Preferential allotment is a process where a company issues shares to a select group of investors at a predetermined price, often to raise capital quickly or strengthen strategic partnerships. This method bypasses the public offering route and offers existing shareholders a chance to buy shares at a favorable rate, safeguarding their stake. Discover how preferential allotment can impact Your investment strategy and corporate growth by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
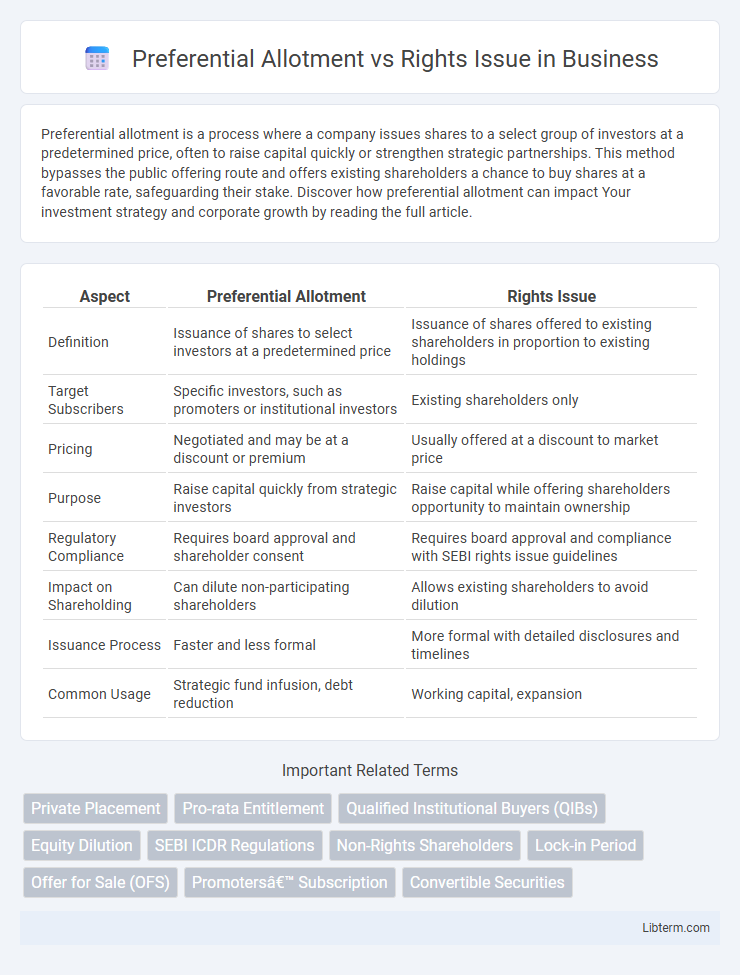
| Aspect | Preferential Allotment | Rights Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Issuance of shares to select investors at a predetermined price | Issuance of shares offered to existing shareholders in proportion to existing holdings |
| Target Subscribers | Specific investors, such as promoters or institutional investors | Existing shareholders only |
| Pricing | Negotiated and may be at a discount or premium | Usually offered at a discount to market price |
| Purpose | Raise capital quickly from strategic investors | Raise capital while offering shareholders opportunity to maintain ownership |
| Regulatory Compliance | Requires board approval and shareholder consent | Requires board approval and compliance with SEBI rights issue guidelines |
| Impact on Shareholding | Can dilute non-participating shareholders | Allows existing shareholders to avoid dilution |
| Issuance Process | Faster and less formal | More formal with detailed disclosures and timelines |
| Common Usage | Strategic fund infusion, debt reduction | Working capital, expansion |
Introduction to Preferential Allotment and Rights Issue
Preferential allotment is a method of capital raising where shares are issued to a select group of investors at a predetermined price, often used by companies to quickly infuse funds without public solicitation. Rights issue allows existing shareholders to purchase additional shares in proportion to their current holdings at a discounted price, aiming to maintain control and provide equal opportunity. Both methods serve distinct strategic purposes in corporate finance, catering to different investor groups and capital requirements.
Definition and Core Concepts
Preferential allotment is a method where companies issue shares to a selected group of investors at a predetermined price, often to raise capital quickly and strategically. Rights issue involves offering existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares at a discounted price in proportion to their current holdings, ensuring equity dilution is minimized. Both methods serve corporate finance goals but differ in investor targeting and share allocation processes.
Key Regulatory Frameworks
Preferential allotment and rights issues are governed by distinct regulatory frameworks under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) guidelines, with preferential allotment regulated primarily by SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2018, and rights issues governed by SEBI (Issue of Capital and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2018, specifically Chapter V. Preferential allotment involves issuing shares to select investors at a determined price without offering to existing shareholders, requiring compliance with pricing formulae and disclosures under Regulation 164, while rights issues mandate offering securities to existing shareholders in proportion to their holdings to protect their pre-emptive rights. Both methods also align with Companies Act, 2013 provisions related to issue of shares, approvals, and disclosures, ensuring transparency and fairness in corporate capital raising activities.
Eligibility and Participation Criteria
In preferential allotment, companies offer shares to a selected group of investors such as promoters, institutional investors, or existing shareholders, based on their eligibility criteria defined by the company and regulatory guidelines. Rights issues require companies to extend the offer to existing shareholders, allowing them to participate in proportion to their current shareholding, ensuring equitable participation rights. Eligibility for preferential allotment is more discretionary, while rights issues mandate participation exclusively by current shareholders within the rights issue subscription period.
Procedures and Issuance Process
Preferential allotment involves issuing shares to a select group of investors, such as promoters or institutional investors, following a board resolution and compliance with SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) guidelines, including pricing determined by a qualified valuer and approval from shareholders through a special resolution. Rights issue requires offering new shares to existing shareholders in proportion to their current holdings, adhering to procedures outlined in the Companies Act, including filing a draft letter of offer with SEBI, dispatching the letter of offer to shareholders, and obtaining regulatory approvals before the shares can be issued. While preferential allotment allows for faster issuance without the need for issuing a letter of offer, rights issues mandate strict disclosure and procedural compliances to protect the rights of the existing shareholders.
Pricing Mechanism and Valuation
Preferential allotment pricing is typically determined through negotiated pricing based on recent market trends or a predefined discount to the current market price, allowing flexibility to attract strategic investors quickly. Rights issue pricing is usually set at a discount to the current market price to encourage existing shareholders to participate, maintaining proportional ownership and minimizing dilution. Valuation in preferential allotments often involves detailed analysis of investor profile and strategic value, whereas rights issues rely more on market-driven valuation reflecting shareholder equity stakes.
Impact on Shareholding and Ownership Structure
Preferential allotment results in the issuance of shares to selected investors at a predetermined price, leading to immediate dilution of existing shareholders' ownership percentage and potential changes in control dynamics. Rights issues offer existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares proportionate to their current holdings, helping maintain their ownership stake if fully subscribed. Both methods impact shareholding patterns, but preferential allotment can introduce new strategic investors, while rights issues primarily preserve existing ownership structure.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Preferential allotment enables companies to raise capital quickly by issuing shares to select investors, offering flexibility and potentially higher pricing, but it may dilute existing shareholders' equity and lead to control dilution. Rights issues provide existing shareholders the opportunity to maintain their proportional ownership by purchasing additional shares at a discount, ensuring fair treatment and minimizing dilution, yet the process can be time-consuming and may not guarantee full subscription. Companies must weigh the speed and strategic benefits of preferential allotment against the shareholder empowerment and lower dilution risk associated with rights issues.
Use Cases and Strategic Considerations
Preferential allotment is used by companies seeking quick capital infusion from selected investors, often to fund expansion or pay off debt without diluting control among existing shareholders. Rights issues are strategically deployed to raise capital from current shareholders, maintaining ownership balance while signaling confidence in the company's future. Choosing between these instruments depends on factors like urgency, shareholder composition, and the desired impact on equity distribution.
Comparative Analysis: Preferential Allotment vs Rights Issue
Preferential allotment involves issuing shares to a select group of investors at a predetermined price, often used for raising capital quickly without offering shares to existing shareholders. Rights issue grants existing shareholders the opportunity to buy additional shares at a discounted price in proportion to their current holdings, protecting their ownership stake and minimizing dilution. While preferential allotment provides flexibility and speed, rights issues emphasize shareholder participation and maintain equitable ownership distribution.
Preferential Allotment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com