Segmentation divides your target market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behavior, or preferences, enabling more precise and effective marketing strategies. Understanding these segments helps tailor your messaging and product offerings to meet specific needs, increasing customer engagement and conversion rates. Explore the rest of this article to discover the best segmentation techniques for your business success.
Table of Comparison
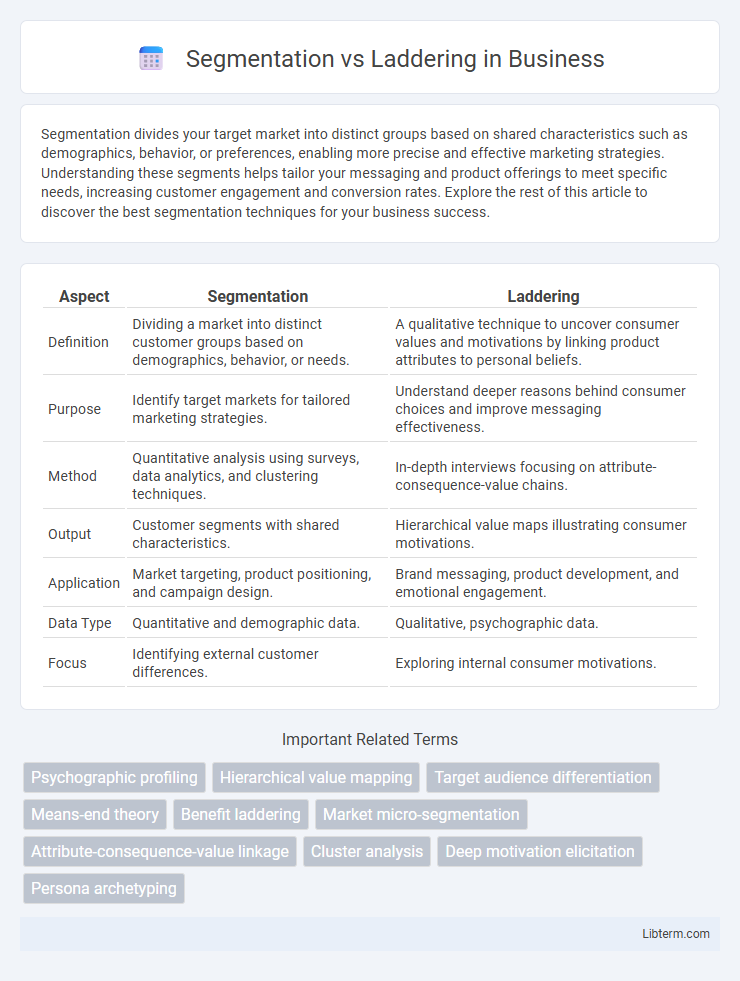
| Aspect | Segmentation | Laddering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dividing a market into distinct customer groups based on demographics, behavior, or needs. | A qualitative technique to uncover consumer values and motivations by linking product attributes to personal beliefs. |
| Purpose | Identify target markets for tailored marketing strategies. | Understand deeper reasons behind consumer choices and improve messaging effectiveness. |
| Method | Quantitative analysis using surveys, data analytics, and clustering techniques. | In-depth interviews focusing on attribute-consequence-value chains. |
| Output | Customer segments with shared characteristics. | Hierarchical value maps illustrating consumer motivations. |
| Application | Market targeting, product positioning, and campaign design. | Brand messaging, product development, and emotional engagement. |
| Data Type | Quantitative and demographic data. | Qualitative, psychographic data. |
| Focus | Identifying external customer differences. | Exploring internal consumer motivations. |
Introduction to Segmentation and Laddering
Segmentation divides a market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as demographics, behaviors, or needs to tailor marketing strategies effectively. Laddering is a qualitative research technique that uncovers consumers' underlying motivations by linking product attributes to personal values through sequential questioning. Combining segmentation with laddering enhances understanding of target audiences by revealing both surface-level profiles and deep psychological drivers.
Defining Market Segmentation
Market segmentation involves dividing a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups of consumers based on shared characteristics such as demographics, psychographics, geographic location, or behavior. This process enables businesses to target specific audiences with tailored marketing strategies, improving relevance and customer engagement. Unlike laddering, which explores underlying consumer motivations, segmentation focuses on categorizing the market to enhance product positioning and communication effectiveness.
What is the Laddering Technique?
The laddering technique is a qualitative research method used to uncover consumers' underlying values, motivations, and decision-making processes by exploring connections between product attributes, consequences, and personal values. Unlike segmentation, which categorizes consumers into groups based on demographics or behaviors, laddering digs deeper into why consumers prefer certain products by probing through a series of "why" questions to reveal hierarchical cognitive structures. This method enables marketers to align messaging and product development with core psychological drivers, enhancing emotional engagement and brand loyalty.
Key Differences: Segmentation vs. Laddering
Segmentation divides a market into distinct groups based on demographics, behaviors, or needs to tailor marketing strategies effectively. Laddering uncovers consumers' underlying values and motivations by linking product attributes to personal benefits and emotional drivers through in-depth interviews. While segmentation targets external characteristics for broad market division, laddering delves into psychological factors to guide emotional branding and product positioning.
Purpose and Goals of Each Approach
Segmentation aims to divide a broad market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics or behaviors to tailor marketing strategies and improve targeting efficiency. Laddering focuses on uncovering the deep underlying motivations and values that drive consumer decisions by exploring connections between product attributes, consequences, and personal values. While segmentation enhances market precision by categorizing consumers, laddering provides qualitative insights into why consumers make specific choices, supporting more emotionally resonant messaging.
Methodologies Used in Segmentation and Laddering
Segmentation employs methodologies such as demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral analysis to categorize consumers into distinct groups based on shared characteristics. Laddering utilizes in-depth qualitative techniques like cognitive interviewing and means-end chain analysis to uncover the underlying values and motivations driving consumer choices. While segmentation focuses on identifying target market clusters, laddering digs deeper into consumers' personal beliefs to inform product positioning and messaging strategies.
Benefits and Limitations of Segmentation
Segmentation enhances marketing effectiveness by dividing a broad consumer base into distinct groups based on demographics, behavior, or psychographics, allowing tailored messaging that drives engagement and conversion rates. Its limitations include potential oversimplification of diverse consumer needs and the risk of excluding niche markets, which can reduce overall reach and effectiveness. Despite these challenges, segmentation remains crucial for resource optimization and targeting precision in competitive markets.
Advantages and Challenges of Laddering
Laddering offers deeper insights into consumer motivations by uncovering the emotional and psychological drivers behind purchasing decisions, which enhances targeted marketing strategies. The approach presents challenges such as requiring skilled interviewers to avoid bias and eliciting honest, introspective responses, making it time-consuming and resource-intensive. Despite these difficulties, laddering's ability to link product attributes to personal values improves product positioning and customer satisfaction analytics.
Practical Applications: When to Use Each Method
Segmentation excels in practical applications where market differentiation and customer targeting require clear grouping based on demographics, behaviors, or preferences, enabling tailored marketing strategies and product development. Laddering is ideal for in-depth qualitative research aimed at uncovering consumers' underlying values and motivations through attribute-consequence-value chains, informing brand positioning and messaging. Use segmentation for broad market analysis and audience categorization, while laddering suits detailed consumer insight generation and emotional connection building.
Conclusion: Integrating Segmentation and Laddering for Optimal Insights
Integrating segmentation and laddering methodologies enhances marketing strategies by combining detailed audience grouping with deep motivational insights. Segmentation identifies distinct consumer clusters based on demographics, behaviors, and psychographics, while laddering uncovers the underlying values driving their choices. This integration enables businesses to tailor personalized messaging that resonates emotionally and functionally, improving campaign effectiveness and customer engagement.
Segmentation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com