A joint venture combines the strengths of two or more businesses to achieve a specific goal, sharing resources, risks, and rewards. This strategic partnership allows companies to enter new markets, innovate, and expand more efficiently. Discover how a joint venture can transform your business by reading the full article.
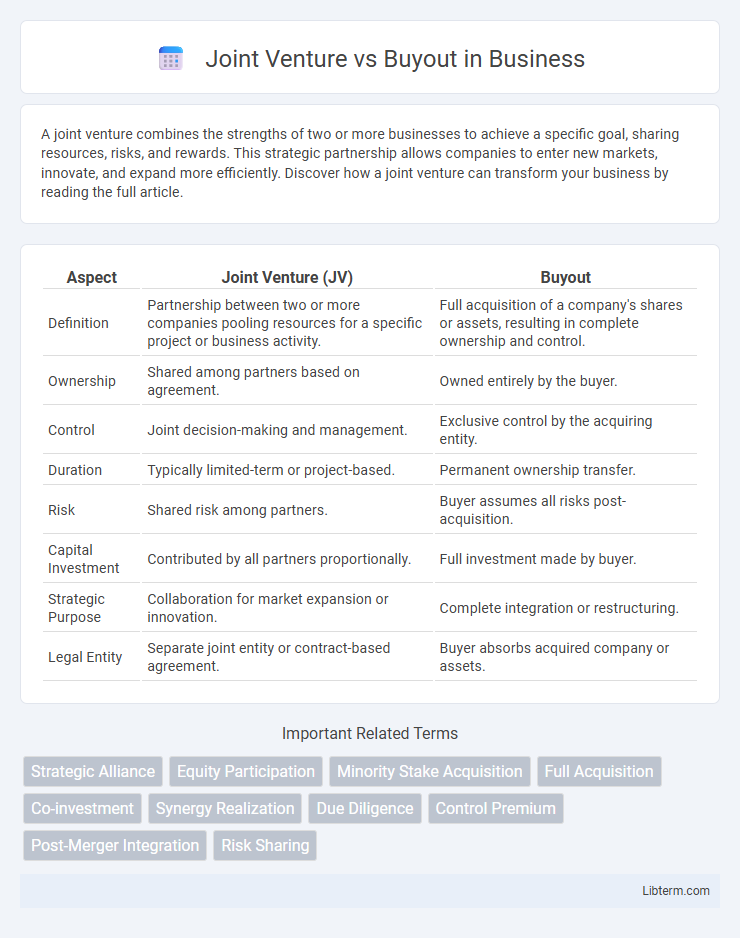
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Joint Venture (JV) | Buyout |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between two or more companies pooling resources for a specific project or business activity. | Full acquisition of a company's shares or assets, resulting in complete ownership and control. |
| Ownership | Shared among partners based on agreement. | Owned entirely by the buyer. |
| Control | Joint decision-making and management. | Exclusive control by the acquiring entity. |
| Duration | Typically limited-term or project-based. | Permanent ownership transfer. |
| Risk | Shared risk among partners. | Buyer assumes all risks post-acquisition. |
| Capital Investment | Contributed by all partners proportionally. | Full investment made by buyer. |
| Strategic Purpose | Collaboration for market expansion or innovation. | Complete integration or restructuring. |
| Legal Entity | Separate joint entity or contract-based agreement. | Buyer absorbs acquired company or assets. |
Understanding Joint Ventures and Buyouts
Joint ventures involve two or more parties pooling resources to achieve a specific business objective while maintaining their separate identities, fostering collaboration and shared risk. Buyouts occur when one entity acquires controlling interest or full ownership of another company, often leading to complete integration and operational control. Understanding the strategic, financial, and legal differences between joint ventures and buyouts is crucial for aligning business goals and optimizing investment outcomes.
Key Differences Between Joint Ventures and Buyouts
Joint ventures involve two or more entities sharing resources, risks, and management to achieve a common business goal, whereas buyouts occur when one company acquires controlling interest in another, obtaining full ownership and decision-making power. Joint ventures typically require collaborative governance and profit-sharing arrangements without transferring complete ownership, while buyouts result in a single entity's control and integration of the acquired business. The duration of joint ventures is often limited and project-specific, contrasting with buyouts that aim for long-term consolidation and strategic expansion.
Strategic Objectives: JV vs Buyout
Joint ventures enable companies to achieve strategic objectives by combining complementary resources and sharing risks while maintaining independent operations. Buyouts provide full control over the acquired company, allowing for unified strategic direction and faster decision-making. Firms pursuing market expansion and innovation often prefer joint ventures, whereas those seeking complete integration and asset consolidation typically opt for buyouts.
Financial Implications and Investment Risks
Joint ventures typically require shared capital contributions, distributing financial risks and potential profits between partners, which can enhance resource pooling but complicate control over financial decisions. Buyouts demand substantial upfront investment or financing, concentrating financial risk on the buyer while granting full control and benefiting solely from future returns. Evaluating cash flow impact, debt obligations, and potential returns is critical in both strategies to align with long-term financial goals and risk tolerance.
Control and Decision-Making Authority
In a joint venture, control and decision-making authority are typically shared between the partnering entities, requiring consensus and collaborative management. In contrast, a buyout grants full control and unilateral decision-making power to the acquiring party, allowing for streamlined strategic direction and operational adjustments. This distinction significantly impacts governance structures, risk exposure, and the agility of business responses.
Legal Structures and Regulatory Considerations
Joint ventures typically involve contractual agreements between two or more entities to collaborate while maintaining separate legal identities, often structured as partnerships or limited liability companies subject to specific regulatory approvals depending on the jurisdiction. Buyouts result in one party acquiring majority or full ownership, leading to consolidated control under corporate or limited liability frameworks, necessitating compliance with merger control laws and antitrust regulations. Understanding the legal structures helps navigate regulatory considerations such as shareholder rights, reporting obligations, and competition law enforcement.
Integration Process and Cultural Alignment
The integration process in a joint venture requires careful coordination between partners to blend operational systems while respecting each entity's corporate culture, which often involves deliberate efforts toward cultural alignment to avoid conflicts. In contrast, a buyout leads to greater control and unilateral decision-making, enabling faster integration but necessitating comprehensive change management to address possible culture clashes from absorbing a new organization. Effective cultural alignment in both scenarios hinges on transparent communication, shared values, and employee engagement to ensure seamless collaboration and sustained business performance.
Taxation Impacts of Joint Ventures and Buyouts
Taxation impacts of joint ventures and buyouts vary significantly, with joint ventures typically involving pass-through taxation where income or losses are allocated directly to partners based on their ownership share, avoiding double taxation. In contrast, buyouts often trigger taxable events such as capital gains taxes for the selling shareholders and potential step-up in asset basis for the acquiring entity, influencing overall tax liabilities. Strategic tax planning is crucial in both scenarios to optimize deductions, manage tax exposure, and comply with relevant IRS regulations on partnership income and corporate acquisitions.
Ideal Scenarios for Choosing JV or Buyout
A Joint Venture is ideal when companies seek to share resources, risks, and expertise for a specific project or market entry without full ownership commitment. A Buyout suits scenarios where a firm aims for complete control, integration, and long-term strategic influence over the target business. JV is preferred for limited collaboration and flexibility, while Buyout is optimal for consolidation and full asset acquisition.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Growth Strategy
Choosing between a joint venture and a buyout depends on a company's strategic goals, financial capacity, and risk tolerance. Joint ventures offer shared resources and market entry flexibility, ideal for companies seeking collaboration without full ownership. Buyouts provide complete control and long-term asset acquisition, suitable for firms aiming for maximum influence and integrated growth.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com