Direct ownership provides you with full control over assets, allowing for transparent decision-making and straightforward management. This form of ownership eliminates intermediaries, ensuring that all benefits and liabilities directly impact the owner. Explore the rest of the article to understand the advantages and considerations of direct ownership in various contexts.
Table of Comparison
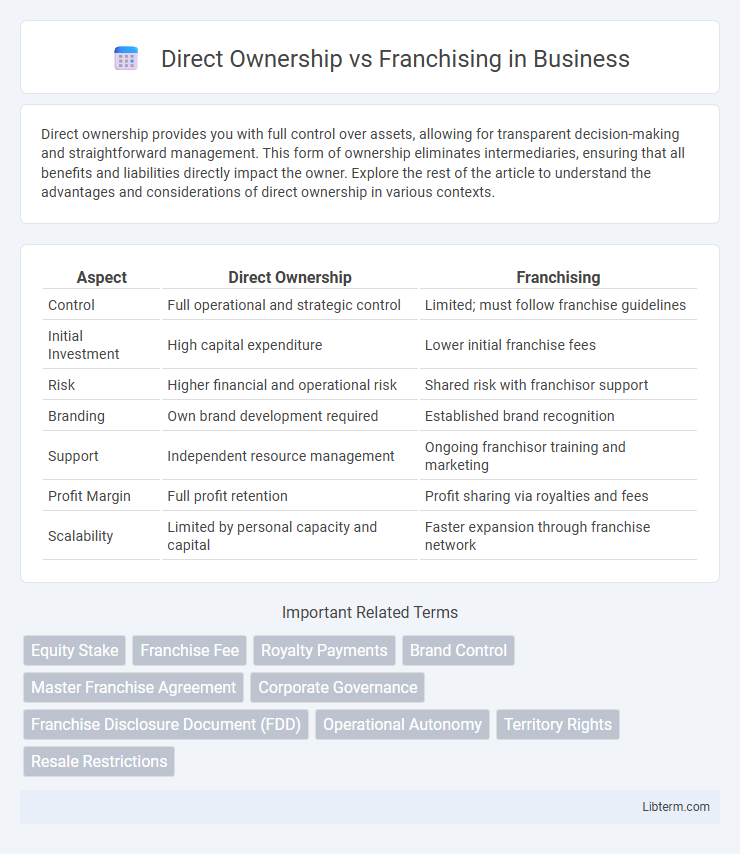
| Aspect | Direct Ownership | Franchising |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full operational and strategic control | Limited; must follow franchise guidelines |
| Initial Investment | High capital expenditure | Lower initial franchise fees |
| Risk | Higher financial and operational risk | Shared risk with franchisor support |
| Branding | Own brand development required | Established brand recognition |
| Support | Independent resource management | Ongoing franchisor training and marketing |
| Profit Margin | Full profit retention | Profit sharing via royalties and fees |
| Scalability | Limited by personal capacity and capital | Faster expansion through franchise network |
Introduction to Ownership Models
Direct ownership involves a business controlling all operational aspects and assets, enabling complete authority over brand management and customer experience. Franchising allows expansion by licensing brand rights to independent operators, providing a scalable model with reduced capital investment and shared risk. Understanding these models is essential for strategic decisions in market entry, growth, and resource allocation.
What is Direct Ownership?
Direct ownership refers to a business model where a company maintains full control and operational responsibility over its locations or assets, without involving third-party franchisees. This approach enables direct oversight of branding, customer experience, and financial management, ensuring consistency across all outlets. Companies like Starbucks often use direct ownership to preserve quality standards and rapid adaptability in decision-making.
What is Franchising?
Franchising is a business model where a franchisor grants a franchisee the rights to operate a business using the franchisor's brand, products, and operational support in exchange for fees or royalties. This system enables rapid expansion with lower capital investment by leveraging the franchisee's local market knowledge and resources. Franchisees benefit from established brand recognition, proven business models, and ongoing training while maintaining independent ownership.
Key Differences Between Direct Ownership and Franchising
Direct ownership involves full control and responsibility over business operations, assets, and profits, allowing for complete decision-making authority. Franchising grants the right to operate under an established brand name, requiring adherence to franchisor guidelines while benefiting from brand recognition and support. The key difference lies in control levels, investment risk, and operational autonomy, with direct ownership demanding higher capital and full accountability, contrasted by franchising's shared risk and standardized procedures.
Advantages of Direct Ownership
Direct ownership offers complete control over business operations, branding, and strategic decisions, enabling faster adaptation to market changes and consistent quality standards. It allows for higher profit retention without franchise fees or royalty payments, maximizing revenue potential for the owner. Furthermore, direct ownership facilitates stronger customer relationships and deeper understanding of local market dynamics, contributing to sustainable business growth.
Advantages of Franchising
Franchising offers rapid market expansion with reduced capital investment, leveraging the franchisee's local knowledge and motivation to drive business growth. It minimizes operational risks for the franchisor by transferring daily management responsibilities to the franchisee, ensuring consistent brand presence with shared financial risk. Franchise agreements facilitate standardized processes and brand consistency while enabling faster penetration into diverse markets.
Challenges of Direct Ownership
Direct ownership poses significant challenges, including substantial upfront capital investment and the responsibility of managing all operational aspects such as staffing, supply chain, and compliance. Owners face increased risk exposure due to sole liability for business performance and potential market fluctuations. Maintaining consistent brand standards and customer experience across multiple locations also demands extensive management expertise and resources.
Challenges of Franchising
Franchising presents challenges such as maintaining consistent brand standards across diverse franchise locations and ensuring effective communication between franchisor and franchisees. Franchisees often face restrictions on operational decisions, limiting flexibility and innovation. Conflict resolution and compliance monitoring require significant resources to avoid legal disputes and protect the franchise reputation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Model
When deciding between direct ownership and franchising, key factors include control, financial resources, and risk tolerance. Direct ownership offers full operational control and higher profit margins but requires significant capital and management expertise. Franchising involves lower upfront investment and shared brand recognition, with potential limitations on autonomy and revenue sharing obligations.
Which Model is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between direct ownership and franchising depends on your business goals, available capital, and desire for control. Direct ownership offers full control and profit retention but requires significant investment and operational involvement. Franchising allows faster expansion with lower capital but involves sharing profits and less day-to-day control.
Direct Ownership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com