Equal interest is a crucial concept in partnerships and joint ventures, ensuring that all parties share ownership and profits fairly based on their contributions. This balanced approach fosters trust and collaboration, preventing disputes that can arise from unequal stakes. Discover how equal interest impacts your business agreements and how to implement it effectively by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
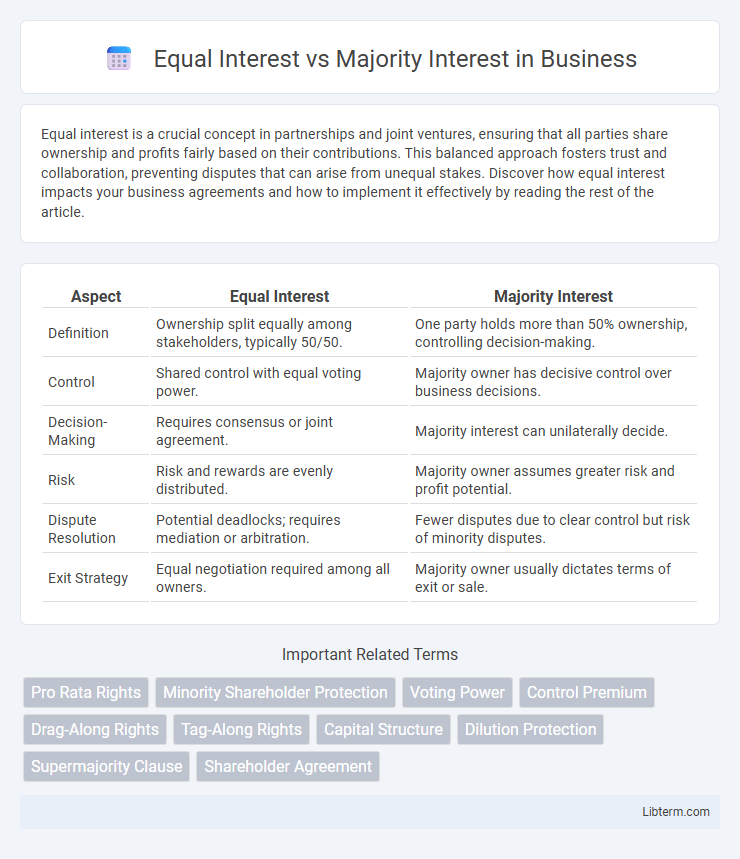
| Aspect | Equal Interest | Majority Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ownership split equally among stakeholders, typically 50/50. | One party holds more than 50% ownership, controlling decision-making. |
| Control | Shared control with equal voting power. | Majority owner has decisive control over business decisions. |
| Decision-Making | Requires consensus or joint agreement. | Majority interest can unilaterally decide. |
| Risk | Risk and rewards are evenly distributed. | Majority owner assumes greater risk and profit potential. |
| Dispute Resolution | Potential deadlocks; requires mediation or arbitration. | Fewer disputes due to clear control but risk of minority disputes. |
| Exit Strategy | Equal negotiation required among all owners. | Majority owner usually dictates terms of exit or sale. |
Understanding Equal Interest and Majority Interest
Equal interest refers to a situation where two or more parties hold identical ownership percentages or rights in a particular asset, business, or investment, ensuring balanced control and profit sharing. Majority interest occurs when one party owns more than 50% of the entity, granting them decisive control over decisions and strategic direction. Understanding the distinction between equal and majority interest is crucial for evaluating power dynamics, governance, and potential conflicts within partnerships or corporations.
Key Differences Between Equal and Majority Interest
Equal interest entails all parties holding identical ownership percentages, ensuring equal voting rights and profit distribution, which promotes balanced decision-making. Majority interest refers to ownership exceeding 50%, granting controlling authority in business decisions and priority in profit allocation. The key difference lies in control dynamics, where equal interest fosters shared governance, while majority interest enables dominance by the principal stakeholder.
Legal Definitions and Implications
Equal interest refers to ownership where all parties hold identical shares and have the same rights and responsibilities under the law, ensuring balanced control and decision-making power. Majority interest occurs when one party owns more than 50% of the voting rights or equity, granting them control over business decisions and influencing corporate governance. Legal implications include the ability of majority interest holders to dictate terms, approve or reject actions, and potentially override minority interests in corporate resolutions.
Advantages of Equal Interest
Equal interest ownership ensures balanced decision-making power among all parties, preventing dominance by any single shareholder and fostering collaboration. This structure simplifies profit distribution, as stakeholders receive an identical share, promoting transparency and fairness. Equal interest also enhances trust and long-term partnership stability by aligning incentives and encouraging mutual responsibility.
Advantages of Majority Interest
Majority interest provides greater control over decision-making processes and strategic direction within a company, enabling stakeholders to influence key policies and operations effectively. This ownership level often allows for easier approval of corporate actions, such as mergers, acquisitions, or amendments to bylaws, without requiring consensus from minority shareholders. With majority interest, investors can secure leadership positions, ensuring alignment between management actions and shareholder goals, which typically enhances corporate stability and growth potential.
Impact on Decision-Making and Control
Equal interest in a business means all parties share decision-making power equally, requiring unanimous agreement for key actions and potentially slowing down the process. Majority interest grants control to the shareholder or group holding over 50% of ownership, enabling them to unilaterally influence strategic decisions and company policies. This control dynamic impacts governance efficiency, with majority interest often leading to faster decisions but less input from minority stakeholders.
Scenarios Where Equal Interest is Preferred
Equal interest is preferred in joint ventures or partnerships where balanced decision-making authority prevents dominance by one party, ensuring mutual trust and collaboration. It is ideal in family businesses or startups founded by co-founders seeking to maintain equal control and shared risks. In investment scenarios where parties aim for equitable profit distribution and risk-sharing, equal interest structures promote fairness and transparency.
Scenarios Favoring Majority Interest
Scenarios favoring majority interest typically arise in corporate governance when decisive control is necessary to implement strategic decisions or resolve disputes among shareholders. Majority interest holders possess the voting power to influence board appointments, dividend policies, and mergers or acquisitions, providing stability and clear direction during critical business phases. This control is particularly advantageous in private companies or closely held corporations where swift decision-making outweighs the need for equal consensus.
Resolving Conflicts: Equal vs Majority Stakeholders
Conflicts between equal interest stakeholders often require structured negotiation and consensus-building techniques to ensure equitable decision-making and avoid deadlocks. Majority interest stakeholders typically hold the power to unilaterally resolve disputes through voting rights or controlling shares, enabling more decisive management but risking minority disenfranchisement. Effective conflict resolution strategies include establishing clear governance policies, dispute resolution mechanisms, and shareholder agreements tailored to balance power dynamics between equal and majority stakeholders.
Choosing the Right Interest Structure for Your Business
Choosing the right interest structure for your business depends on your goals for control and decision-making power. Equal interest grants all partners identical ownership percentages, promoting collaborative management and shared risks, while majority interest gives one party over 50% ownership, enabling decisive control and streamlined decisions. Evaluating factors such as governance flexibility, investor expectations, and profit distribution strategies is essential for selecting the optimal ownership model.
Equal Interest Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com