Third-party technology integrates external solutions into your existing systems, enhancing functionality and streamlining processes without extensive in-house development. Leveraging these technologies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enable faster innovation. Discover how adopting third-party technology can transform your operations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
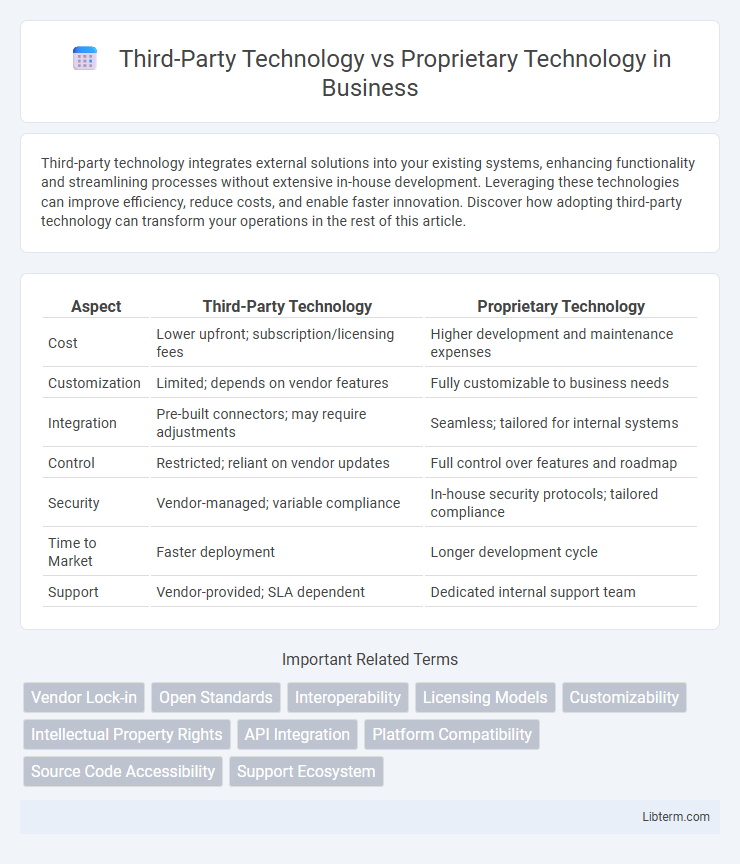
| Aspect | Third-Party Technology | Proprietary Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower upfront; subscription/licensing fees | Higher development and maintenance expenses |
| Customization | Limited; depends on vendor features | Fully customizable to business needs |
| Integration | Pre-built connectors; may require adjustments | Seamless; tailored for internal systems |
| Control | Restricted; reliant on vendor updates | Full control over features and roadmap |
| Security | Vendor-managed; variable compliance | In-house security protocols; tailored compliance |
| Time to Market | Faster deployment | Longer development cycle |
| Support | Vendor-provided; SLA dependent | Dedicated internal support team |
Introduction to Third-Party and Proprietary Technology
Third-party technology refers to software or hardware developed by external providers, enabling businesses to integrate specialized solutions without in-house development. Proprietary technology is created and owned exclusively by a company, providing unique features and competitive advantages that are not available to others. Understanding these technologies helps organizations decide between customizable external products and exclusive internal innovations.
Defining Third-Party Technology
Third-party technology refers to software, hardware, or services developed and maintained by external companies or organizations rather than the primary business using them. This technology enables businesses to integrate specialized solutions without the need for in-house development, often enhancing scalability and reducing costs. Common examples include cloud services from providers like Amazon Web Services and software plugins developed by independent vendors.
Understanding Proprietary Technology
Proprietary technology refers to systems, software, or hardware developed and controlled exclusively by a single organization, often protected by patents, copyrights, or trade secrets to maintain competitive advantage. Understanding proprietary technology involves recognizing its custom-built nature tailored to specific business needs, ensuring unique functionality and tighter integration with existing processes. Companies leveraging proprietary technology benefit from enhanced security, exclusive features, and direct vendor support, but may face higher costs and potential vendor lock-in compared to third-party solutions.
Key Differences Between Third-Party and Proprietary Systems
Third-party technology refers to software or hardware developed by external vendors, offering broad compatibility, cost-effectiveness, and ease of integration compared to proprietary technology exclusively created and controlled by a single company, ensuring tailored customization and enhanced security. Third-party systems often provide greater flexibility and innovation through widespread adoption and community support, whereas proprietary systems guarantee better performance optimization and dedicated technical support within a closed ecosystem. Understanding these key differences helps businesses decide between adaptable, scalable solutions and specialized, tightly controlled platforms based on their operational priorities and resource availability.
Advantages of Third-Party Technology
Third-party technology offers significant cost savings by eliminating the need for in-house development and maintenance, allowing businesses to allocate resources more efficiently. Access to cutting-edge innovations and regular updates from specialized vendors ensures enhanced performance, security, and compliance with industry standards. Integration flexibility and broad compatibility with multiple platforms accelerate deployment and improve scalability across diverse operational environments.
Benefits of Proprietary Technology
Proprietary technology offers tailored solutions that provide a competitive edge through unique features and functionalities exclusive to a business. It allows greater control over software updates, security protocols, and customization, ensuring alignment with specific operational needs. Investing in proprietary technology can enhance intellectual property value and reduce dependency on external vendors.
Potential Risks and Limitations
Third-party technology presents risks such as limited control over updates, potential security vulnerabilities, and dependency on external vendors for support and maintenance. Proprietary technology can lead to vendor lock-in, limited interoperability, and higher costs due to exclusive licensing and customization requirements. Both options require thorough risk assessment to balance innovation benefits against operational limitations and long-term sustainability.
Industry Use Cases and Applications
Third-party technology offers scalable solutions widely adopted in industries like retail and finance for rapid integration and cost efficiency, while proprietary technology provides tailored systems optimized for unique operational needs in sectors such as aerospace and pharmaceuticals. Companies in manufacturing utilize third-party software for supply chain management due to interoperability, whereas proprietary platforms deliver enhanced security and customization critical for defense and healthcare applications. The choice between third-party and proprietary technology is driven by factors including industry regulations, innovation demands, and the strategic importance of intellectual property.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Technology Solution
Choosing between third-party technology and proprietary technology requires evaluating factors such as cost, customization, integration capabilities, and support availability. Third-party solutions often offer quicker deployment and lower initial investment, while proprietary technology enables tailored features and exclusive control over system updates. Assessing long-term scalability, vendor reliability, and security compliance ensures alignment with organizational goals and risk management policies.
Future Trends in Technology Adoption
Future trends indicate a growing reliance on third-party technology due to its scalability, cost efficiency, and rapid integration capabilities. Proprietary technology will maintain its relevance in sectors demanding high security and customized solutions, particularly in defense and healthcare industries. Hybrid approaches combining third-party platforms with proprietary enhancements are expected to dominate, optimizing innovation while safeguarding intellectual property.
Third-Party Technology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com