Market extension mergers occur when two companies operating in different geographic markets combine to expand their customer base and increase market reach. This type of merger helps businesses access new regions and capitalize on untapped opportunities without developing entirely new products. Discover how market extension mergers can strategically enhance your company's growth potential in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
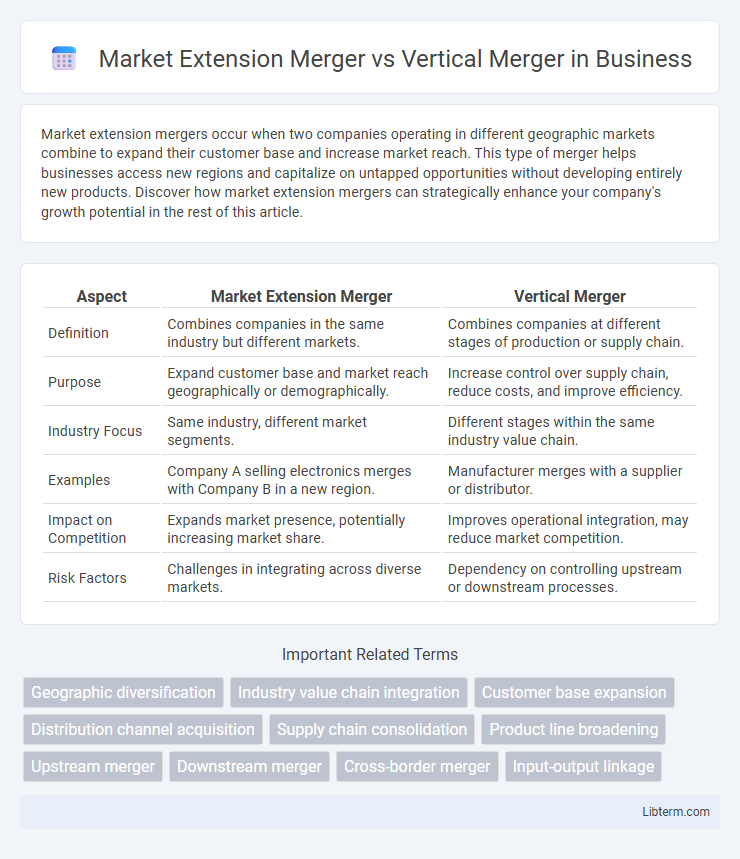
| Aspect | Market Extension Merger | Vertical Merger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines companies in the same industry but different markets. | Combines companies at different stages of production or supply chain. |
| Purpose | Expand customer base and market reach geographically or demographically. | Increase control over supply chain, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. |
| Industry Focus | Same industry, different market segments. | Different stages within the same industry value chain. |
| Examples | Company A selling electronics merges with Company B in a new region. | Manufacturer merges with a supplier or distributor. |
| Impact on Competition | Expands market presence, potentially increasing market share. | Improves operational integration, may reduce market competition. |
| Risk Factors | Challenges in integrating across diverse markets. | Dependency on controlling upstream or downstream processes. |
Introduction to Market Extension Merger and Vertical Merger
Market extension mergers occur when companies operating in different markets merge to expand their geographic reach and customer base, enhancing market penetration and distribution channels. Vertical mergers involve firms at different stages of the supply chain combining to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve control over production and distribution processes. Both merger types strategically aim to strengthen competitive positioning but focus on distinct aspects of business integration and market expansion.
Defining Market Extension Mergers
Market extension mergers occur when two companies operating in different geographic markets with the same product combine to expand their market reach and customer base. This strategic move contrasts with vertical mergers, which involve companies at different stages of the supply chain integrating to enhance efficiency and control. Market extension mergers drive growth by increasing market penetration and leveraging existing product lines across new regions.
Understanding Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers involve the consolidation of companies operating at different stages within the same supply chain, such as a manufacturer merging with a supplier or distributor. This type of merger aims to enhance operational efficiency, reduce production costs, and improve supply chain coordination by integrating upstream and downstream processes. Understanding vertical mergers is crucial for evaluating their impact on market competition, potential barriers to entry, and overall industry control.
Key Differences Between Market Extension and Vertical Mergers
Market extension mergers occur between companies operating in the same industry but in different markets, aiming to increase market reach and customer base, while vertical mergers happen between firms at different stages of the supply chain to improve operational efficiency and control. Market extension mergers primarily focus on geographic expansion and access to new segments, whereas vertical mergers emphasize enhancing production processes, reducing costs, and securing supply chains. The key difference lies in their strategic objectives: market extension mergers drive market diversification, while vertical mergers target integration and coordination along the value chain.
Benefits of Market Extension Mergers
Market extension mergers enable companies to expand their customer base by entering new geographic markets, increasing overall market reach and sales potential. They facilitate economies of scale through combined distribution channels, reducing costs and enhancing competitiveness. By leveraging established brand recognition across different regions, market extension mergers drive faster growth and improved market penetration compared to vertical mergers.
Advantages of Vertical Mergers
Vertical mergers enhance supply chain efficiency by integrating different production stages, reducing costs and improving coordination. They increase control over raw materials and distribution channels, leading to greater market stability and reduced dependency on suppliers. These mergers also foster innovation through closer collaboration between manufacturing and distribution units, driving competitive advantage.
Challenges and Risks in Both Merger Types
Market extension mergers face challenges in integrating diverse customer bases and overcoming brand loyalty issues, risking customer attrition and market misalignment. Vertical mergers encounter risks related to supply chain integration, potential regulatory scrutiny for antitrust concerns, and difficulties in synchronizing operational processes across different production stages. Both merger types must manage cultural clashes and system incompatibilities, which can lead to operational disruptions and reduced synergy realization.
Strategic Considerations for Businesses
Market extension mergers enable businesses to expand their geographic reach and access new customer segments, enhancing market share and revenue streams. Vertical mergers focus on integrating supply chain components, improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and increasing control over production processes. Strategic considerations include assessing market overlap, potential synergies, regulatory challenges, and long-term growth objectives for both merger types.
Real-World Examples of Market Extension vs Vertical Mergers
Market extension mergers occur when companies operating in different geographical markets combine, such as the 2016 merger of France's Orange and Spain's Jazztel, which expanded Orange's market reach in Spain. Vertical mergers involve companies at different stages of the supply chain, exemplified by Amazon's acquisition of Whole Foods in 2017, integrating retail and distribution to control more of the value chain. These mergers illustrate strategic growth either by expanding market presence or enhancing supply chain efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Merger Strategy
Selecting the appropriate merger strategy depends on company goals and market positioning, with market extension mergers expanding geographical reach and customer base, while vertical mergers streamline supply chains and improve operational efficiency. Market extension mergers optimize revenue growth through access to new markets, whereas vertical mergers enhance control over production and reduce costs, supporting competitive advantage. Careful evaluation of strategic objectives and industry dynamics is essential for maximizing synergy and long-term value creation.
Market Extension Merger Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com