Offshoring allows businesses to reduce operational costs by relocating processes to countries with lower labor expenses, improving overall efficiency. This strategy can enhance access to skilled talent pools and global markets, boosting competitiveness. Explore the article to understand how offshoring can transform your business operations.
Table of Comparison
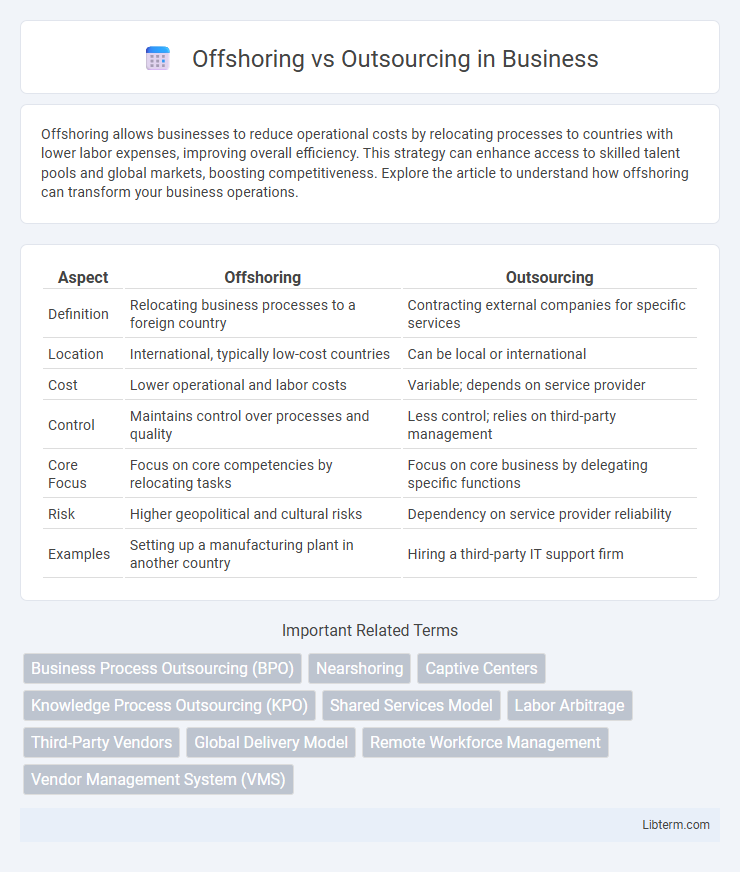
| Aspect | Offshoring | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating business processes to a foreign country | Contracting external companies for specific services |
| Location | International, typically low-cost countries | Can be local or international |
| Cost | Lower operational and labor costs | Variable; depends on service provider |
| Control | Maintains control over processes and quality | Less control; relies on third-party management |
| Core Focus | Focus on core competencies by relocating tasks | Focus on core business by delegating specific functions |
| Risk | Higher geopolitical and cultural risks | Dependency on service provider reliability |
| Examples | Setting up a manufacturing plant in another country | Hiring a third-party IT support firm |
Introduction to Offshoring and Outsourcing
Offshoring involves relocating business processes or services to another country to leverage cost advantages, access specialized skills, or expand global presence. Outsourcing refers to contracting external organizations or third-party vendors to perform specific tasks, functions, or services, regardless of geographic location. Both strategies aim to improve operational efficiency, reduce expenses, and focus on core competencies but differ in control, location, and organizational structure.
Defining Offshoring: Key Characteristics
Offshoring involves relocating business processes or services to a foreign country to leverage cost advantages, specialized skills, or favorable economic conditions. Key characteristics include establishing owned subsidiaries or dedicated offshore teams abroad, maintaining direct control over operations, and capitalizing on time zone differences for around-the-clock productivity. This strategy differs from outsourcing by emphasizing ownership and control rather than contracting third-party vendors.
Understanding Outsourcing: Core Concepts
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or tasks to external service providers to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Key concepts include contract management, service level agreements (SLAs), and vendor relationship management, which ensure quality and accountability in outsourced services. Understanding the strategic objectives behind outsourcing helps companies optimize resource allocation and focus on core competencies.
Offshoring vs Outsourcing: Main Differences
Offshoring involves relocating business processes or services to a different country, primarily to reduce operational costs and access global talent, while outsourcing refers to delegating specific tasks or functions to third-party providers regardless of their location. Offshoring can be a form of outsourcing if the third-party provider is located abroad, but outsourcing does not necessarily imply crossing borders. Key differences include control over operations, communication challenges, and strategic goals, with offshoring often focusing on cost savings through geographic relocation and outsourcing emphasizing specialized expertise.
Benefits of Offshoring for Businesses
Offshoring enables businesses to significantly reduce labor and operational costs by relocating processes to countries with lower wage standards. It provides access to a global talent pool with specialized skills and expertise, enhancing innovation and productivity. Furthermore, offshoring allows companies to operate around the clock by leveraging different time zones, improving efficiency and accelerating project timelines.
Advantages of Outsourcing Services
Outsourcing services offer significant cost savings by leveraging specialized expertise and reducing overhead expenses. It enhances operational efficiency through access to advanced technologies and skilled professionals without the need for long-term investments. Businesses also benefit from increased flexibility, allowing them to scale resources up or down based on demand and focus on core competencies.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Offshoring involves relocating business processes to a different country, which can introduce risks such as cultural differences, communication barriers, and compliance with foreign regulations. Outsourcing, the practice of contracting third-party vendors for specific services, may lead to challenges including loss of control over quality, data security concerns, and dependency on external providers. Both strategies require careful management to mitigate risks like intellectual property theft, hidden costs, and potential negative impacts on customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing
Evaluating cost efficiency, quality control, and cultural alignment is crucial when choosing between offshoring and outsourcing. Businesses must assess the impact on communication, legal regulations, and data security in the destination country or external vendor. Analyzing time zone differences and scalability options further determines the suitability of each strategy for long-term operational goals.
Industry Use Cases and Examples
Offshoring involves relocating business processes or production to another country, often to capitalize on lower labor costs, as seen in the manufacturing sector where companies like Apple utilize factories in China. Outsourcing contracts specific functions or services to third-party providers, exemplified by IT firms subcontracting software development to specialized companies such as Infosys. In the automotive industry, offshoring assembly plants to Mexico complements outsourcing parts production to vendors across Asia, optimizing both cost and supply chain efficiency.
Conclusion: Which Option is Right for You?
Choosing between offshoring and outsourcing depends on your company's strategic priorities, cost considerations, and control preferences. Offshoring typically offers significant cost savings by relocating operations to low-cost countries, while outsourcing provides flexibility and access to specialized expertise without long-term commitments. Evaluating factors such as operational control, communication ease, and scalability will help determine which approach aligns best with your business goals.
Offshoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com