Cost plus pricing sets product prices by adding a fixed profit margin to the total production cost, ensuring expenses are covered and profits secured. This method simplifies pricing decisions and helps maintain consistent profitability, especially in manufacturing and retail. Explore the rest of the article to understand how cost plus pricing can optimize your business strategy.
Table of Comparison
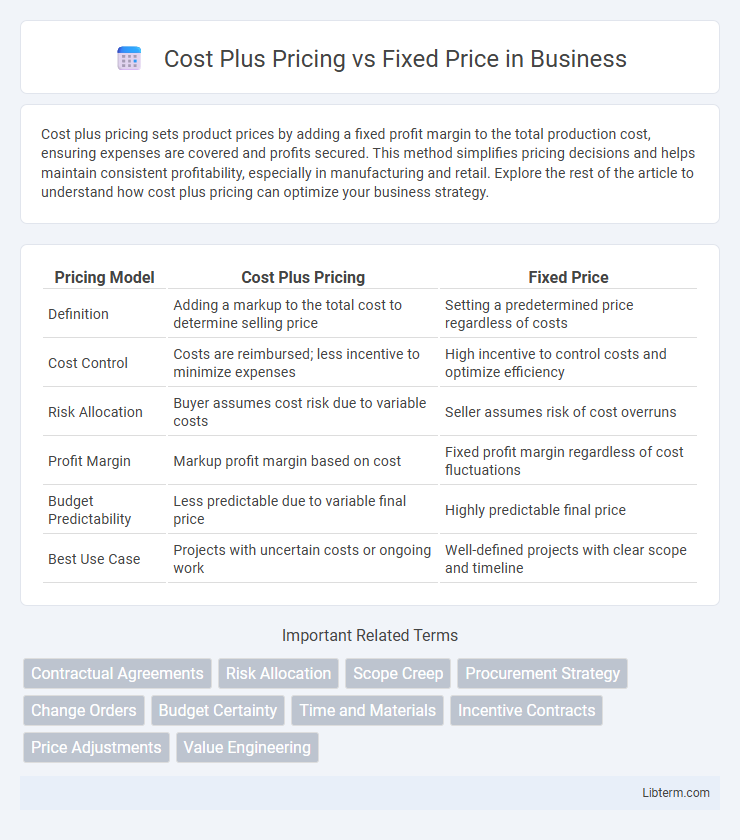
| Pricing Model | Cost Plus Pricing | Fixed Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding a markup to the total cost to determine selling price | Setting a predetermined price regardless of costs |
| Cost Control | Costs are reimbursed; less incentive to minimize expenses | High incentive to control costs and optimize efficiency |
| Risk Allocation | Buyer assumes cost risk due to variable costs | Seller assumes risk of cost overruns |
| Profit Margin | Markup profit margin based on cost | Fixed profit margin regardless of cost fluctuations |
| Budget Predictability | Less predictable due to variable final price | Highly predictable final price |
| Best Use Case | Projects with uncertain costs or ongoing work | Well-defined projects with clear scope and timeline |
Introduction to Cost Plus Pricing and Fixed Price
Cost Plus Pricing calculates the total production cost and adds a specific profit margin, ensuring all expenses are covered while generating profit. Fixed Price sets a predetermined amount for a product or service regardless of actual costs, offering budget certainty for clients. Companies often choose between Cost Plus Pricing and Fixed Price based on project scope, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
Key Differences Between Cost Plus and Fixed Price Models
Cost Plus Pricing charges the buyer for actual project costs plus a fixed profit margin, offering flexibility in scope changes and cost variations. Fixed Price contracts set a predetermined total cost for the entire project, providing budget certainty but less adaptability to unforeseen expenses. The key difference lies in risk allocation, with Cost Plus shifting cost risk to the buyer and Fixed Price placing it on the seller.
How Cost Plus Pricing Works
Cost Plus Pricing calculates the final price by adding a predetermined profit margin to the actual cost of production, ensuring all expenses are covered before profit. This method allows businesses to adjust prices based on fluctuations in material costs, labor, and overhead, providing a flexible pricing model. Cost Plus Pricing is commonly used in industries with variable project costs, such as construction and manufacturing, offering transparency and minimizing financial risk.
How Fixed Price Contracts Operate
Fixed price contracts operate by establishing a predetermined amount for the entire project or service, regardless of actual costs incurred. This pricing model transfers financial risk to the contractor, who must manage costs efficiently to maintain profitability. Clients benefit from budget certainty, as payments remain consistent and predictable throughout the contract duration.
Pros and Cons of Cost Plus Pricing
Cost Plus Pricing offers the advantage of ensuring all production costs are covered, reducing the risk of underpricing and allowing for stable profit margins. However, it can lead to inefficiencies since there is less incentive to control costs, potentially resulting in higher prices for customers. This method lacks competitive pricing dynamics and may cause challenges in markets with price-sensitive consumers.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Price Contracts
Fixed price contracts offer budget certainty and reduce financial risk by establishing a set price for project delivery, making them ideal for well-defined scopes. However, they can limit flexibility, potentially leading to disputes if project requirements change or unforeseen issues arise, as adjustments often require contract renegotiation. Fixed price agreements incentivize efficiency but may result in lower quality or reduced scope if contractors aim to maximize profit within the fixed budget.
Scenarios Best Suited for Cost Plus Pricing
Cost Plus Pricing is best suited for projects with high uncertainty in costs, such as custom manufacturing, research and development, or government contracts where expenses can fluctuate significantly. This pricing model allows businesses to cover actual costs plus a guaranteed profit margin, reducing financial risk. It is ideal when project scope or resource use cannot be precisely estimated upfront, ensuring transparency and flexibility in billing.
When to Choose Fixed Price Over Cost Plus
Fixed price contracts are ideal when project scope and specifications are clearly defined and risks are low, providing budget certainty and simplifying financial management. This pricing model suits clients seeking predictable expenses and contractors confident in their ability to meet requirements without unanticipated costs. Fixed price is often chosen for projects with established timelines and deliverables to minimize disputes and streamline contract administration.
Industry Use Cases: Cost Plus vs Fixed Price
Cost plus pricing is widely used in industries with high uncertainty and variable costs, such as construction and defense contracting, where precise cost tracking ensures profitability despite fluctuating expenses. Fixed price contracts dominate in software development and manufacturing sectors, where the scope and deliverables are clearly defined, allowing businesses to manage budgets and timelines efficiently. Understanding the specific risk tolerance and project complexity in industries helps companies choose between cost plus and fixed price pricing models to optimize financial outcomes.
Final Thoughts: Selecting the Right Pricing Strategy
Choosing between Cost Plus Pricing and Fixed Price strategies depends on project scope clarity and risk tolerance; Cost Plus Pricing suits projects with uncertain costs by ensuring profit margins, while Fixed Price offers budget predictability but requires accurate initial estimates. Businesses with fluctuating material costs benefit from Cost Plus, whereas clients favor Fixed Price for financial certainty. Evaluating project complexity, cost variability, and client preferences ensures alignment with organizational goals and market conditions.
Cost Plus Pricing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com