Outsourcing allows businesses to delegate non-core tasks to external experts, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. It enables companies to focus on their primary objectives while leveraging specialized skills and resources. Explore the full article to discover how outsourcing can transform your business strategy.
Table of Comparison
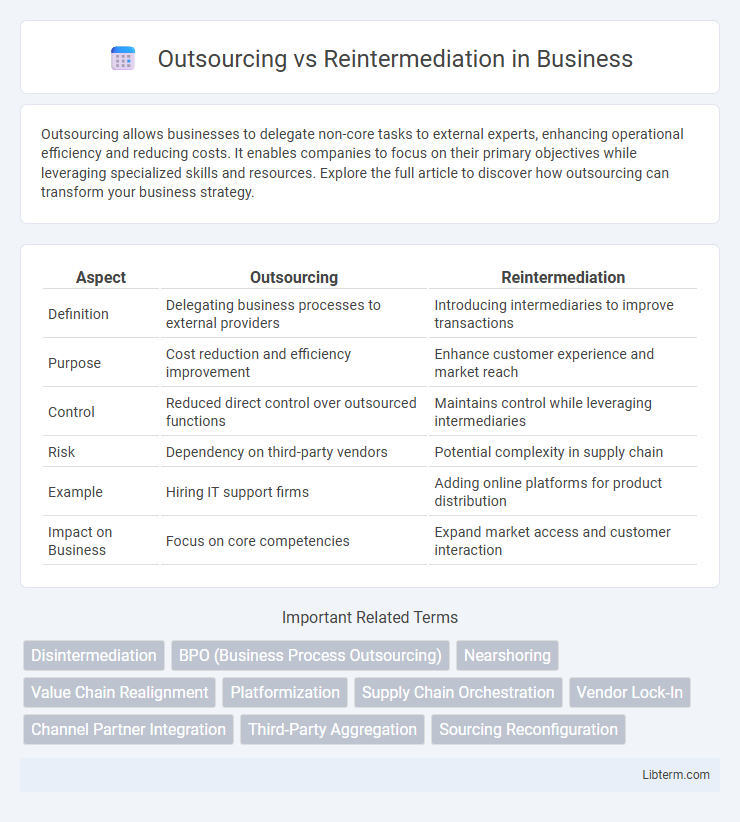
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Reintermediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delegating business processes to external providers | Introducing intermediaries to improve transactions |
| Purpose | Cost reduction and efficiency improvement | Enhance customer experience and market reach |
| Control | Reduced direct control over outsourced functions | Maintains control while leveraging intermediaries |
| Risk | Dependency on third-party vendors | Potential complexity in supply chain |
| Example | Hiring IT support firms | Adding online platforms for product distribution |
| Impact on Business | Focus on core competencies | Expand market access and customer interaction |
Understanding Outsourcing: Definition and Key Concepts
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or services to external providers to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Key concepts include contract management, service level agreements (SLAs), and vendor selection, which ensure quality and accountability. This strategic approach enables companies to focus on core competencies while leveraging specialized expertise from third-party vendors.
What is Reintermediation? Modern Business Perspectives
Reintermediation refers to the process of reintroducing intermediaries into a supply chain or business transaction where direct interactions had previously replaced them, often driven by advancements in digital technology and shifting market demands. In modern business perspectives, reintermediation leverages new digital platforms, data analytics, and personalized services to add value, improve customer experience, and enable more efficient distribution channels. This strategic approach contrasts with outsourcing by emphasizing the creation or restoration of value-adding roles rather than merely delegating tasks to external providers.
The Evolution from Disintermediation to Reintermediation
The evolution from disintermediation to reintermediation reflects a transformative shift in supply chain and business models where initial efforts to eliminate intermediaries gave way to reintroducing value-added intermediaries. Outsourcing capitalizes on external specialists for cost-efficiency and expertise, while reintermediation integrates new digital intermediaries that enhance connectivity, transparency, and customer experience. This dynamic showcases how businesses leverage strategic partnerships and technology platforms, balancing direct control with specialized external facilitation to optimize operational and market outcomes.
Core Benefits of Outsourcing for Organizations
Outsourcing enables organizations to focus on their core competencies by delegating non-core functions to specialized providers, leading to enhanced efficiency and cost savings. It provides access to advanced technologies and expert resources without significant upfront investments, facilitating scalability and innovation. This strategic allocation of tasks helps improve service quality, drive operational flexibility, and optimize resource management.
Reintermediation: Advantages and Strategic Applications
Reintermediation restores and enhances the role of intermediaries in supply chains, enabling firms to optimize customer engagement and streamline distribution channels. The strategic application of reintermediation leverages digital platforms and data analytics to create personalized customer experiences, improve market reach, and increase operational efficiency. Advantages include greater control over brand identity, improved customer insights, and the ability to adapt swiftly to market changes, positioning companies competitively in dynamic environments.
Comparing Costs: Outsourcing vs Reintermediation
Outsourcing often reduces operational costs by leveraging external providers' economies of scale, minimizing labor and infrastructure expenses. Reintermediation may increase costs due to adding new intermediaries, which can introduce additional fees and complexity to supply chains. Analyzing total cost of ownership reveals outsourcing typically offers greater cost-efficiency, while reintermediation enhances control and customization at higher expenditures.
Risk Factors and Challenges for Both Approaches
Outsourcing involves delegating business processes to external vendors, posing risks such as loss of control, data security breaches, and dependency on third-party providers, which can lead to service disruptions. Reintermediation, which reintroduces intermediaries into direct digital transactions, faces challenges like increased operational complexity, potential delays in communication, and risk of reduced customer satisfaction due to additional layers. Both approaches must address compliance with regulatory standards and manage the trade-offs between cost savings and quality control to mitigate financial and reputational risks.
Impact on Supply Chain Management
Outsourcing in supply chain management enhances efficiency by delegating non-core activities to specialized third-party providers, reducing operational costs and improving focus on strategic functions. Reintermediation introduces new intermediaries or digital platforms, increasing transparency, real-time data exchange, and collaboration across supply chain nodes, thereby optimizing responsiveness and agility. Both strategies reshape supply chain dynamics by balancing cost reduction, control, and connectivity to drive competitive advantage.
Which Model Suits Your Business? Decision Criteria
Choosing between outsourcing and reintermediation depends on factors such as cost-efficiency, control over processes, and expertise requirements. Outsourcing is ideal for businesses seeking to reduce operational costs and leverage specialized skills without expanding internal resources. Reintermediation suits companies aiming to enhance customer engagement and innovate by adding new intermediaries that provide additional value or services.
Future Trends: Outsourcing and Reintermediation in a Digital Economy
Future trends in outsourcing emphasize automation and AI integration to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, while reintermediation leverages advanced digital platforms to create new value chains and improve customer engagement. The digital economy fosters hybrid models combining outsourcing with reintermediation, allowing businesses to optimize operations and innovate service delivery through data-driven insights. Emerging technologies like blockchain and IoT further disrupt traditional outsourcing, enabling transparent, decentralized processes alongside reintermediation strategies that enhance trust and collaboration across ecosystems.
Outsourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com