Cross-selling boosts your sales by recommending complementary products or services that enhance the customer's original purchase. This strategy increases average order value and strengthens customer loyalty by meeting broader needs. Explore the article to discover effective cross-selling techniques that can elevate your business revenue.
Table of Comparison
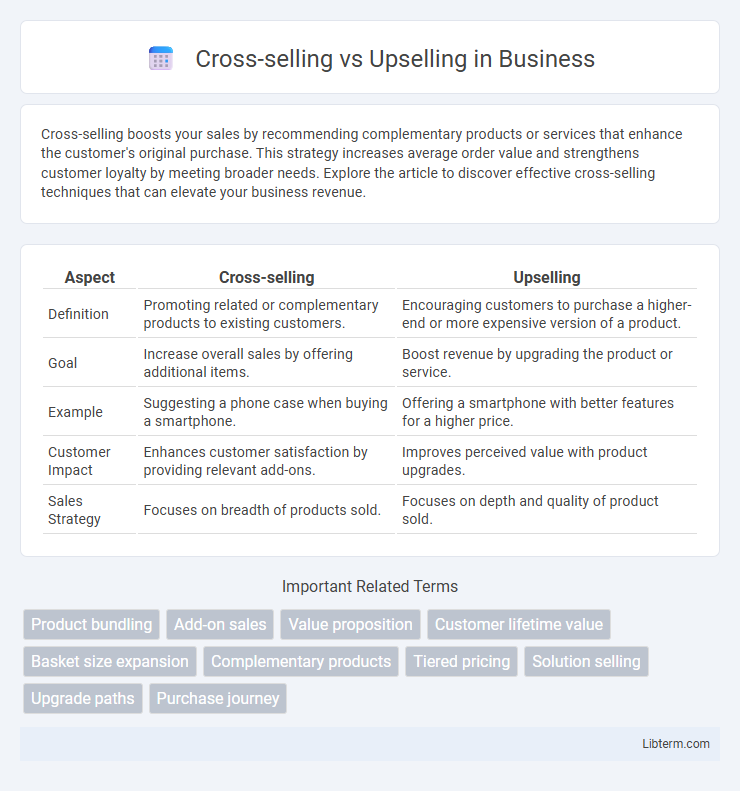
| Aspect | Cross-selling | Upselling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Promoting related or complementary products to existing customers. | Encouraging customers to purchase a higher-end or more expensive version of a product. |
| Goal | Increase overall sales by offering additional items. | Boost revenue by upgrading the product or service. |
| Example | Suggesting a phone case when buying a smartphone. | Offering a smartphone with better features for a higher price. |
| Customer Impact | Enhances customer satisfaction by providing relevant add-ons. | Improves perceived value with product upgrades. |
| Sales Strategy | Focuses on breadth of products sold. | Focuses on depth and quality of product sold. |
Introduction to Cross-selling and Upselling
Cross-selling involves suggesting complementary products or services to enhance the initial purchase, increasing overall transaction value and customer satisfaction. Upselling encourages customers to buy a higher-end version or upgrade of the chosen item, boosting revenue and improving the buyer's experience. Both strategies rely on understanding customer needs and purchasing behavior to maximize sales opportunities effectively.
Defining Cross-selling: What You Need to Know
Cross-selling involves offering customers complementary products or services related to their initial purchase to enhance their overall experience and increase transaction value. It leverages customer data and purchase history to recommend relevant add-ons, such as accessories for electronics or side dishes in restaurants. Effective cross-selling improves customer satisfaction and boosts revenue by fulfilling broader customer needs within a single buying journey.
Upselling Explained: An Overview
Upselling involves encouraging customers to purchase a higher-end product or add features that increase the value and price of their original selection, boosting revenue per transaction. Effective upselling strategies leverage customer insights and product benefits to highlight enhanced functionality or premium quality, often resulting in greater customer satisfaction and loyalty. Implementing upselling techniques in e-commerce or retail settings significantly boosts average order value and maximizes profit margins without acquiring new customers.
Key Differences Between Cross-selling and Upselling
Cross-selling involves offering complementary products or services to enhance the customer's original purchase, while upselling encourages customers to buy a more expensive version or upgrade of the same product. Cross-selling targets broadening the scope of the transaction with related items, typically increasing overall order value by adding new categories. Upselling focuses on product enhancement and premium features, driving higher revenue per item by persuading buyers to select superior options.
Benefits of Cross-selling Strategies
Cross-selling strategies enhance customer value by promoting complementary products that meet specific needs, increasing average order value and boosting overall revenue. Effective cross-selling leverages personalized recommendations, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty by offering relevant solutions rather than just additional items. Businesses implementing cross-selling benefit from stronger customer relationships and higher lifetime value, creating sustainable growth opportunities.
Advantages of Effective Upselling
Effective upselling increases average transaction value by encouraging customers to purchase higher-end products or premium features, boosting revenue without acquiring new customers. It enhances customer satisfaction by offering tailored solutions that better meet individual needs and deliver greater value. Upselling also helps build long-term loyalty by positioning the brand as a trusted advisor focused on optimal customer outcomes.
Use Cases: When to Cross-sell vs Upsell
Cross-selling is ideal when customers show interest in complementary products, such as offering a laptop sleeve with a laptop purchase to enhance utility. Upselling works best when customers are ready to upgrade, like suggesting a higher-end smartphone model with better features for a slightly higher price. Businesses increase revenue by strategically applying cross-selling during initial purchases and upselling when customers seek premium options.
Best Practices for Cross-selling and Upselling
Effective cross-selling involves recommending complementary products that enhance the customer's primary purchase, improving both customer satisfaction and average order value. Upselling works best when highlighting premium product features or upgrades that align closely with the customer's needs and preferences, boosting revenue without seeming pushy. Leveraging data analytics to personalize offers and timing recommendations during the checkout process are proven best practices for maximizing cross-selling and upselling success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Cross-selling and upselling strategies often fail due to recommending irrelevant products or services that do not align with the customer's current needs or preferences, leading to frustration and lost sales opportunities. Neglecting to train sales teams on product knowledge and customer behavior results in ineffective communication and missed chances to highlight genuine value additions. Overloading customers with too many options or aggressive pitches can cause decision paralysis and damage long-term customer relationships.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Cross-selling and Upselling
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for cross-selling include the attach rate, which measures the average number of additional products or services sold alongside the primary purchase. Upselling success is often tracked through average order value (AOV) and conversion rate, reflecting how effectively higher-priced items or upgrades are sold. Customer lifetime value (CLV) gauges the long-term impact of both strategies by assessing overall revenue generated from customers over time.
Cross-selling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com