Performance shares are a form of equity compensation awarded to employees based on the achievement of specific financial or operational goals set by the company. These shares align employee incentives with shareholder interests, driving motivation and long-term company growth. Discover how performance shares can impact your compensation strategy and financial future by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
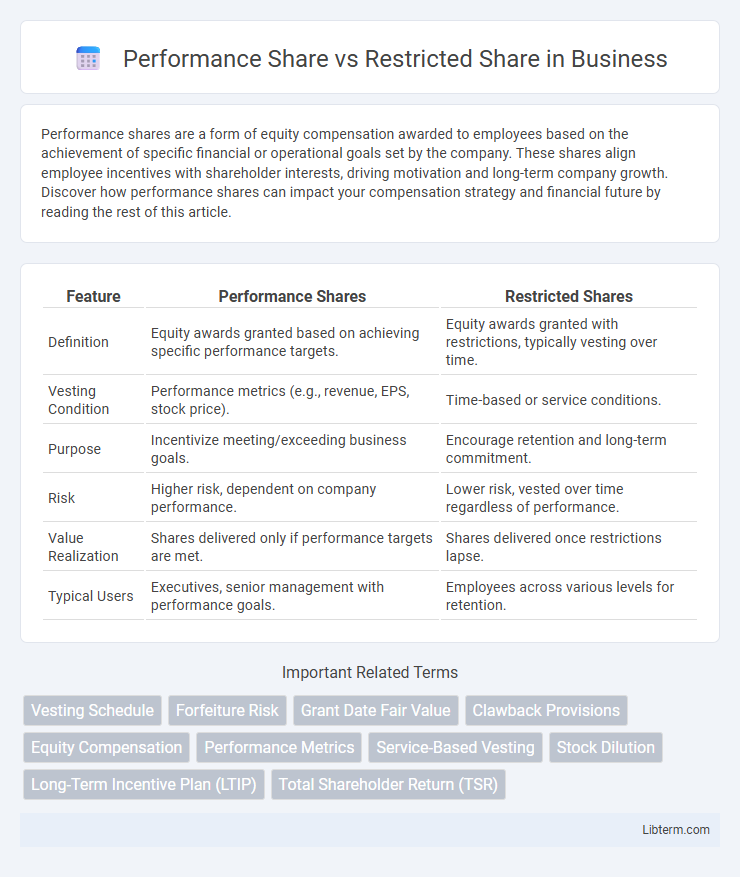
| Feature | Performance Shares | Restricted Shares |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Equity awards granted based on achieving specific performance targets. | Equity awards granted with restrictions, typically vesting over time. |
| Vesting Condition | Performance metrics (e.g., revenue, EPS, stock price). | Time-based or service conditions. |
| Purpose | Incentivize meeting/exceeding business goals. | Encourage retention and long-term commitment. |
| Risk | Higher risk, dependent on company performance. | Lower risk, vested over time regardless of performance. |
| Value Realization | Shares delivered only if performance targets are met. | Shares delivered once restrictions lapse. |
| Typical Users | Executives, senior management with performance goals. | Employees across various levels for retention. |
Overview of Performance Shares and Restricted Shares
Performance shares are equity awards granted based on achieving specific financial or operational goals, offering potential upside only if predetermined performance metrics are met within a set timeframe. Restricted shares provide employees with actual ownership of company stock upfront, subject to vesting schedules and restrictions on transferability, regardless of performance outcomes. Both serve as retention tools but differ in risk, reward structure, and alignment with shareholder value creation.
Key Differences Between Performance Shares and Restricted Shares
Performance shares are equity awards granted based on achieving specific performance targets, typically tied to company financial metrics like earnings per share or total shareholder return, whereas restricted shares are granted outright but subject to vesting conditions such as continued employment over a set period. Performance shares provide greater alignment with shareholder interests by rewarding only upon performance achievement, while restricted shares offer guaranteed equity retention if the vesting terms are met, offering more predictable value to recipients. The distinct difference lies in the risk and reward profile: performance shares carry performance risk with potential for higher upside, whereas restricted shares carry less risk but often have fewer upside incentives.
How Performance Shares Work
Performance shares are equity awards granted to employees that vest only when specific company performance targets, such as revenue growth, earnings per share, or total shareholder return, are achieved within a set timeframe. The number of shares earned depends on the level of goal attainment, aligning employee incentives with company success and shareholder value. Unlike restricted shares, performance shares do not grant immediate ownership but require meeting predefined metrics to realize value.
How Restricted Shares Work
Restricted shares are company stocks granted to employees with specific limitations on transferability and sale until certain conditions, such as vesting periods or performance goals, are met. These shares often require the employee to remain with the company for a predetermined time before full ownership is granted, aligning employee interests with company performance. Upon vesting, restrictions lift, allowing employees to sell or transfer the stock, which typically retains value regardless of short-term company performance.
Eligibility Criteria for Performance and Restricted Shares
Eligibility criteria for performance shares typically require specific company financial targets or individual performance metrics tied to role or seniority. Restricted shares are often granted based on employment status, length of service, or position within the organization, with fewer performance conditions attached. Both share types may demand continued employment during the vesting period, but performance shares emphasize measurable results for qualification.
Vesting Schedules: Performance Shares vs Restricted Shares
Performance shares vest based on achieving specified company financial or operational goals over a multi-year performance period, aligning employee incentives with long-term business success. Restricted shares typically vest based on continued employment over a fixed time frame, such as graded vesting over three to five years, regardless of company performance. Performance share vesting schedules often include cliffs or periodic assessments, whereas restricted shares use time-based vesting without performance contingencies.
Tax Implications of Performance and Restricted Shares
Performance shares are typically taxed as ordinary income upon vesting based on the fair market value, with potential capital gains tax applied if shares are held post-vesting. Restricted shares are also taxed as ordinary income at vesting unless the employee makes an 83(b) election, which shifts tax liability to the grant date, potentially resulting in lower overall taxes if the shares appreciate. Both equity types require careful tax planning to optimize timing of income recognition and capital gains treatment.
Advantages of Performance Shares
Performance shares offer advantages by directly aligning employee rewards with measurable company milestones, fostering motivation to achieve specific financial or operational goals. These shares typically vest only when predefined performance criteria are met, ensuring that value creation and shareholder interests are prioritized. This results in enhanced accountability and incentivizes sustained company growth compared to restricted shares that vest solely based on tenure.
Advantages of Restricted Shares
Restricted shares grant employees immediate ownership with voting rights and dividends, fostering a stronger sense of company loyalty. They reduce the risk of dilution compared to stock options and typically have clearer tax implications. This form of equity incentive aligns employee interests with long-term company performance through vesting schedules that encourage retention.
Choosing the Right Equity Incentive: Performance vs Restricted Shares
Performance shares offer equity incentives tied to specific financial or operational targets, aligning employee rewards with company performance metrics like earnings per share or revenue growth. Restricted shares provide immediate ownership with vesting schedules but lack performance conditions, making them simpler and reducing risk for employees. Choosing between performance and restricted shares depends on the company's strategic goals, desired employee motivation, and risk tolerance, with performance shares driving outcomes while restricted shares incentivize retention.
Performance Share Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com