Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions involve companies selling products or services directly to other businesses rather than individual consumers. This model focuses on building long-term relationships, customized solutions, and often involves larger order volumes with negotiated pricing. Explore the article to uncover key strategies that can enhance Your B2B success.
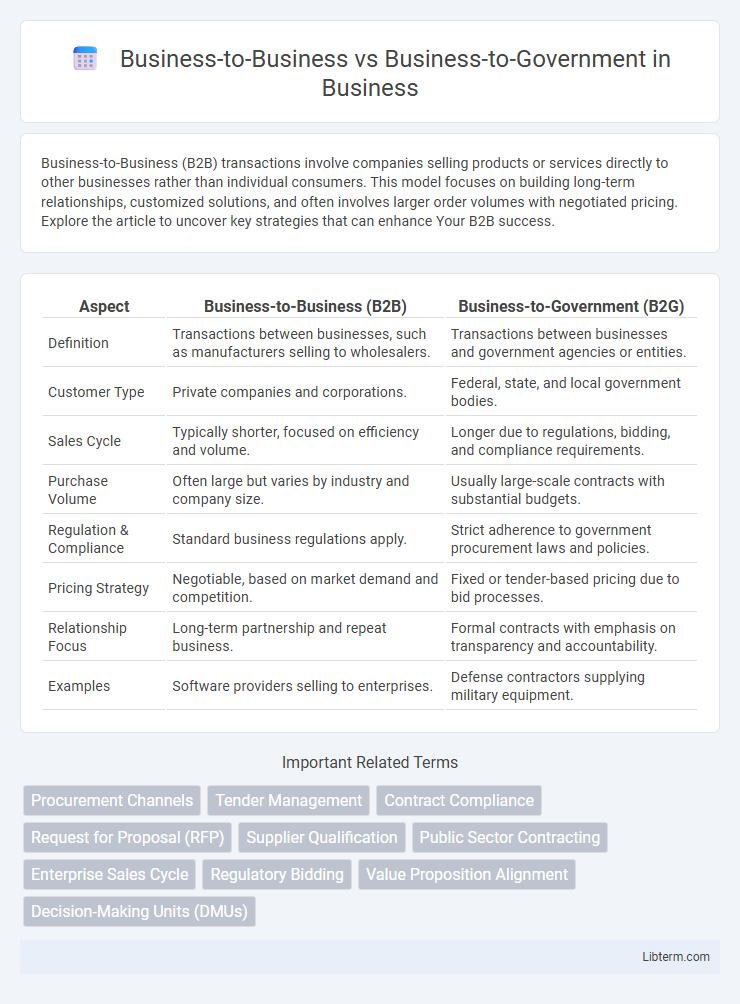
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Business-to-Business (B2B) | Business-to-Government (B2G) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transactions between businesses, such as manufacturers selling to wholesalers. | Transactions between businesses and government agencies or entities. |
| Customer Type | Private companies and corporations. | Federal, state, and local government bodies. |
| Sales Cycle | Typically shorter, focused on efficiency and volume. | Longer due to regulations, bidding, and compliance requirements. |
| Purchase Volume | Often large but varies by industry and company size. | Usually large-scale contracts with substantial budgets. |
| Regulation & Compliance | Standard business regulations apply. | Strict adherence to government procurement laws and policies. |
| Pricing Strategy | Negotiable, based on market demand and competition. | Fixed or tender-based pricing due to bid processes. |
| Relationship Focus | Long-term partnership and repeat business. | Formal contracts with emphasis on transparency and accountability. |
| Examples | Software providers selling to enterprises. | Defense contractors supplying military equipment. |
Understanding Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Government (B2G)
Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions involve companies selling products or services directly to other businesses, emphasizing long-term relationships, bulk orders, and tailored solutions that enhance operational efficiency. Business-to-Government (B2G) focuses on supplying governmental agencies, requiring compliance with strict regulatory standards, formal bidding processes, and transparency to meet public sector procurement policies. Understanding the differences between B2B and B2G is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies, contract management, and navigating unique industry-specific requirements.
Key Differences Between B2B and B2G
B2B transactions primarily target private sector companies, focusing on products and services that enhance business operations, while B2G transactions involve selling goods or services to government agencies with strict regulatory compliance and procurement procedures. B2G often requires navigating complex bidding processes, longer sales cycles, and adherence to public accountability standards, contrasting with B2B's typically faster and more flexible negotiations. Understanding these differences is crucial for tailoring marketing strategies, contract management, and relationship-building approaches unique to each sector.
Customer Segments and Decision-Making Processes
Business-to-Business (B2B) customer segments primarily include private companies across various industries such as manufacturing, technology, and services, whereas Business-to-Government (B2G) segments consist of federal, state, and local government agencies. B2B decision-making processes generally involve multiple stakeholders such as procurement managers, technical experts, and finance teams who prioritize cost efficiency and long-term partnerships. In contrast, B2G decision-making is often governed by strict regulatory compliance, public procurement laws, and includes formal tendering procedures with committees or elected officials overseeing contract awards.
Sales Cycle: B2B vs. B2G
The sales cycle in Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions typically involves multiple decision-makers and can range from weeks to months, driven by profit-oriented negotiations and market competition. In Business-to-Government (B2G) sales, the cycle is generally longer and more complex due to regulatory compliance, formal bidding processes, and strict procurement guidelines, often extending several months to over a year. B2G sales require extensive documentation and adherence to government standards, whereas B2B sales prioritize relationship building and faster deal closures.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Business-to-Business (B2B) transactions primarily adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards such as ISO certifications and contract law, emphasizing commercial compliance and data protection frameworks like GDPR. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) interactions demand strict adherence to government procurement policies, public sector transparency laws, and specific regulatory frameworks including FAR (Federal Acquisition Regulation) in the U.S. Compliance in B2G also involves detailed reporting, audit readiness, and often meeting socio-economic criteria such as minority-owned or small business certifications.
Contract Management in B2B and B2G
Contract management in Business-to-Business (B2B) typically involves negotiating terms, performance standards, and service-level agreements between private companies to optimize collaboration and ensure mutual profitability. In Business-to-Government (B2G) contract management, compliance with strict regulatory requirements, transparency protocols, and public accountability significantly influence contract execution and administration. Effective B2G contract management demands rigorous documentation, adherence to procurement laws, and responsiveness to government audits to maintain trust and secure long-term partnerships.
Marketing Strategies for B2B and B2G
Marketing strategies for Business-to-Business (B2B) emphasize relationship-building, personalized communication, and value-driven content to address industry-specific pain points and demonstrate return on investment. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) marketing requires navigating complex procurement processes, complying with regulatory standards, and leveraging certifications or past performance in public sector projects. Both strategies prioritize trust and credibility but differ in targeting decision-making units and aligning with distinct budget cycles and compliance requirements.
Challenges Unique to B2B and B2G Markets
Business-to-Business (B2B) markets face challenges including longer sales cycles, complex decision-making processes involving multiple stakeholders, and the need for customized solutions to meet specific industry requirements. Business-to-Government (B2G) markets encounter unique obstacles such as navigating stringent regulatory compliance, extended procurement procedures, and intense competition due to public sector transparency and accountability. Both B2B and B2G require robust relationship management and strategic alignment with client needs, but B2G demands additional expertise in government contracting and policy adherence.
Technology Adoption in B2B and B2G
Technology adoption in Business-to-Business (B2B) environments often emphasizes scalability, integration with existing enterprise systems, and ROI-driven solutions tailored to industry-specific needs. In contrast, Business-to-Government (B2G) technology adoption prioritizes compliance with regulatory standards, security protocols, and long-term sustainability to meet public sector requirements. Both sectors invest heavily in digital transformation but differ in procurement processes, with B2G typically involving more rigorous bidding and approval cycles.
Future Trends in B2B and B2G Relationships
Future trends in Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Government (B2G) relationships emphasize digital transformation, with increased adoption of AI-driven analytics, blockchain for secure transactions, and cloud-based platforms to streamline procurement processes. Enhanced data interoperability and cybersecurity protocols are critical as B2B firms and government agencies seek transparency and efficiency in supply chain management. Emerging technologies like IoT and 5G connectivity further enable real-time collaboration and decision-making, driving innovation across both sectors.
Business-to-Business Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com