Stock options provide employees the opportunity to buy company shares at a predetermined price, aligning their interests with the company's growth and success. These financial instruments can significantly enhance your compensation by offering potential gains when the stock price rises. Explore the rest of this article to understand how stock options work and how they can benefit you.
Table of Comparison
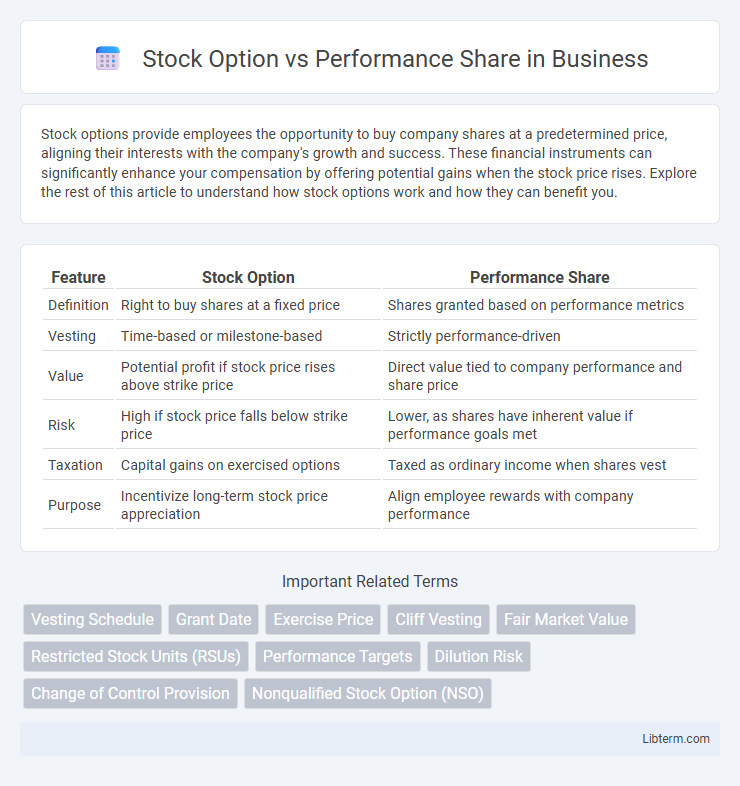
| Feature | Stock Option | Performance Share |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Right to buy shares at a fixed price | Shares granted based on performance metrics |
| Vesting | Time-based or milestone-based | Strictly performance-driven |
| Value | Potential profit if stock price rises above strike price | Direct value tied to company performance and share price |
| Risk | High if stock price falls below strike price | Lower, as shares have inherent value if performance goals met |
| Taxation | Capital gains on exercised options | Taxed as ordinary income when shares vest |
| Purpose | Incentivize long-term stock price appreciation | Align employee rewards with company performance |
Introduction to Stock Options and Performance Shares
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, incentivizing long-term value creation by aligning employee interests with shareholder growth. Performance shares are equity awards that vest based on meeting specific financial or operational goals, directly linking compensation to company performance metrics. Both tools serve as strategic incentives, but stock options reward stock price appreciation while performance shares emphasize achieving measurable corporate objectives.
Key Differences Between Stock Options and Performance Shares
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, typically benefiting from stock price appreciation over time, while performance shares are awarded based on meeting specific company performance targets, usually tied to metrics like earnings per share or total shareholder return. Stock options carry the risk of becoming worthless if the stock price falls below the exercise price, whereas performance shares hold value only if predetermined performance goals are achieved, aligning compensation directly with company success. Vesting schedules differ as stock options usually vest over time, but performance shares vest only after performance criteria are met, emphasizing results-driven rewards.
How Stock Options Work
Stock options grant employees the right to purchase company shares at a predetermined price, known as the exercise or strike price, after a vesting period, allowing potential gains if the market price exceeds this price. Employees benefit from stock options when the company's stock price rises above the strike price, enabling profits through exercising options and selling shares. Unlike performance shares, which are awarded based on meeting specific company goals, stock options depend primarily on stock price appreciation to create value for the employee.
Understanding Performance Shares
Performance shares are equity awards granted to employees based on achieving specific financial or operational goals, aligning employee incentives with company performance metrics like revenue growth or earnings per share. Unlike stock options, which provide the right to buy shares at a predetermined price, performance shares are granted outright if performance criteria are met, offering direct ownership without the need for exercise. These shares encourage long-term commitment by tying rewards to sustained company success and shareholder value creation.
Advantages of Stock Options
Stock options provide employees with the potential to benefit from stock price appreciation, aligning their interests directly with shareholder value creation. They offer leverage, allowing employees to control more shares with less initial investment compared to purchasing actual stock. Tax advantages may apply, as options are often taxed at capital gains rates upon exercise and sale, which can be more favorable than ordinary income tax.
Benefits of Performance Shares
Performance shares provide employees with ownership stakes that directly align with company goals, promoting long-term value creation and retention. Unlike stock options, performance shares carry intrinsic value even if the stock price falls, reducing risk for recipients. These equity awards incentivize sustained performance by linking vesting to measurable corporate milestones, enhancing motivation and shareholder alignment.
Tax Implications for Stock Options vs Performance Shares
Stock options are generally taxed at the time of exercise, where the difference between the grant price and the market price is considered ordinary income, while performance shares are taxed when they vest as ordinary income based on the fair market value of the shares received. With stock options, capital gains tax applies on any subsequent appreciation after exercise, whereas for performance shares, the holding period for capital gains taxation starts after vesting. Tax treatment varies by jurisdiction but commonly includes payroll taxes on the income portion for both stock options and performance shares, impacting overall employee tax liability.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Retention
Stock options create a direct link between employee effort and potential financial gain by allowing employees to purchase shares at a fixed price, fostering motivation through possible equity growth. Performance shares reward employees with stock based on achieving specific company targets, enhancing retention by aligning long-term incentives with corporate success. Both instruments promote engagement, but performance shares typically drive sustained commitment due to their contingent, results-driven nature.
Suitability for Companies: Stock Options vs Performance Shares
Stock options suit companies seeking to incentivize employees with potential future equity gains tied directly to stock price appreciation, aligning personal gains with market performance. Performance shares are more suitable for firms emphasizing achievement of specific financial or operational targets, rewarding employees only upon meeting predefined goals. Organizations aiming for precise goal alignment and shareholder value creation often prefer performance shares, while those prioritizing long-term market value growth lean towards stock options.
Choosing the Right Equity Compensation Plan
Choosing the right equity compensation plan depends on aligning company goals with employee incentives; stock options provide potential upside by granting the right to buy shares at a fixed price, motivating employees to increase stock value over time. Performance shares tie rewards directly to meeting specific financial or operational targets, fostering accountability and ensuring compensation reflects company performance. Evaluating factors like company growth stage, risk tolerance, and shareholder expectations helps determine whether stock options or performance shares better drive long-term value.
Stock Option Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com