A well-drafted contract clearly outlines the rights and obligations of all parties involved, minimizing the risk of disputes and ensuring legal protection. Understanding key elements such as terms, conditions, and breach consequences empowers you to negotiate favorable agreements confidently. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to create effective contracts and safeguard your interests.
Table of Comparison
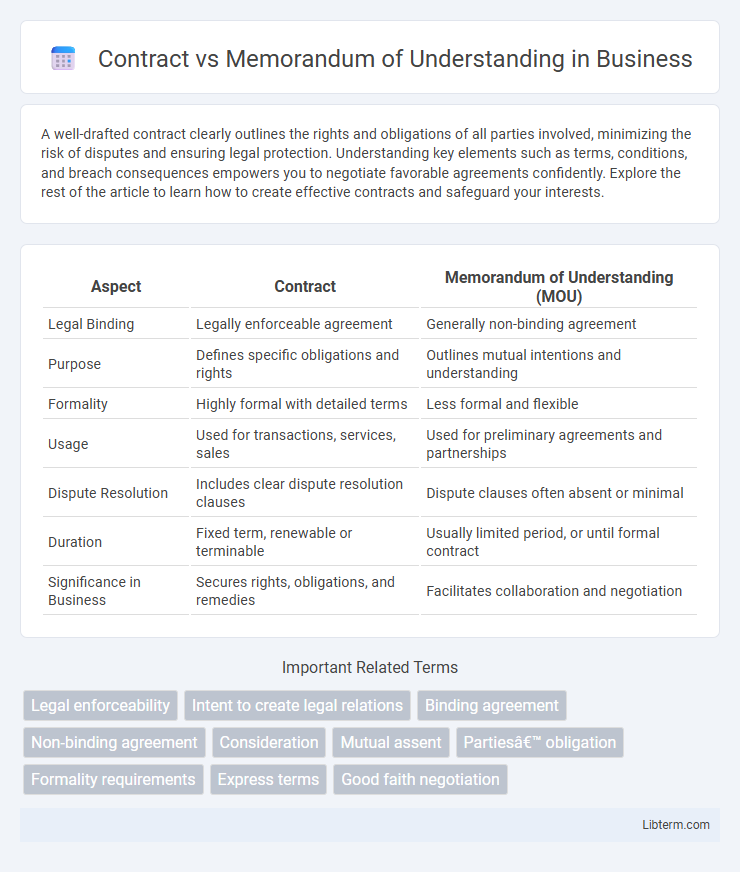
| Aspect | Contract | Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Binding | Legally enforceable agreement | Generally non-binding agreement |
| Purpose | Defines specific obligations and rights | Outlines mutual intentions and understanding |
| Formality | Highly formal with detailed terms | Less formal and flexible |
| Usage | Used for transactions, services, sales | Used for preliminary agreements and partnerships |
| Dispute Resolution | Includes clear dispute resolution clauses | Dispute clauses often absent or minimal |
| Duration | Fixed term, renewable or terminable | Usually limited period, or until formal contract |
| Significance in Business | Secures rights, obligations, and remedies | Facilitates collaboration and negotiation |
Introduction to Contracts and Memorandums of Understanding
Contracts are legally binding agreements between parties that outline specific obligations, rights, and remedies enforceable by law, typically requiring offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual intent. Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) serve as formal but generally non-binding statements of intent, establishing a framework for cooperation or negotiation without creating enforceable legal commitments. Both documents play crucial roles in defining relationships and expectations, but contracts carry legal consequences while MOUs prioritize clarity and mutual understanding.
Definition of a Contract
A contract is a legally binding agreement between two or more parties that outlines specific rights and obligations enforceable by law. It requires an offer, acceptance, consideration, mutual consent, and lawful purpose to create valid legal enforceability. Unlike a Memorandum of Understanding, which is often non-binding, a contract provides clear remedies and consequences in case of breach.
Definition of a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU)
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is a formal but non-binding agreement between parties outlining their mutual intentions and responsibilities without creating legally enforceable obligations. Unlike contracts, MOUs serve as a preliminary framework to clarify the terms of cooperation and expectations before finalizing a definitive contract. MOUs typically detail the scope, purpose, and roles of involved parties while emphasizing collaboration and good faith rather than legal commitment.
Key Legal Differences Between Contracts and MOUs
Contracts create legally binding obligations with enforceable terms, whereas Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) typically outline mutual intentions without legal enforceability. Contracts require offer, acceptance, consideration, and clear terms, while MOUs may lack these elements and serve as preliminary agreements or frameworks. Courts generally enforce contracts based on their elements, but MOUs are often viewed as expressions of goodwill or negotiation records without obligatory commitments.
Enforceability: Contract vs Memorandum of Understanding
Contracts are legally binding agreements enforceable by law, requiring clear offer, acceptance, and consideration to establish obligations between parties. Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) generally lack enforceability as they outline intentions or preliminary agreements without creating formal legal obligations. Courts typically prioritize contracts for dispute resolution, while MOUs serve as non-binding frameworks guiding future negotiations.
Essential Elements of a Binding Contract
A binding contract requires offer, acceptance, mutual consent, consideration, capacity, and legality to be legally enforceable. Each party must voluntarily agree to the terms, providing something of value in exchange while possessing the legal ability to contract. In contrast, a Memorandum of Understanding outlines general intentions without necessarily fulfilling these essential legal elements, thus lacking enforceable obligations.
Typical Uses of Contracts
Contracts are typically used in business transactions, employment agreements, and service provisions where legally binding obligations and enforceable terms are essential. They establish clear roles, responsibilities, payment terms, and penalties for breach, ensuring legal protection for all parties involved. Contracts also govern the sale of goods, leases, and confidentiality agreements, providing a structured framework for complex or high-stakes arrangements.
Common Applications of MOUs
Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) are frequently used in business partnerships, government agreements, and academic collaborations to outline mutual intentions without creating legally binding obligations. They serve as preliminary frameworks in joint ventures, research projects, and inter-organizational alliances, facilitating clear communication and shared objectives. Unlike contracts, MOUs emphasize cooperation and understanding rather than enforceable commitments, making them ideal for exploratory or non-binding agreements.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Contract vs MOU
Contracts provide legally binding agreements that enforce obligations and offer clear remedies in case of breach, ensuring security and predictability in business relationships. Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) allow flexible, non-binding agreements that facilitate collaboration and outline mutual intentions without legal repercussions, making them ideal for preliminary arrangements. While contracts can limit flexibility due to strict terms, MOUs may lack enforceability, potentially leading to misunderstandings or disputes.
Choosing Between a Contract and a Memorandum of Understanding
Choosing between a contract and a memorandum of understanding (MOU) depends on the level of legal enforceability and formality required in the agreement. Contracts are legally binding documents that outline specific obligations and remedies, suitable for transactions requiring strict accountability and legal protection. MOUs serve as preliminary agreements to establish mutual understanding and intentions without creating enforceable rights, ideal for collaborative projects or negotiations in their early stages.
Contract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com