Organic growth focuses on expanding your business through internal resources, emphasizing customer retention, product development, and market penetration. This sustainable approach helps create long-term value by enhancing brand loyalty and improving operational efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to discover proven strategies for driving organic growth in your company.
Table of Comparison
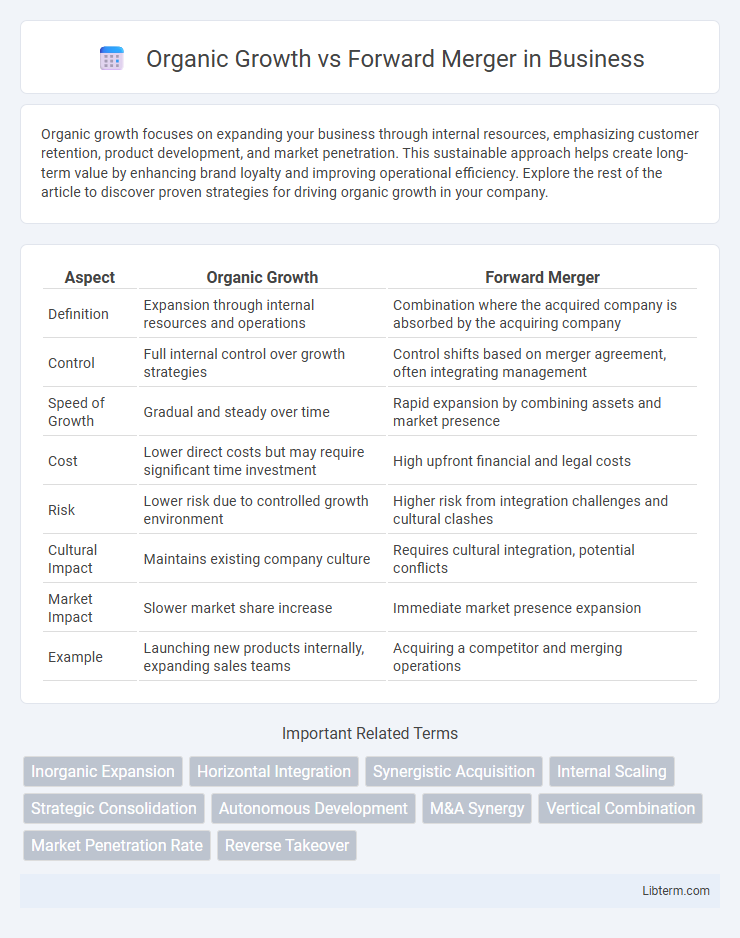
| Aspect | Organic Growth | Forward Merger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expansion through internal resources and operations | Combination where the acquired company is absorbed by the acquiring company |
| Control | Full internal control over growth strategies | Control shifts based on merger agreement, often integrating management |
| Speed of Growth | Gradual and steady over time | Rapid expansion by combining assets and market presence |
| Cost | Lower direct costs but may require significant time investment | High upfront financial and legal costs |
| Risk | Lower risk due to controlled growth environment | Higher risk from integration challenges and cultural clashes |
| Cultural Impact | Maintains existing company culture | Requires cultural integration, potential conflicts |
| Market Impact | Slower market share increase | Immediate market presence expansion |
| Example | Launching new products internally, expanding sales teams | Acquiring a competitor and merging operations |
Understanding Organic Growth: Definition and Key Drivers
Organic growth refers to the expansion of a company's revenue and operations through internal efforts such as increasing sales, enhancing product offerings, and improving customer retention without relying on mergers or acquisitions. Key drivers of organic growth include innovation in product development, effective marketing strategies, expansion into new markets, and operational efficiencies that boost profitability. Companies prioritize organic growth to build sustainable value and maintain control over their business evolution.
What is a Forward Merger? Structures and Examples
A forward merger is a corporate restructuring where the acquiring company absorbs the target company, resulting in the target ceasing to exist and its assets and liabilities merging into the acquirer. This structure typically involves the target company being fully integrated as a subsidiary or division, enhancing operational efficiency and market reach through consolidation. Well-known examples include Disney's acquisition of Marvel Entertainment, where Marvel was fully integrated under Disney's corporate umbrella, illustrating a classic forward merger aimed at leveraging brand synergy and expanding content offerings.
Core Differences: Organic Growth vs Forward Merger
Organic growth involves expanding a company's operations internally through increased output, customer acquisition, or new product development, emphasizing gradual and sustainable progress. In contrast, a forward merger combines two companies with the acquired firm being absorbed into the acquiring entity, allowing rapid market expansion and resource consolidation. Core differences lie in control retention, risk exposure, and time frame, with organic growth focusing on internal scalability and forward merger prioritizing strategic acquisition-driven growth.
Strategic Advantages of Organic Growth
Organic growth allows companies to build a strong, sustainable foundation by leveraging existing resources and capabilities without the complexities of integration or cultural clashes. This strategy enables greater control over business development, fostering innovation and adaptability through incremental improvements. It also minimizes financial risks and preserves brand identity, enhancing long-term competitive advantage compared to the uncertainties inherent in forward mergers.
Forward Mergers: Key Benefits and Opportunities
Forward mergers offer significant benefits, including accelerated market expansion and immediate access to established customer bases. This strategy enables companies to integrate resources efficiently, reducing time-to-market for new products and services. Forward mergers also present opportunities for enhanced competitive positioning and stronger economies of scale in dynamic industries.
Risks and Challenges in Organic Expansion
Organic growth faces risks such as market saturation, limited speed of expansion, and high internal resource dependency, which can constrain scalability and diversification efforts. Challenges include managing operational inefficiencies, aligning company culture during rapid growth, and navigating unpredictable market conditions that may impact demand. This makes organic expansion less flexible compared to forward mergers, which can rapidly acquire new capabilities and market access.
Potential Pitfalls of Forward Mergers
Forward mergers often face significant challenges such as integration difficulties, cultural clashes, and regulatory hurdles that can impede smooth consolidation. Overestimating synergies and underestimating costs may lead to financial strain and diminished shareholder value. Poor alignment of strategic goals between merging entities frequently results in operational inefficiencies and stalled growth.
Financial Implications: Comparing Growth Methods
Organic growth enhances financial stability by relying on reinvested earnings, leading to gradual revenue increases without incurring significant debt. Forward mergers often result in immediate market expansion and asset acquisition but can introduce higher financial risks through integration costs and potential debt financing. Evaluating these growth methods requires analyzing cash flow impacts, debt levels, and long-term profitability to determine the most financially viable strategy.
Choosing the Right Growth Strategy: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right growth strategy depends on factors such as market conditions, resource availability, and long-term business goals. Organic growth offers greater control and sustainability by expanding internal capabilities, while forward mergers provide rapid market access and competitive advantage through acquisition. Careful assessment of financial capacity, integration risk, and cultural alignment ensures optimal decision-making between organic growth and forward merger strategies.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Organic Growth and Forward Mergers
Case studies highlight Amazon's organic growth through continuous innovation and customer-centric expansion, exemplifying how reinvested profits can fuel scalable success. In contrast, Facebook's acquisition of Instagram showcases a forward merger strategy that rapidly augmented market share and diversified revenue streams. Both approaches provide valuable insights into leveraging internal development and strategic mergers to achieve competitive advantage and sustained growth.
Organic Growth Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com