Stock options provide a powerful way to invest in a company's future growth by giving you the right to buy shares at a predetermined price. They offer potential financial rewards if the company's stock price rises, making them an attractive tool for building wealth. Explore this article to understand how stock options work and how they can benefit your investment strategy.
Table of Comparison
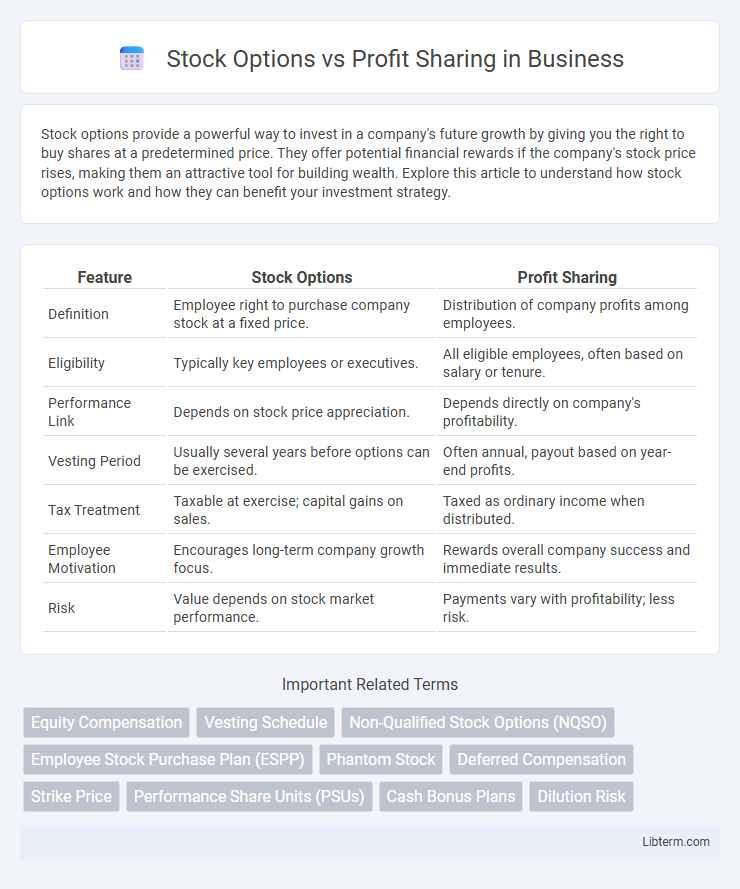
| Feature | Stock Options | Profit Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee right to purchase company stock at a fixed price. | Distribution of company profits among employees. |
| Eligibility | Typically key employees or executives. | All eligible employees, often based on salary or tenure. |
| Performance Link | Depends on stock price appreciation. | Depends directly on company's profitability. |
| Vesting Period | Usually several years before options can be exercised. | Often annual, payout based on year-end profits. |
| Tax Treatment | Taxable at exercise; capital gains on sales. | Taxed as ordinary income when distributed. |
| Employee Motivation | Encourages long-term company growth focus. | Rewards overall company success and immediate results. |
| Risk | Value depends on stock market performance. | Payments vary with profitability; less risk. |
Introduction to Stock Options and Profit Sharing
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, aligning their interests with company growth and offering potential financial gains as stock value increases. Profit sharing distributes a portion of company profits directly to employees, creating immediate monetary rewards tied to business performance. Both incentives motivate employees but differ in structure, timing, and risk exposure, impacting employee engagement and retention strategies.
Key Differences Between Stock Options and Profit Sharing
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, offering potential capital gains if the stock value increases. Profit sharing distributes a portion of company profits directly to employees, usually as cash or contributions to retirement plans, reflecting the company's financial performance. Stock options align employees' interests with long-term company growth, while profit sharing provides immediate or short-term financial rewards based on profitability.
How Stock Options Work
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, after a vesting period. This mechanism aligns employee incentives with company performance by allowing profit from stock appreciation above the strike price. Exercising stock options requires understanding expiration dates and potential tax implications based on holding periods and exercise timing.
How Profit Sharing Plans Operate
Profit sharing plans distribute a portion of a company's profits directly to employees, typically based on a predetermined formula linked to company earnings and individual compensation. These plans incentivize employee performance by aligning rewards with overall business success, often resulting in lump-sum payments or contributions to retirement accounts. Unlike stock options that grant the right to purchase shares at a set price, profit sharing provides immediate or deferred financial benefits tied to the company's profitability.
Advantages of Stock Options for Employees
Stock options offer employees the advantage of potential significant financial gains through the appreciation of company stock, aligning their interests with long-term corporate growth and success. These options provide a tangible sense of ownership and motivation to contribute to increasing the company's market value, often leading to higher employee retention. Unlike profit sharing, stock options enable employees to benefit from stock price increases even during periods when profit distribution may be limited or delayed.
Benefits of Profit Sharing for Employees
Profit sharing offers employees a direct stake in company success, aligning their interests with organizational goals and boosting motivation. Unlike stock options, profit sharing provides immediate, tangible rewards without requiring employees to purchase shares or worry about stock market volatility. This approach often enhances job satisfaction and financial security by delivering regular cash bonuses tied to company profitability.
Employer Considerations: Costs and Implementation
Employers must evaluate the upfront administrative and legal costs associated with stock options, including compliance with securities regulations and ongoing valuation expenses. Profit sharing plans typically involve predictable expense allocations tied to company profitability, simplifying budgeting but requiring sustainable cash flow management. Implementation of stock options demands detailed plan design to align with long-term business goals, whereas profit sharing necessitates transparent profit calculation methods and clear communication to ensure employee motivation and retention.
Tax Implications: Stock Options vs Profit Sharing
Stock options are often subject to capital gains tax upon exercise and sale, potentially offering lower tax rates compared to ordinary income tax on profit-sharing distributions. Profit sharing is typically taxed as ordinary income when received, resulting in higher immediate tax liabilities for employees. Employers and employees must consider these tax differences carefully when choosing between stock options and profit-sharing plans to maximize financial benefits.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Stock options align employee interests with company performance by offering potential financial rewards tied to stock price appreciation, which can significantly boost motivation and long-term commitment. Profit sharing provides employees with a direct share of the company's earnings, fostering a sense of ownership and immediate reward that enhances job satisfaction and retention. Both methods positively influence employee motivation and retention but differ in immediacy and risk exposure, with stock options appealing to growth-focused employees and profit sharing rewarding stable profitability.
Choosing the Right Plan for Your Organization
Evaluating stock options versus profit sharing requires analyzing your organization's long-term goals and employee engagement strategies. Stock options incentivize employees by providing ownership stakes that potentially increase in value, aligning their interests with company growth and retention. Profit sharing offers direct cash rewards based on company performance, fostering immediate motivation but with less emphasis on equity accumulation.
Stock Options Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com