Acquisition is a vital strategy for business growth, involving the purchase of one company by another to enhance market share, diversify offerings, or gain competitive advantage. Effective acquisition requires thorough due diligence, strategic planning, and integration efforts to maximize returns and minimize risks. Discover how you can leverage acquisition to transform your company's future in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
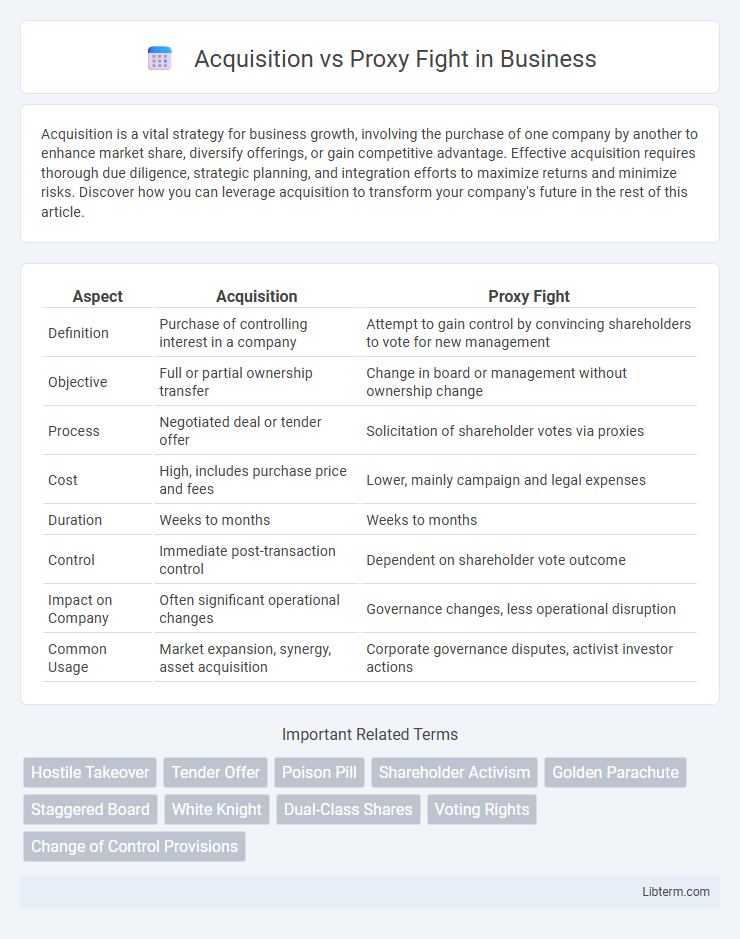
| Aspect | Acquisition | Proxy Fight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purchase of controlling interest in a company | Attempt to gain control by convincing shareholders to vote for new management |
| Objective | Full or partial ownership transfer | Change in board or management without ownership change |
| Process | Negotiated deal or tender offer | Solicitation of shareholder votes via proxies |
| Cost | High, includes purchase price and fees | Lower, mainly campaign and legal expenses |
| Duration | Weeks to months | Weeks to months |
| Control | Immediate post-transaction control | Dependent on shareholder vote outcome |
| Impact on Company | Often significant operational changes | Governance changes, less operational disruption |
| Common Usage | Market expansion, synergy, asset acquisition | Corporate governance disputes, activist investor actions |
Understanding Acquisitions in Corporate Strategy
Acquisitions involve one company purchasing another to achieve rapid growth, market expansion, or access to new technologies, often leading to full ownership and integration. This strategic move enhances competitive advantage by consolidating resources and streamlining operations. Understanding acquisitions in corporate strategy requires analyzing financial performance, cultural fit, and synergy potential to ensure long-term value creation.
What is a Proxy Fight?
A proxy fight occurs when a group of shareholders attempts to gain control of a company by persuading other shareholders to vote in favor of their proposed board members during a shareholder meeting. Unlike an acquisition, where a company buys another firm's shares or assets outright, a proxy fight is a battle for influence through voting rights without immediate ownership transfer. Proxy fights often arise during contested mergers, management disputes, or efforts to change corporate strategy.
Key Differences Between Acquisition and Proxy Fight
An acquisition involves one company purchasing another to gain control, typically through negotiation and agreement, while a proxy fight occurs when shareholders attempt to influence or replace management by soliciting proxy votes. Acquisitions usually result in a straightforward change of ownership, whereas proxy fights maintain the company's independence but shift board control or strategic direction. Key differences include the method of control transfer, the role of shareholder approval, and the typical outcomes regarding ownership and governance.
Motivations Behind Acquisitions
Acquisitions are often motivated by the desire to achieve strategic growth, increase market share, or gain access to new technologies and customer bases. Companies pursue acquisitions to enhance competitive advantage, achieve economies of scale, and diversify product portfolios. In contrast, proxy fights typically arise from shareholder dissatisfaction and attempts to influence corporate governance rather than direct operational expansion.
Triggers for Proxy Fights
Proxy fights are typically triggered when shareholders or activist investors are dissatisfied with a company's management or strategic direction, seeking to change the board of directors without outright acquiring the company. Common catalysts include poor financial performance, governance issues, or controversial corporate decisions that erode shareholder value. In contrast, acquisitions involve a direct purchase or merger, with proxy fights serving as an alternative method to influence or gain control without a full takeover.
Shareholder Roles in Acquisitions vs Proxy Battles
Shareholders play distinct roles in acquisitions and proxy fights, with acquisitions typically involving shareholder approval to accept or reject a buyout offer based on valuation assessments. In proxy fights, shareholders actively engage by voting on contested board member nominations or corporate policies, often influenced by competing factions seeking control. The level of shareholder activism and strategic communication differs, as acquisitions prioritize financial terms while proxy battles emphasize governance and strategic direction.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Acquisition involves a thorough due diligence process to ensure compliance with antitrust laws and securities regulations, while proxy fights require adherence to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, particularly the proxy solicitation rules under SEC Rule 14a-9. Legal considerations in acquisitions often include filing requirements with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the Department of Justice (DOJ) under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Act, whereas proxy fights focus on shareholder communication and disclosures to prevent misinformation and manipulation. Both strategies demand meticulous regulatory compliance to avoid penalties, with acquisitions emphasizing transaction approvals and proxy fights highlighting shareholder voting rights and proxy disclosures.
Financial Implications: Acquisition vs Proxy Fight
Acquisitions typically require a significant upfront financial investment, including purchase premiums and transaction fees, impacting cash flow and potentially increasing debt levels. Proxy fights, while generally less costly upfront, can lead to extensive legal and campaigning expenses and may result in stock price volatility affecting shareholder value. Both strategies influence capital structure and investor perception, but acquisitions often involve more direct financial commitments compared to the strategic maneuvering costs of proxy battles.
Case Studies: Notable Acquisitions and Proxy Fights
The acquisition of WhatsApp by Facebook in 2014 exemplifies a strategic purchase aimed at expanding market reach and technology integration. The 2008 proxy fight at Yahoo, led by activist shareholder Carl Icahn, highlighted shareholder activism challenging management decisions and prompting corporate governance reforms. These cases emphasize distinct corporate control tactics--acquisitions involve outright ownership transfer while proxy fights focus on changing board composition to influence corporate policy.
Strategic Outcomes and Long-Term Impacts
Acquisition typically leads to a more controlled integration process, enabling companies to align strategic goals and achieve synergies such as expanded market share or enhanced capabilities. Proxy fights often result in significant management changes and can disrupt organizational stability, influencing shareholder value through altered corporate governance. Long-term impacts of acquisitions usually involve sustained growth and cohesion, whereas proxy fights may trigger ongoing volatility and uncertainty in company direction.
Acquisition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com