Conglomerate integration involves the strategic merging of companies from diverse industries to diversify risks and expand market presence. This approach enables businesses to leverage varied expertise and resources, fostering innovation and financial stability across different sectors. Explore the full article to understand how conglomerate integration can transform Your business strategy and drive sustainable growth.
Table of Comparison
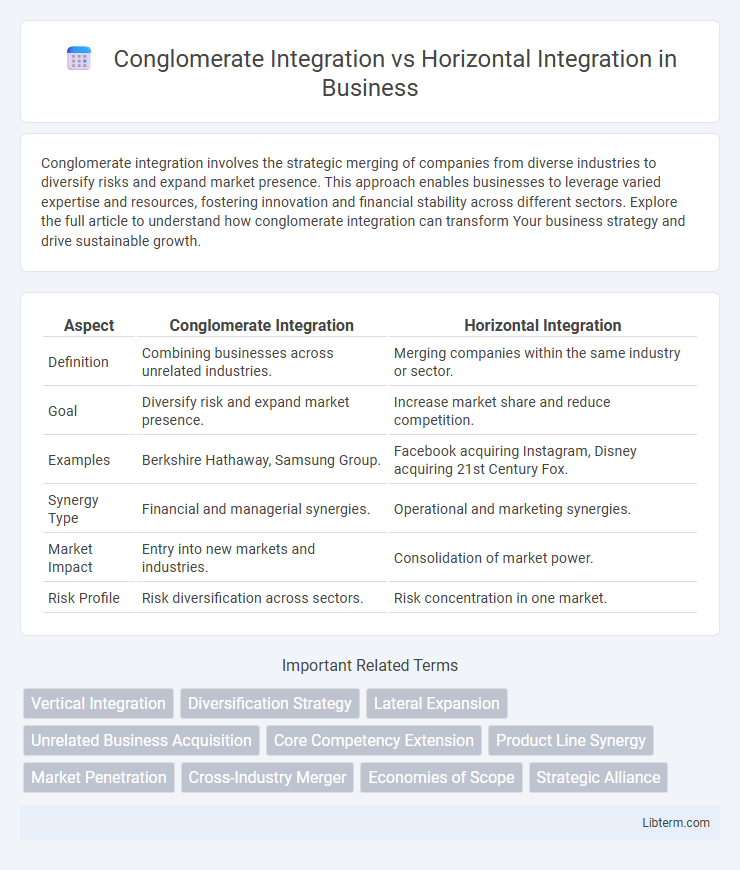
| Aspect | Conglomerate Integration | Horizontal Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining businesses across unrelated industries. | Merging companies within the same industry or sector. |
| Goal | Diversify risk and expand market presence. | Increase market share and reduce competition. |
| Examples | Berkshire Hathaway, Samsung Group. | Facebook acquiring Instagram, Disney acquiring 21st Century Fox. |
| Synergy Type | Financial and managerial synergies. | Operational and marketing synergies. |
| Market Impact | Entry into new markets and industries. | Consolidation of market power. |
| Risk Profile | Risk diversification across sectors. | Risk concentration in one market. |
Introduction to Business Integration Strategies
Business integration strategies encompass conglomerate integration, which involves merging companies from unrelated industries to diversify operations and reduce risk, and horizontal integration, where firms within the same industry combine to increase market share and achieve economies of scale. Conglomerate integration allows businesses to enter new markets and leverage cross-industry synergies, whereas horizontal integration strengthens competitive positioning by consolidating similar product lines or services. Understanding these distinct approaches helps organizations tailor growth tactics aligned with their strategic objectives and industry dynamics.
Defining Conglomerate Integration
Conglomerate integration refers to the merger or acquisition of companies operating in entirely different industries, creating a diversified business portfolio that reduces risk by spreading investments across unrelated markets. This strategy contrasts with horizontal integration, which involves combining firms within the same industry to increase market share and achieve economies of scale. By focusing on unrelated sectors, conglomerate integration aims to maximize financial stability and growth opportunities through diversification rather than market concentration.
Understanding Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration involves the acquisition or merger of companies operating within the same industry and at the same stage of production, aiming to increase market share and reduce competition. This strategy allows firms to achieve economies of scale, expand their product offerings, and enhance competitive positioning within the market. Unlike conglomerate integration, which diversifies across different industries, horizontal integration concentrates on strengthening core business activities and consolidating industry presence.
Key Differences Between Conglomerate and Horizontal Integration
Conglomerate integration involves the merger of companies operating in unrelated industries, focusing on diversification and risk reduction, while horizontal integration refers to the consolidation of firms within the same industry aimed at increasing market share and reducing competition. Key differences include the diversification strategy in conglomerate integration versus market dominance in horizontal integration, as well as the nature of synergy: operational efficiencies in horizontal integration compared to financial and managerial synergies in conglomerate integration. Horizontal integration impacts industry structure and competition directly, whereas conglomerate integration influences portfolio diversification and financial stability.
Advantages of Conglomerate Integration
Conglomerate integration offers significant advantages by diversifying business risks across unrelated industries, reducing dependence on a single market and enhancing overall corporate stability. This strategy fosters financial synergies, enabling resource sharing and capital allocation efficiency, which can improve profitability and growth potential. Moreover, conglomerate integration provides access to new markets and customer bases, strengthening the company's competitive position and long-term resilience.
Benefits of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration enhances market share by merging with or acquiring competitors in the same industry, leading to increased economies of scale and reduced operational costs. It fosters greater market power, allowing companies to influence pricing and negotiate better terms with suppliers and distributors. Horizontal integration also facilitates diversification of product offerings within the same market, improving customer reach and brand recognition.
Risks and Challenges of Conglomerate Integration
Conglomerate integration involves merging firms from unrelated industries, posing significant risks such as managerial complexity and inefficiencies due to lack of industry-specific knowledge. Challenges include difficulties in resource allocation and cultural integration across diverse business units, which can lead to reduced synergy and poor financial performance. This contrasts with horizontal integration, where firms combine within the same industry, generally facing fewer integration challenges and more predictable operational alignment.
Potential Drawbacks of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration, which involves merging companies within the same industry, can lead to potential drawbacks such as reduced competition and increased market monopoly, resulting in higher prices for consumers. This strategy may also cause integration challenges like cultural clashes and operational redundancies, affecting overall efficiency. Furthermore, regulatory scrutiny and antitrust issues frequently arise, posing legal risks and potentially hindering business growth.
Real-World Examples: Conglomerate vs Horizontal Integration
Conglomerate integration occurs when a corporation acquires companies in unrelated industries, exemplified by Berkshire Hathaway's diverse holdings from insurance to utilities, showcasing risk diversification and market expansion strategies. Horizontal integration involves merging with or acquiring competitors within the same industry, such as Facebook's acquisition of Instagram, enhancing market share and reducing competition. Both strategies serve distinct growth objectives: conglomerate integration targets portfolio diversification, while horizontal integration emphasizes industry dominance.
Choosing the Right Integration Strategy for Your Business
Choosing the right integration strategy depends on your business goals and market dynamics; conglomerate integration involves merging with unrelated businesses to diversify risk, while horizontal integration focuses on acquiring competitors to increase market share and reduce competition. Assessing industry conditions, company resources, and long-term objectives helps determine whether expanding into new markets or consolidating existing market presence aligns best with growth plans. Strategic alignment with operational capabilities and financial strength ensures choosing an integration path that maximizes synergy and shareholder value.
Conglomerate Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com