Redemption rights give property owners the legal ability to reclaim their property after a foreclosure by paying the owed debt within a specific time frame. Understanding these rights protects Your interests and ensures you know the steps to regain ownership. Explore the rest of the article to learn how redemption rights impact your property and what actions you can take.
Table of Comparison
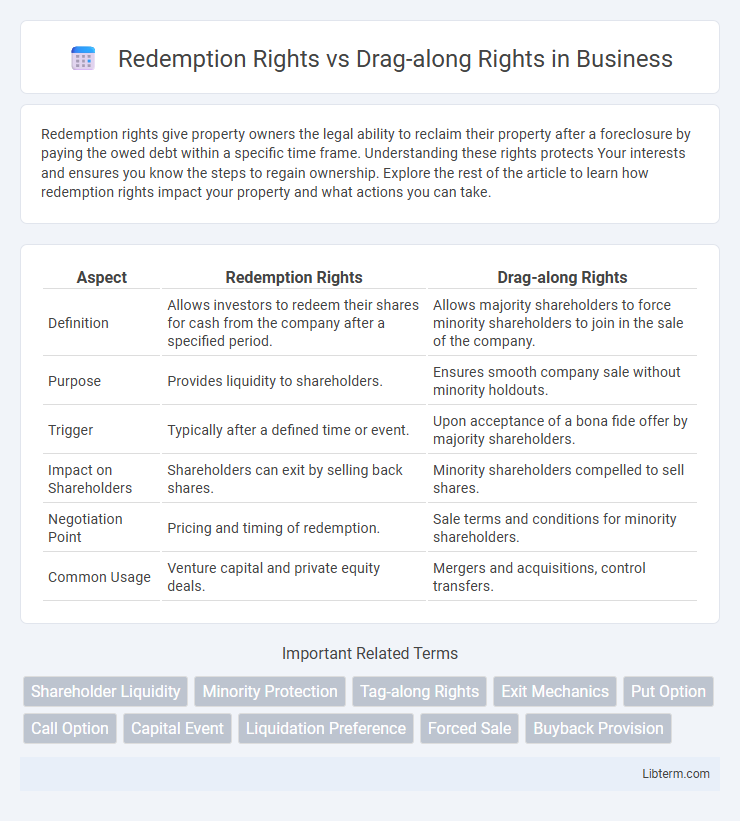
| Aspect | Redemption Rights | Drag-along Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allows investors to redeem their shares for cash from the company after a specified period. | Allows majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in the sale of the company. |
| Purpose | Provides liquidity to shareholders. | Ensures smooth company sale without minority holdouts. |
| Trigger | Typically after a defined time or event. | Upon acceptance of a bona fide offer by majority shareholders. |
| Impact on Shareholders | Shareholders can exit by selling back shares. | Minority shareholders compelled to sell shares. |
| Negotiation Point | Pricing and timing of redemption. | Sale terms and conditions for minority shareholders. |
| Common Usage | Venture capital and private equity deals. | Mergers and acquisitions, control transfers. |
Understanding Redemption Rights
Redemption rights allow investors to require a company to repurchase their shares at a predetermined price, providing a clear exit strategy and capital protection. These rights are commonly negotiated in venture capital agreements to ensure investors can recover their investment if the company underperforms or fails to achieve liquidity events. Understanding redemption rights is crucial for aligning investor interests with company growth and managing financial risk.
Defining Drag-along Rights
Drag-along rights are contractual provisions that allow majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring all shares are sold under the same terms. These rights protect majority investors by enabling them to sell the entire business without minority shareholder blockage, facilitating smoother exit strategies. Unlike redemption rights, which allow shareholders to require the company to buy back their shares, drag-along rights focus on collective transfer during third-party acquisitions.
Key Differences Between Redemption and Drag-along Rights
Redemption rights allow shareholders to require the company to repurchase their shares under specific conditions, often providing a guaranteed exit or liquidity event. Drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of the company, ensuring the sale can proceed without holdouts. Key differences include redemption rights focusing on individual shareholder exit options while drag-along rights prioritize facilitating a collective sale controlled by majority investors.
Legal Framework Governing Both Rights
Redemption rights and drag-along rights are governed by corporate and securities law frameworks that define shareholder protections and obligations during equity transactions. Redemption rights, typically outlined in shareholder agreements or corporate charters, allow investors to require a company to repurchase shares under specific conditions, regulated by statutes like the Delaware General Corporation Law or the UK's Companies Act 2006. Drag-along rights compel minority shareholders to sell their shares alongside majority holders during a sale, enforcing exit strategies within legal boundaries to prevent oppression, and are often embedded in contractual agreements subject to jurisdictional enforcement under contract law.
Advantages of Redemption Rights for Investors
Redemption rights offer investors the advantage of liquidity by allowing them to sell their shares back to the company at a predetermined price, reducing exit risk. These rights provide a safeguard in cases where the company fails to achieve expected performance or liquidity events, ensuring investors can recover their capital. This mechanism enhances investor confidence by offering a structured and predictable means to realize returns.
Benefits of Drag-along Rights for Majority Shareholders
Drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring a smoother and faster transaction process. These rights protect majority shareholders by preventing minority holdouts from blocking or delaying lucrative exit opportunities, maximizing the value realization during M&A activities. By streamlining decision-making and sale execution, drag-along rights improve the marketability and attractiveness of shares for majority holders in venture capital or private equity investments.
Typical Scenarios for Exercising Redemption Rights
Redemption rights are typically exercised in scenarios where investors seek to exit an investment by compelling the company to repurchase their shares after a specified period or trigger event, such as failure to achieve key milestones or an IPO. These rights provide a clear exit strategy for preferred shareholders, especially in private equity or venture capital settings where liquidity options are limited. In contrast, drag-along rights are invoked to force minority shareholders to join a sale initiated by majority shareholders, ensuring a smooth transfer of control without blocking minority dissent.
Situations Triggering Drag-along Rights
Situations triggering drag-along rights often arise when majority shareholders decide to sell their stake to a third party, compelling minority shareholders to join the sale under the same terms. This mechanism protects the majority's ability to execute a full company sale without minority holdouts obstructing the transaction. Redemption rights, in contrast, are typically activated when minority shareholders seek to exit investments, allowing them to require the company or majority shareholders to repurchase their shares.
Negotiating Redemption and Drag-along Clauses in Agreements
Negotiating redemption rights involves defining the conditions under which investors can require the company to repurchase their shares, ensuring liquidity options while balancing financial burden on the business. Drag-along rights negotiation centers on protecting majority shareholders by compelling minority shareholders to join in the sale of the company, streamlining exit strategies and maximizing deal attractiveness. Careful clause drafting must align redemption triggers and drag-along provisions with the company's long-term strategy, investor expectations, and governance structure to avoid conflicts and ensure smooth transactional outcomes.
FAQs on Redemption and Drag-along Rights
Redemption rights allow investors to require a company to repurchase their shares under specified conditions, offering an exit strategy and protection against illiquidity. Drag-along rights empower majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of the company, ensuring unified exit opportunities and preventing holdouts. Frequently asked questions on redemption and drag-along rights address their triggering events, valuation methods for repurchase, and the scope of minority shareholder obligations during a sale.
Redemption Rights Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com