An open market purchase occurs when a company buys its own shares from the stock market to reduce the number of outstanding shares and increase shareholder value. This strategic move can impact stock prices and earnings per share, making it a critical decision for investors to monitor. Explore the rest of the article to understand how open market purchases can affect your investment portfolio.
Table of Comparison
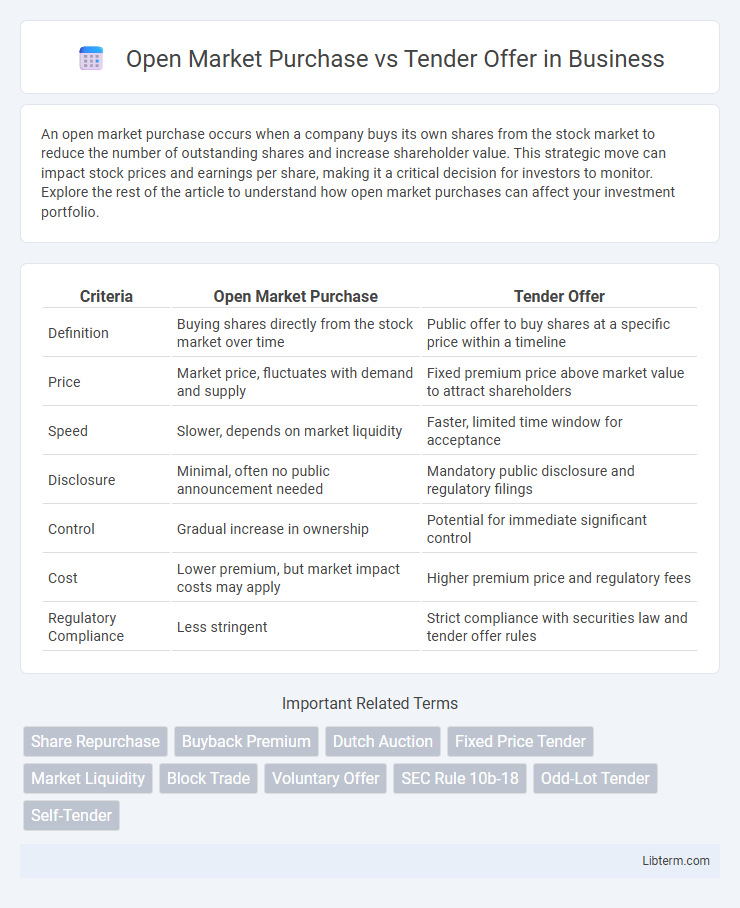
| Criteria | Open Market Purchase | Tender Offer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying shares directly from the stock market over time | Public offer to buy shares at a specific price within a timeline |
| Price | Market price, fluctuates with demand and supply | Fixed premium price above market value to attract shareholders |
| Speed | Slower, depends on market liquidity | Faster, limited time window for acceptance |
| Disclosure | Minimal, often no public announcement needed | Mandatory public disclosure and regulatory filings |
| Control | Gradual increase in ownership | Potential for immediate significant control |
| Cost | Lower premium, but market impact costs may apply | Higher premium price and regulatory fees |
| Regulatory Compliance | Less stringent | Strict compliance with securities law and tender offer rules |
Introduction to Share Repurchase Methods
Share repurchase methods primarily include open market purchases and tender offers, each serving as strategic tools for companies to return capital to shareholders. Open market purchases involve buying shares directly from the stock exchange over time, allowing flexibility and gradual impact on stock price. Tender offers present a fixed price to shareholders for a limited period, often at a premium, facilitating a faster reduction in outstanding shares and signaling strong management confidence.
What is an Open Market Purchase?
An Open Market Purchase is a method by which a company buys back its own shares directly from the stock market at prevailing market prices. This approach offers flexibility, allowing the company to acquire shares gradually over time without setting a fixed price or maximum number of shares. Compared to a Tender Offer, Open Market Purchases provide more discretion and less immediate impact on the stock price, as transactions occur within normal trading activities.
What is a Tender Offer?
A tender offer is a public, open bid by an investor or company to purchase a significant number of shares directly from shareholders at a specified price, often above the market value. This method allows the bidder to quickly acquire control or a substantial stake in the target company, bypassing the open market. Unlike open market purchases, tender offers are typically time-limited and subject to regulatory disclosures to ensure fairness and transparency.
Key Differences Between Open Market Purchase and Tender Offer
Open Market Purchase involves buying shares directly on the stock exchange at market prices, allowing companies to repurchase stock incrementally and with market-driven flexibility. Tender Offer is a formal proposal to shareholders to buy a specified number of shares at a premium price, often used to acquire a controlling interest or complete buybacks quickly. Key differences include method of transaction, pricing control--market price versus fixed premium--and speed and scale of share repurchase.
Advantages of Open Market Purchases
Open market purchases offer flexibility and gradual acquisition of shares, allowing companies to buy stock at prevailing market prices without signaling large-scale buybacks. This method minimizes market disruption and helps maintain stock price stability compared to tender offers, which are often large, one-time transactions. Open market purchases provide management discretion for timing and volume, enabling strategic repurchases aligned with cash flow and market conditions.
Advantages of Tender Offers
Tender offers provide a strategic advantage by enabling acquirers to quickly secure a substantial portion of shares directly from shareholders at a premium price, often leading to faster control acquisition compared to open market purchases. They offer transparency and a defined timeframe, which can limit market speculation and reduce price volatility during the transaction. This method also allows for targeting specific shareholder groups, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the acquisition process.
Disadvantages of Open Market Purchases
Open market purchases can lead to market price fluctuations, causing unpredictability in the cost of acquiring shares. These transactions often require more time to accumulate significant stakes, potentially reducing their effectiveness in quickly influencing ownership or control. Unlike tender offers, open market purchases may signal less commitment to shareholders, possibly impacting investor confidence negatively.
Disadvantages of Tender Offers
Tender offers often involve higher costs due to premiums paid above the market price, increasing the financial burden on the acquiring firm. The process can trigger regulatory scrutiny and shareholder lawsuits, complicating and delaying the transaction. Limited time frames for shareholders to decide may result in lower participation rates compared to open market purchases.
Factors Influencing Company’s Repurchase Method Choice
Companies choose between open market purchases and tender offers based on factors such as repurchase scale, timing flexibility, and market impact. Open market purchases allow gradual buying at prevailing prices, minimizing immediate market disruption, while tender offers provide a faster and larger-scale repurchase at a specific price, often at a premium. Regulatory constraints, available cash reserves, and the desire to signal confidence to investors also critically influence the preferred repurchase strategy.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Buyback Strategy
Choosing the right buyback strategy depends on a company's specific financial goals and market conditions. Open market purchases offer flexibility and gradual share repurchase, suitable for companies aiming for steady market support without significant price impact. Tender offers provide a faster, more controlled buyback method, ideal for firms seeking to repurchase a large percentage of shares quickly at a premium price.
Open Market Purchase Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com