issuers and Underwriters
Underwriting commission directly affects the net proceeds an issuer receives, as it represents the fee paid to underwriters for their services, reducing the issuer's capital raised. The underwriting spread, which includes the commission and other fees, impacts underwriters by determining their potential profit margin from the securities offering. Both terms influence the financial outcomes for issuers and underwriters, with higher commissions and spreads increasing costs for issuers while enhancing compensation for underwriters.
Market Standards and Regulatory Considerations
Underwriting commission typically represents a fixed percentage fee paid to underwriters for services rendered, often ranging between 2% to 5% in equity offerings, while underwriting spread denotes the difference between the price paid by investors and the price received by the issuer, serving as the underwriters' gross profit. Market standards dictate specific ranges for these fees based on deal size and complexity, with larger deals often commanding lower percentage spreads to remain competitive. Regulatory considerations, such as SEC rules and fair disclosure requirements, ensure transparency and prohibit excessive compensation, mandating detailed disclosures of underwriting compensation in offering documents to protect investor interests.
Comparative Advantages for Investors
Underwriting commission refers to the fee paid to underwriters for managing and distributing an offering, generally expressed as a percentage of the total deal size, while underwriting spread represents the difference between the price at which underwriters purchase securities from the issuer and the price at which they sell them to investors. Investors benefit from the underwriting spread as it reflects the risk-adjusted price margin underwriters accept, often leading to better pricing accuracy and reduced issuance costs. Choosing offerings with favorable underwriting commissions and spreads can enhance investor returns by minimizing fees and aligning price incentives between issuers and underwriters.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Commission and Spread
Choosing between underwriting commission and underwriting spread depends on the specific financial goals and risk preferences of the issuer and underwriter. Underwriting commissions provide a fixed percentage fee based on the total offering amount, ensuring predictable compensation for services rendered, while underwriting spreads represent the difference between the price paid by underwriters and the price at which securities are sold to investors, reflecting both compensation and risk exposure. Evaluating factors such as transaction size, market conditions, and the desired alignment of incentives helps determine the optimal structure for underwriting costs.
Underwriting Commission Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com