Profit represents the financial gain achieved when revenue exceeds expenses, serving as a critical indicator of business success and sustainability. Understanding the types of profit, including gross, operating, and net profit, can help you optimize financial strategies and boost overall performance. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to maximize your profit effectively.
Table of Comparison
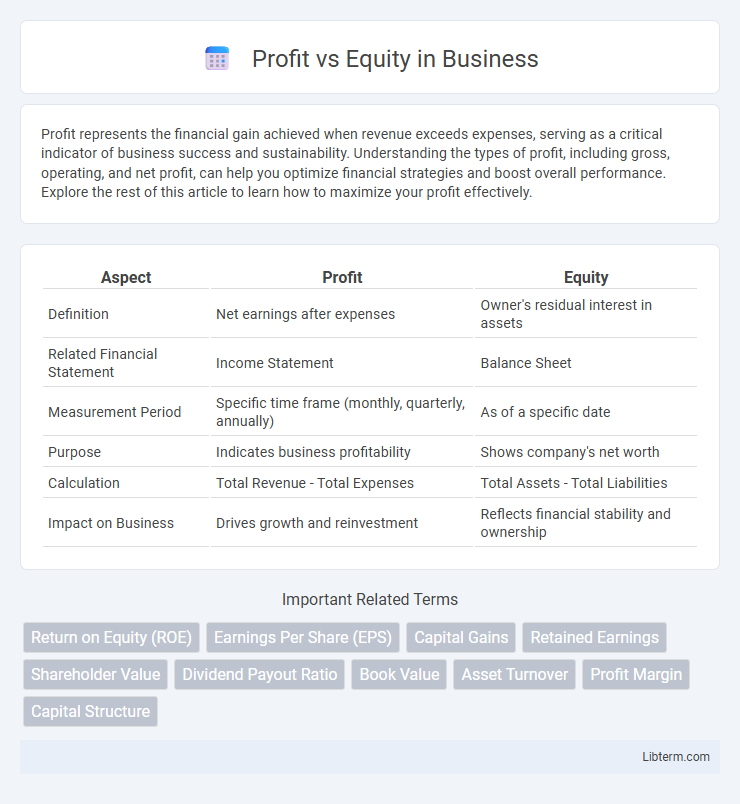
| Aspect | Profit | Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net earnings after expenses | Owner's residual interest in assets |
| Related Financial Statement | Income Statement | Balance Sheet |
| Measurement Period | Specific time frame (monthly, quarterly, annually) | As of a specific date |
| Purpose | Indicates business profitability | Shows company's net worth |
| Calculation | Total Revenue - Total Expenses | Total Assets - Total Liabilities |
| Impact on Business | Drives growth and reinvestment | Reflects financial stability and ownership |
Understanding Profit: Definition and Importance
Profit represents the financial gain realized when revenue exceeds expenses over a specific period, serving as a key indicator of a company's operational efficiency and viability. It is essential for sustaining business activities, funding growth initiatives, and attracting investors by demonstrating the capacity to generate returns. Understanding profit enables stakeholders to assess performance, make informed decisions, and ensure long-term financial stability.
Equity Explained: What It Means in Business
Equity in business represents the ownership interest held by shareholders or business owners, signifying their claim on company assets after liabilities are settled. It includes contributed capital, retained earnings, and accumulated other comprehensive income, reflecting the net value of the company. Unlike profit, which measures financial performance over a period, equity provides a snapshot of the company's financial health and long-term value.
Key Differences Between Profit and Equity
Profit represents the financial gain a company earns during a specific period, calculated as revenue minus expenses, while equity refers to the owner's residual interest in the assets of the business after deducting liabilities. Profit affects equity by increasing retained earnings, thereby boosting the overall value of shareholders' equity on the balance sheet. Understanding the distinction highlights profit as a flow metric measuring performance, whereas equity is a stock metric representing the company's net worth at a point in time.
How Profit Impacts Equity Growth
Profit directly influences equity growth by increasing retained earnings, which are a core component of shareholders' equity on the balance sheet. Higher profits result in greater reinvestment capacity, enhancing the company's net asset value and financial stability. Consistently positive profit margins lead to sustained equity growth, attracting investors and improving the firm's market valuation.
The Role of Retained Earnings in Equity
Retained earnings represent the portion of net profit that is reinvested into the company rather than distributed as dividends, directly increasing shareholders' equity. This accumulation of retained earnings strengthens the equity base, providing internally generated capital for business expansion, debt reduction, and operational stability. Monitoring retained earnings is crucial for understanding how effectively a company converts profits into long-term equity growth.
Profit vs Equity: Implications for Investors
Profit represents a company's financial gain during a specific period, reflecting its operational efficiency and growth potential, while equity indicates the residual interest shareholders hold after liabilities are deducted from assets. Investors analyzing profit focus on short-term performance and return on investment, whereas equity provides insight into long-term value, stability, and ownership stake. Understanding the balance between profit and equity helps investors assess sustainability, risk, and overall financial health before making investment decisions.
Short-Term Profitability vs Long-Term Equity Value
Short-term profitability measures a company's immediate financial performance, highlighting net income and cash flow within a fiscal quarter or year. Long-term equity value reflects the sustainable growth of shareholders' investments, driven by retained earnings, asset appreciation, and strategic business decisions over extended periods. Balancing short-term profit generation with long-term equity growth ensures robust financial health and maximizes shareholder wealth.
Profit and Equity in Financial Statements
Profit represents the net earnings of a company during a specific period, reflecting its operational efficiency and revenue generation after deducting expenses, taxes, and costs. Equity, also known as shareholders' equity or net assets, is the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities, as reported on the balance sheet. While profit impacts equity by increasing retained earnings, equity provides a snapshot of the company's financial position, combining profit, invested capital, and reserves.
Strategies to Balance Profit and Equity
Implementing strategies to balance profit and equity involves aligning financial goals with sustainable growth and stakeholder value. Companies can optimize profit margins while ensuring fair equity distribution by adopting transparent financial reporting, reinvesting earnings for long-term stability, and engaging in equitable shareholder practices. Prioritizing stakeholder engagement and sustainable investment decisions promotes harmony between profitability and equitable resource allocation.
Profit vs Equity: Which Should Take Priority?
Profit represents a company's financial gains over a specific period, indicating operational success, while equity reflects the residual interest in the assets after liabilities, showcasing long-term value and ownership. Prioritizing profit facilitates immediate business growth and liquidity, but emphasizing equity ensures sustainable financial health and investor confidence. Companies balancing profit and equity optimize both short-term performance and long-term stability, crucial for strategic decision-making and shareholder value maximization.
Profit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com